Photo illustration: Facebook Social Graph vs Twitter Social Graph
Facebook Social Graph maps comprehensive connections among users, pages, and interactions to enable personalized content delivery, while Twitter Social Graph centers on follower relationships and real-time information flow. Explore the differences and impacts of these social graphs in this article.
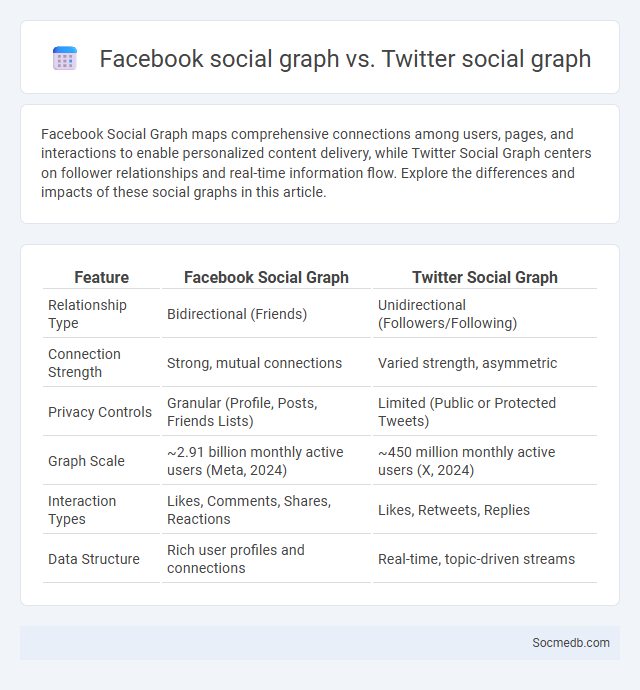
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facebook Social Graph | Twitter Social Graph |
|---|---|---|
| Relationship Type | Bidirectional (Friends) | Unidirectional (Followers/Following) |
| Connection Strength | Strong, mutual connections | Varied strength, asymmetric |
| Privacy Controls | Granular (Profile, Posts, Friends Lists) | Limited (Public or Protected Tweets) |
| Graph Scale | ~2.91 billion monthly active users (Meta, 2024) | ~450 million monthly active users (X, 2024) |
| Interaction Types | Likes, Comments, Shares, Reactions | Likes, Retweets, Replies |
| Data Structure | Rich user profiles and connections | Real-time, topic-driven streams |
Introduction to Social Graphs
Social graphs represent the network of relationships between individuals or entities on social media platforms, mapping connections such as friendships, followers, and interactions. Understanding social graphs enables the analysis of user behavior, community formation, and information flow within networks. Platforms like Facebook, LinkedIn, and Twitter leverage social graph data to personalize content, improve recommendations, and enhance user engagement.
Understanding the Concept of Social Graph
The social graph represents the network of relationships and interactions between individuals on social media platforms, mapping how users connect and engage with each other. By analyzing your social graph, social media platforms can recommend relevant content, friends, and communities tailored to your interests and behaviors. Understanding this concept helps you leverage social media more effectively to build stronger connections and enhance your online presence.
Facebook Social Graph: Structure and Features
The Facebook Social Graph represents the complex network of users, their relationships, and interactions, structuring connections through nodes (users) and edges (relationships). Key features include friend connections, likes, shares, comments, and groups, which enable dynamic content discovery and targeted advertising. The Social Graph's structure supports personalized user experiences by mapping social contexts and affinities, enhancing engagement and data-driven insights.
Twitter Social Graph: Structure and Features
The Twitter Social Graph maps the complex network of user connections, highlighting follower and following relationships that shape your information flow. Key features include retweets, mentions, and hashtags that drive content virality and community formation within the graph. Understanding this structure allows you to optimize engagement and strategically grow your influence on the platform.
Key Differences Between Facebook and Twitter Social Graphs
Facebook's social graph centers on mutual friendships and detailed user connections, emphasizing shared interests, groups, and interactions that foster community building. Twitter's social graph is based on asymmetric follower-following relationships, prioritizing content dissemination and real-time engagement over reciprocal connections. These structural differences impact how users discover content, network, and influence information flow on each platform.
Privacy and Data Control in Social Graphs
Privacy and data control within social graphs are essential for protecting user information in social media platforms. Advanced encryption methods and strict access controls help users manage who can view and interact with their personal data and connections. Implementing transparent data policies enhances user trust by allowing individuals to control data sharing and visibility across their social networks.
Impact of Social Graphs on User Experience
Social graphs significantly enhance the user experience by mapping relationships between individuals, enabling personalized content delivery and fostering meaningful interactions. These interconnected networks analyze connections such as friends, followers, and shared interests to tailor your social media feed, improving relevancy and engagement. Leveraging social graph data drives features like friend recommendations, targeted advertising, and community building, which collectively enrich your overall platform experience.
Applications of Social Graphs in Social Networking
Social graphs play a critical role in social networking by mapping relationships and interactions between users, enabling personalized content delivery and enhanced user engagement. Platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn leverage social graphs to recommend friends, groups, and professional connections based on shared interests and mutual contacts. Analyzing social graphs also helps detect influential users, improve targeted advertising, and combat misinformation by understanding information flow patterns.
Challenges and Limitations of Social Graphs
Social graphs face challenges such as data privacy concerns, inaccurate relationship representation, and the complexity of dynamic social networks. Algorithms struggle to capture evolving user interactions, leading to limitations in personalized content delivery and influence measurement. These constraints hinder the potential of social graphs in providing precise social insights and targeted marketing strategies.
Future Trends in Social Graph Development
Social graph development is increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance user connectivity and personalized content delivery. Advances in decentralized social networks and blockchain technology aim to improve data privacy and user control over personal information. Integration of augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) is expected to create more immersive social experiences, reshaping digital interaction landscapes.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com