Photo illustration: Facebook Social Graph vs LinkedIn Graph
Facebook Social Graph maps personal relationships and interactions among users, highlighting social connections and shared interests. LinkedIn Graph focuses on professional networks, emphasizing career connections, endorsements, and industry relationships. Discover deeper insights by exploring this article.
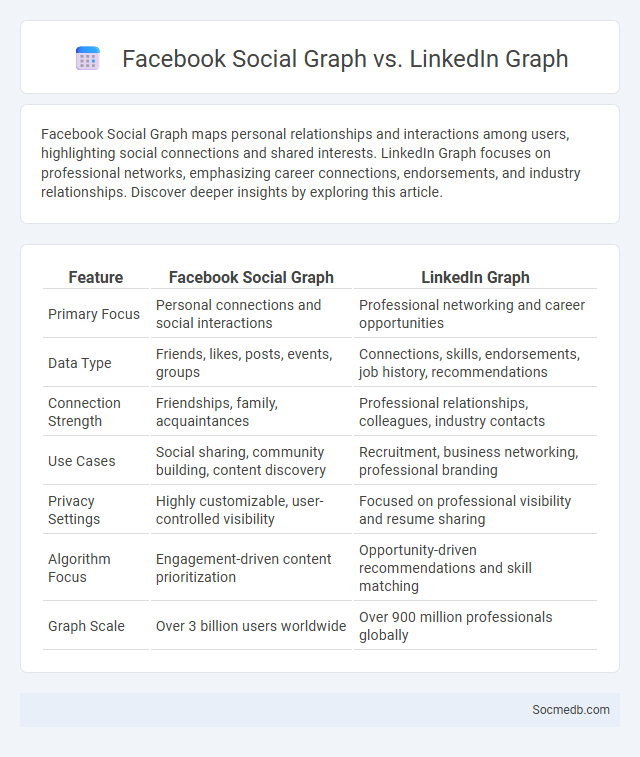
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facebook Social Graph | LinkedIn Graph |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Personal connections and social interactions | Professional networking and career opportunities |
| Data Type | Friends, likes, posts, events, groups | Connections, skills, endorsements, job history, recommendations |
| Connection Strength | Friendships, family, acquaintances | Professional relationships, colleagues, industry contacts |
| Use Cases | Social sharing, community building, content discovery | Recruitment, business networking, professional branding |
| Privacy Settings | Highly customizable, user-controlled visibility | Focused on professional visibility and resume sharing |
| Algorithm Focus | Engagement-driven content prioritization | Opportunity-driven recommendations and skill matching |
| Graph Scale | Over 3 billion users worldwide | Over 900 million professionals globally |
Introduction to Social Graphs
Social graphs represent the complex web of relationships and interactions among users on social media platforms, mapping connections such as friendships, followers, and shared interests. Analyzing social graphs enables platforms to enhance user experience by personalizing content, improving recommendations, and identifying influential nodes within networks. Advanced algorithms leverage social graph data to detect communities, track information flow, and optimize targeted marketing strategies.
Understanding Facebook’s Social Graph
Facebook's Social Graph represents the complex network of connections between users, pages, groups, and events, enabling tailored content delivery and personalized experiences. Your interactions, friendships, likes, and shares contribute to this dynamic map, shaping the information and advertisements you encounter daily. Understanding these relationships helps businesses and individuals optimize engagement by leveraging targeted communication within this interconnected digital ecosystem.
LinkedIn Graph: A Professional Perspective
LinkedIn Graph leverages extensive professional data to map relationships, skills, and industry connections, empowering users to expand their network strategically. Your profile benefits from enhanced visibility through LinkedIn's graph algorithms, which prioritize relevant connections and content to match your career goals. This powerful tool optimizes job searching, recruitment, and industry insights by analyzing patterns in professional interactions and endorsements.
Core Differences: Facebook vs LinkedIn Social Graphs
Facebook's social graph centers on personal connections, emphasizing friendships, family, and casual interests to foster social interactions and content sharing. LinkedIn's social graph prioritizes professional relationships, focusing on colleagues, industry peers, and career networks to support job opportunities and business growth. Understanding these core differences helps you tailor your engagement strategy to maximize outreach and meaningful connections on each platform.
Data Structure and Connectivity Comparison
Social media platforms utilize diverse data structures such as graphs to represent user connections and interactions, optimizing for efficient storage and retrieval of relational data. Connectivity comparison reveals that platforms like Facebook emphasize dense, bidirectional friend networks, while Twitter's structure favors sparse, unidirectional follower connections, impacting information dissemination patterns. Advanced indexing and clustering algorithms enhance scalability and real-time processing across these varied network topologies, supporting personalized content delivery.
Privacy and Security: Facebook vs LinkedIn Graphs
Facebook and LinkedIn graphs differ significantly in terms of privacy and security policies, with Facebook employing more extensive user data collection for personalized advertising, while LinkedIn emphasizes professional networking with stricter data access controls. Facebook's graph exposes users to a broader range of data sharing risks due to its integration across diverse social contexts, whereas LinkedIn prioritizes safeguarding professional identity and connections through limited third-party access. Both platforms use encryption and authentication protocols, but LinkedIn's security measures are tailored to protect career-related information, reflecting their distinct user base priorities.
Use Cases: Personal vs Professional Networking
Social media platforms serve distinct purposes in personal and professional networking, with platforms like Facebook and Instagram facilitating personal connections and sharing moments, while LinkedIn focuses on building professional relationships and career growth. Your use of these networks should align with your objectives, such as expanding friendships or advancing industry expertise. Leveraging the right platform enhances communication effectiveness and helps you achieve targeted social or business outcomes.
Impact on User Experience
Social media platforms significantly enhance user experience by enabling instant communication, personalized content feeds, and interactive features that foster community engagement. Advanced algorithms analyze user behavior to deliver relevant posts, advertisements, and recommendations, increasing user satisfaction and retention. However, the constant flow of information can also lead to cognitive overload and decreased attention spans, impacting overall digital well-being.
Business Applications of Social Graphs
Social graphs enable businesses to analyze customer relationships and interactions, improving targeted marketing strategies and enhancing customer engagement. Leveraging insights from social graph data helps identify influencers, track brand advocacy, and optimize product recommendations. Integrating social graph analytics into CRM systems transforms raw social data into actionable business intelligence, driving growth and customer loyalty.
Future Trends in Social Graph Technology
Future trends in social graph technology highlight the integration of advanced AI algorithms and machine learning to enhance user interaction and personalization. Emerging decentralized social graphs leverage blockchain to increase privacy, data ownership, and security by distributing control away from centralized platforms. Graph databases and real-time analytics continue to evolve, enabling more dynamic relationship mapping and predictive insights for businesses and social networks.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com