Photo illustration: Clickbait vs propaganda
Clickbait uses sensational headlines to drive clicks, while propaganda spreads biased information to manipulate public opinion. Explore the differences and impact of clickbait and propaganda in this article.
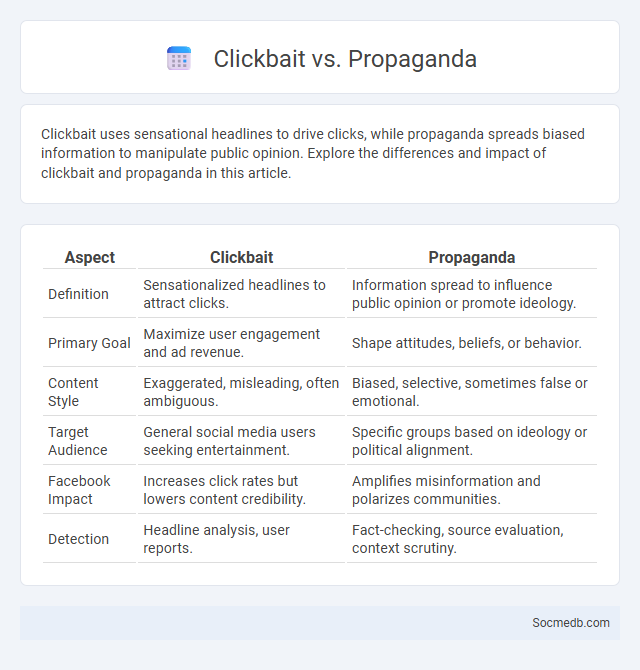
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Clickbait | Propaganda |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sensationalized headlines to attract clicks. | Information spread to influence public opinion or promote ideology. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize user engagement and ad revenue. | Shape attitudes, beliefs, or behavior. |
| Content Style | Exaggerated, misleading, often ambiguous. | Biased, selective, sometimes false or emotional. |
| Target Audience | General social media users seeking entertainment. | Specific groups based on ideology or political alignment. |
| Facebook Impact | Increases click rates but lowers content credibility. | Amplifies misinformation and polarizes communities. |
| Detection | Headline analysis, user reports. | Fact-checking, source evaluation, context scrutiny. |
Understanding Clickbait: Definition and Characteristics
Clickbait refers to misleading or sensationalized headlines designed to attract clicks and drive traffic to websites or social media platforms. These headlines often exaggerate content, provoke curiosity, or use emotionally charged language to manipulate user engagement. Recognizing clickbait is essential for discerning credible information and avoiding misinformation in digital media.
What is Propaganda? Key Features and Purpose
Propaganda is a strategic communication tool designed to influence public opinion and behavior through biased or misleading information. Key features include emotional appeal, repetition, selective presentation of facts, and often a clear agenda to manipulate attitudes or beliefs. The purpose of propaganda is to shape perceptions, control narratives, and mobilize support for political, social, or commercial objectives, frequently seen across social media platforms.
Clickbait vs. Propaganda: Core Differences
Clickbait uses sensationalized headlines and exaggerated content to attract clicks and drive traffic, prioritizing engagement metrics over accuracy. Propaganda, on the other hand, systematically manipulates information to influence public opinion and promote specific political or ideological agendas. Both exploit emotional responses, but clickbait targets curiosity and entertainment, while propaganda aims at shaping beliefs and behaviors.
Techniques Used in Clickbait Headlines
Clickbait headlines often use emotional triggers such as curiosity, urgency, and sensationalism to capture Your attention and increase click-through rates. Techniques include posing questions, using numbers or lists, and creating a sense of exclusivity or mystery that compels readers to engage. Incorporating power words and promising valuable or surprising content are common strategies to drive social media traffic effectively.
Propaganda Strategies in Modern Media
Social media platforms increasingly employ sophisticated propaganda strategies targeting Your perceptions by utilizing algorithm-driven content amplification and emotional appeal techniques. These digital tactics often manipulate information flow to create echo chambers, reinforcing specific narratives while marginalizing dissenting voices. Understanding these methods is crucial for discerning objective truth amid the vast array of curated content in modern media.
Impact of Clickbait on Public Perception
Clickbait headlines on social media manipulate public perception by prioritizing sensationalism over accuracy, often distorting facts to attract clicks. This practice reduces trust in reliable sources and fosters misinformation, impacting Your ability to discern truth from exaggeration. Over time, widespread exposure to clickbait erodes critical thinking and promotes short attention spans, negatively influencing societal discourse.
How Propaganda Shapes Opinions and Behaviors
Social media platforms use sophisticated algorithms to distribute targeted propaganda that manipulates user opinions and behaviors by exploiting cognitive biases and emotional triggers. Viral misinformation campaigns amplify polarized narratives, reinforcing echo chambers and distorting public perception on critical issues like politics, health, and social justice. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for developing media literacy skills and implementing effective content moderation policies to counteract harmful propaganda influence.
Recognizing Clickbait: Tips for Online Readers
Clickbait headlines often use sensational language and exaggerated claims to grab Your attention but rarely deliver on their promises. Identifying phrases like "shocking," "you won't believe," or "this one simple trick" can help you avoid misleading content on social media. Prioritize trustworthy sources and verify information before sharing to enhance Your online reading experience and digital literacy.
Combating Propaganda in the Digital Age
Combating propaganda in the digital age requires advanced algorithms capable of detecting misinformation patterns across social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Machine learning models analyze user-generated content in real-time to identify and flag false narratives, reducing the spread of harmful propaganda. Collaboration between technology companies, governments, and fact-checking organizations enhances the effectiveness of digital tools designed to promote accurate information and safeguard online communities.
The Intersection: When Clickbait Meets Propaganda
Clickbait's sensational headlines exploit emotional triggers to maximize clicks, often distorting facts and amplifying propaganda on social media platforms. Algorithms prioritize engagement over accuracy, causing misleading content to spread rapidly and influencing public opinion through strategically crafted narratives. Your critical evaluation of sources can help counteract the blend of clickbait and propaganda shaping online discourse.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com