Photo illustration: Facebook Social Graph vs Graph Database
Facebook Social Graph maps users, their connections, and interactions to model real-world relationships on a large scale. Graph databases efficiently store and query this complex network data, enabling powerful social insights and recommendations. Explore this article to learn more about their differences and applications.
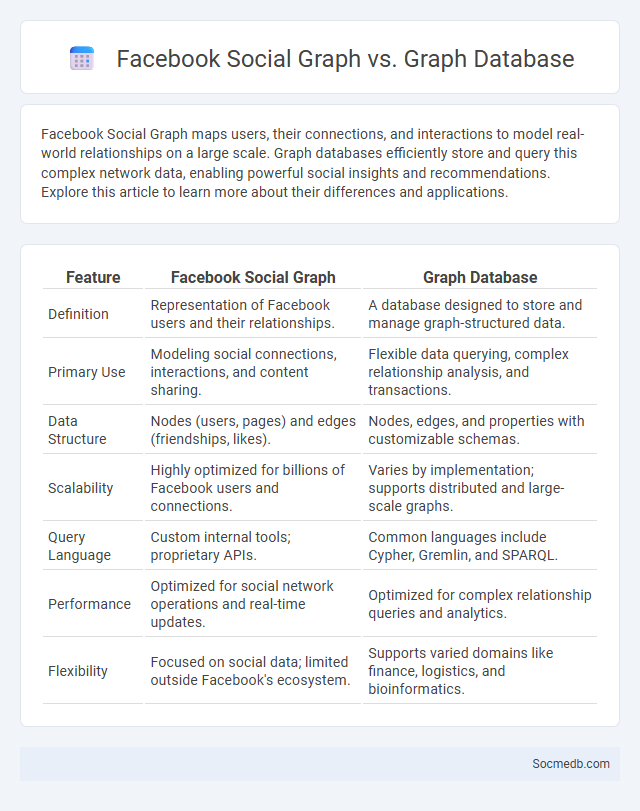
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facebook Social Graph | Graph Database |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Representation of Facebook users and their relationships. | A database designed to store and manage graph-structured data. |
| Primary Use | Modeling social connections, interactions, and content sharing. | Flexible data querying, complex relationship analysis, and transactions. |
| Data Structure | Nodes (users, pages) and edges (friendships, likes). | Nodes, edges, and properties with customizable schemas. |
| Scalability | Highly optimized for billions of Facebook users and connections. | Varies by implementation; supports distributed and large-scale graphs. |
| Query Language | Custom internal tools; proprietary APIs. | Common languages include Cypher, Gremlin, and SPARQL. |
| Performance | Optimized for social network operations and real-time updates. | Optimized for complex relationship queries and analytics. |
| Flexibility | Focused on social data; limited outside Facebook's ecosystem. | Supports varied domains like finance, logistics, and bioinformatics. |
Introduction to Social Graphs and Graph Databases
Social graphs represent the complex relationships and interactions between individuals on social media platforms, mapping connections such as friendships, followers, and shared interests. Graph databases efficiently store and manage this interconnected data, enabling rapid querying and analysis of social networks. Understanding your social graph through graph databases can enhance personalized content delivery and improve engagement strategies.
What is Facebook’s Social Graph?
Facebook's Social Graph is a digital representation of the relationships and interactions among users, pages, events, and objects within the platform. It maps connections such as friendships, likes, comments, and shares, enabling personalized content delivery and targeted advertising. This interconnected data structure powerfully enhances user experience by reflecting real-world social networks and relationships online.
Defining Graph Databases: Core Concepts
Graph databases organize data through nodes, edges, and properties, enabling efficient modeling of relationships and connections in social media platforms. Your social interactions, such as friendships, followers, and content sharing, are represented as interconnected nodes and edges, facilitating complex queries and real-time recommendations. This structure enhances the understanding of user behavior, driving personalized content delivery and improved engagement.
Social Graph: Broader Definition and Applications
The Social Graph represents the intricate network of connections between individuals, organizations, and entities on social media platforms, encompassing relationships, interactions, and shared interests. This concept extends beyond simple friend lists to include various forms of engagement such as likes, comments, and follows, providing a comprehensive map of social connectivity and influence. Understanding your Social Graph enables targeted marketing, improved content recommendations, and enhanced user experience through personalized social interactions.
How Facebook’s Social Graph Differs from Generic Social Graphs
Facebook's Social Graph uniquely maps relationships by emphasizing real-world connections and user-generated content with detailed interaction data, unlike generic social graphs that often rely on simplified or inferred links. It integrates diverse data types such as likes, comments, shares, and event participation to create a multi-dimensional representation of user relationships. This rich, dynamic network allows for personalized experiences, targeted advertising, and advanced social analytics beyond the capabilities of standard social graphs.
Graph Database vs. Facebook Social Graph: Key Distinctions
Graph databases excel in managing complex relationships and interconnected data, enabling efficient queries of social media networks through nodes and edges representing users and interactions. The Facebook Social Graph specifically maps real-world social connections and activities on its platform, leveraging proprietary algorithms and extensive user data to optimize recommendations and content delivery. Key distinctions lie in the Facebook Social Graph's tailored design for large-scale social interactions compared to generic graph databases that serve as versatile tools across various industries.
Real-World Use Cases: Facebook Social Graph vs Graph Databases
Facebook's Social Graph models complex relationships between billions of users, enabling personalized content delivery and targeted advertising through advanced data connections. Graph databases like Neo4j leverage similar graph theory principles to efficiently store and query interconnected data in real-world applications such as recommendation engines, fraud detection, and network analysis. By mirroring social media's relationship-centric data structures, graph databases enhance performance and insights in diverse industries beyond social platforms.
Data Models: Social Graphs vs Graph Databases
Social media platforms leverage social graphs to represent user connections and interactions, capturing complex relationships through nodes and edges that model friendships, followers, and shared content. Graph databases serve as the underlying technology enabling efficient storage, querying, and traversal of these social graphs, optimizing performance for real-time recommendations and network analysis. Key graph database technologies like Neo4j and Amazon Neptune enhance social media data management by supporting scalable, flexible schemas and facilitating advanced analytics on user behavior and content dissemination.
Scalability and Performance Considerations
Efficient social media platforms require scalable architecture to handle millions of concurrent users, with load balancing and distributed databases ensuring seamless performance. Implementing caching strategies and real-time data processing optimizes response times during peak traffic. Cloud-based infrastructures and microservices further enhance scalability, allowing rapid resource allocation based on user demand.
Choosing the Right Solution: Social Graph or Graph Database?
Choosing the right solution for social media analytics depends on your specific needs: social graphs excel at representing and visualizing relationships between users, while graph databases provide robust querying and scalability for complex data interactions. Graph databases like Neo4j or Amazon Neptune store and manage vast networks efficiently, enabling real-time insights and personalized recommendations. Your decision impacts how effectively you can analyze connections, detect patterns, and enhance user engagement.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com