Photo illustration: Block vs Hide
Blocking on social media restricts all interactions and visibility between users, while hiding limits content visibility without severing connections. Explore the full differences and strategic uses of Block vs Hide in this article.
Table of Comparison
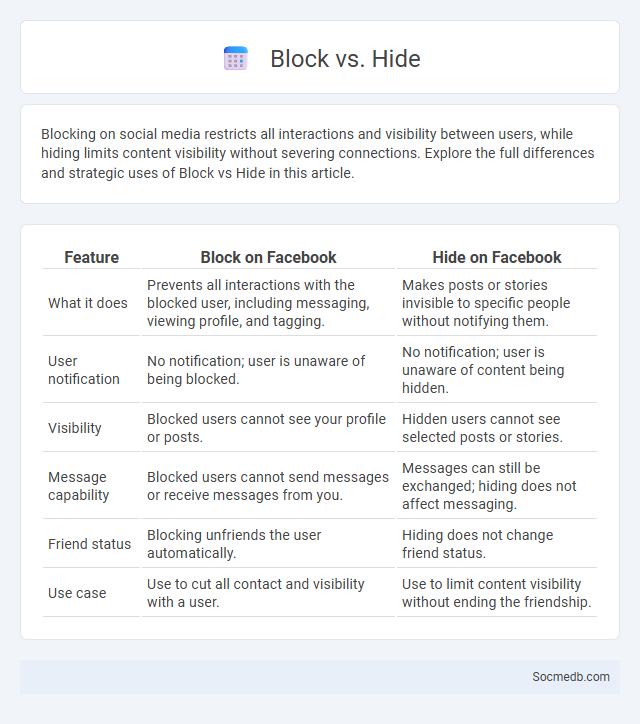
| Feature | Block on Facebook | Hide on Facebook |
|---|---|---|
| What it does | Prevents all interactions with the blocked user, including messaging, viewing profile, and tagging. | Makes posts or stories invisible to specific people without notifying them. |
| User notification | No notification; user is unaware of being blocked. | No notification; user is unaware of content being hidden. |
| Visibility | Blocked users cannot see your profile or posts. | Hidden users cannot see selected posts or stories. |
| Message capability | Blocked users cannot send messages or receive messages from you. | Messages can still be exchanged; hiding does not affect messaging. |
| Friend status | Blocking unfriends the user automatically. | Hiding does not change friend status. |
| Use case | Use to cut all contact and visibility with a user. | Use to limit content visibility without ending the friendship. |
Understanding Block, Hide, and Ban: Key Definitions
Understanding block, hide, and ban on social media platforms is essential for managing your online interactions and privacy. Blocking prevents specific users from seeing your profile or contacting you, while hiding typically conceals certain content from your feed or timeline without notifying others. Banning, commonly used in group or community settings, restricts users' participation entirely, ensuring a safer and more controlled environment for your digital experience.
The Purpose Behind Blocking, Hiding, and Banning
Blocking, hiding, and banning on social media serve to protect your digital environment by preventing harmful interactions, maintaining privacy, and curbing the spread of misinformation. Platforms implement these measures to foster safe, respectful communities and enforce content guidelines that align with their policies. Understanding the purpose behind these actions empowers you to manage your online experience effectively and promotes a healthier social media space.
How ‘Block’ Works: Preventing Interaction
Blocking on social media instantly restricts all forms of communication between you and the blocked user, preventing messages, comments, and profile views. This feature stops any unwanted interaction by effectively erasing your presence from their digital experience, ensuring privacy and control. Your blocked contacts cannot tag you, see your posts, or find your profile, creating a secure barrier against harassment and spam.
The ‘Hide’ Function: Concealing Content Without Cutting Ties
The 'Hide' function on social media platforms allows users to conceal specific posts or comments from their feed without unfriending or unfollowing the content creator, preserving social connections. This feature enhances user control over their online experience by minimizing exposure to unwanted content while maintaining engagement in social networks. By selectively hiding posts, users can curate a more personalized and relevant digital environment without severing relationships.
Blocking vs. Hiding: Main Differences
Blocking on social media prevents any interaction, including messages, profile views, and comments, effectively cutting off all contact between users. Hiding limits the visibility of posts or stories without notifying the other user, allowing content to be unseen without severing the connection. Understanding these distinctions helps users manage privacy and control engagement according to their communication preferences.
What Does ‘Ban’ Mean? Complete Access Denial
A ban on social media means complete access denial, preventing you from logging in, posting, or interacting on the platform. This restriction removes all your content visibility and disables notifications, effectively cutting off your digital presence. Social media bans are enforced to uphold community guidelines and prevent harmful behaviors.
Block vs Ban: When to Use Each Action
Blocking on social media is best used to prevent unwanted interactions from specific users without removing their access to your content, maintaining a boundary without restricting overall platform usage. Banning is a stronger measure, typically reserved for repeated violations or harmful behavior, as it removes a user's ability to access or participate in a community entirely. Choosing between block and ban depends on the severity and frequency of the issue, balancing personal privacy with community safety.
User Experience Impact: Block, Hide, or Ban?
Social media platforms influence Your user experience by offering options to block, hide, or ban content and users, each differing in control and visibility. Blocking prevents any interaction from specific users, enhancing privacy and security, while hiding removes unwanted posts from Your feed without alerting the content creator. Banning, typically used by community moderators, eliminates disruptive users entirely, improving overall platform quality and engagement.
Privacy and Security Implications of Each Action
Every post shared on social media platforms carries potential privacy risks, as personal information can be accessed or exploited by unauthorized users. Adjusting privacy settings to limit audience exposure and avoiding oversharing sensitive data significantly reduce the risk of identity theft and cyberstalking. Regularly updating passwords and enabling two-factor authentication strengthen account security, preventing unauthorized access and safeguarding digital identities.
Choosing the Right Moderation Tool for Your Needs
Selecting the ideal social media moderation tool depends on your platform size, audience engagement, and content type. Look for features like real-time filtering, customizable filters, AI-powered comment analysis, and support for multiple languages to effectively manage user interactions. Your choice should enhance community safety while maintaining seamless user experiences and aligning with your moderation policies.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com