Photo illustration: Facebook vs Apple (Privacy Policies)
Facebook's privacy policies collect extensive user data to tailor advertising, while Apple's approach emphasizes user privacy with features like App Tracking Transparency. Explore this article to understand how these contrasting strategies impact your digital security and online experience.
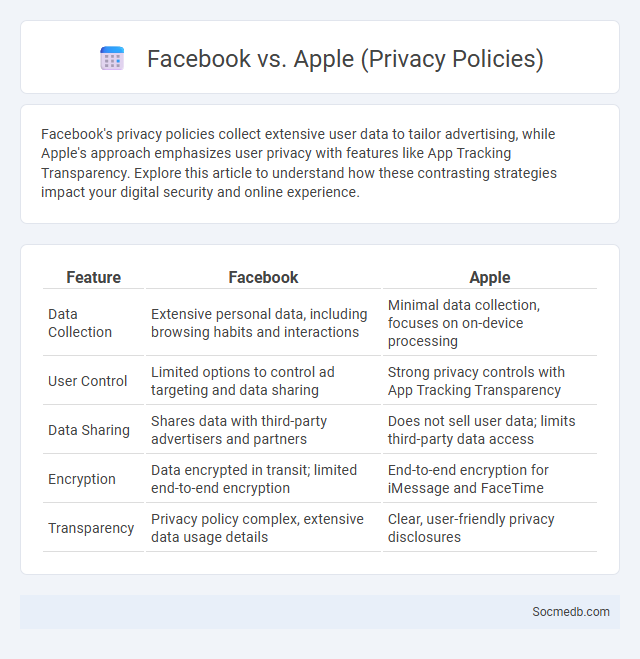
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Apple | |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Extensive personal data, including browsing habits and interactions | Minimal data collection, focuses on on-device processing |
| User Control | Limited options to control ad targeting and data sharing | Strong privacy controls with App Tracking Transparency |
| Data Sharing | Shares data with third-party advertisers and partners | Does not sell user data; limits third-party data access |
| Encryption | Data encrypted in transit; limited end-to-end encryption | End-to-end encryption for iMessage and FaceTime |
| Transparency | Privacy policy complex, extensive data usage details | Clear, user-friendly privacy disclosures |
Introduction: The Battle of Tech Giants
The battle of tech giants unfolds across leading social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and TikTok, each competing to capture user engagement and advertising revenue worldwide. Innovations in algorithm-driven content delivery, data privacy policies, and immersive features such as Stories and Reels drive intense rivalry among Meta, Twitter Inc., ByteDance, and other influential corporations. This competitive landscape shapes global digital communication trends, influencing how billions share information and interact online.
Overview of Facebook's Privacy Policies
Facebook's privacy policies emphasize user control over personal data through customizable settings that manage data sharing, advertising preferences, and profile visibility. The platform employs encryption and secure access protocols to protect user information from unauthorized access and adheres to regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. Continuous updates to these policies address evolving security threats and enhance transparency regarding data collection and usage practices.
Apple's Approach to User Privacy
Apple's approach to user privacy on social media emphasizes end-to-end encryption, strict app tracking transparency, and minimizing data collection to protect user information. The company implements privacy labels on the App Store, informing users about data usage before downloading social media apps. Advanced machine learning on-device ensures personalized experiences without compromising sensitive data in Apple's ecosystem.
Comparing Data Collection Methods
Comparing data collection methods in social media reveals significant differences between passive and active techniques; passive methods like web scraping and API data extraction allow for large-scale, real-time data acquisition, whereas active methods such as surveys and interviews provide deeper user insights but on a smaller scale. API data collection ensures structured, platform-approved access to user interactions and metadata, while web scraping can gather unstructured content but often faces legal and ethical constraints. Optimizing social media analysis requires balancing the breadth of passive data collection with the depth of active user engagement to produce comprehensive, actionable insights.
Transparency and User Control
Social media platforms increasingly prioritize transparency by clearly communicating data collection practices and content moderation policies to build trust with users. Your ability to control privacy settings and customize content feeds empowers you to manage your online experience while safeguarding personal information. Enhanced transparency and user control contribute to a safer, more accountable social media environment.
High-Profile Data Breaches: Case Studies
High-profile data breaches such as the 2018 Facebook-Cambridge Analytica scandal exposed millions of users' personal information, highlighting vulnerabilities in social media data privacy. Twitter's 2020 spear-phishing attack compromised prominent accounts, demonstrating the risks of centralized platform control and insufficient security protocols. These case studies underscore the critical need for enhanced cybersecurity measures and transparent data management practices within social media networks.
Impact on User Trust and Reputation
Social media significantly influences user trust and reputation by shaping public perception through user-generated content and reviews. Negative comments or misinformation can quickly erode trust, affecting brand credibility and customer loyalty. Conversely, consistent positive interactions and transparent communication on social platforms enhance reputation, fostering stronger relationships between users and organizations.
Regulatory Responses and Legal Battles
Regulatory responses to social media platforms have intensified globally, with governments imposing stricter data privacy laws such as the European Union's GDPR and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Legal battles frequently arise around issues like content moderation, misinformation, and antitrust concerns, exemplified by high-profile cases against Facebook and Twitter. These regulatory frameworks and litigation efforts aim to balance user protection with freedom of expression in the digital landscape.
Future Trends in Privacy and Security
Emerging social media platforms are increasingly integrating advanced encryption technologies and AI-driven anomaly detection to enhance user privacy and data security. Regulatory measures such as stricter data protection laws and real-time compliance monitoring are being prioritized to mitigate breaches and unauthorized data sharing. Decentralized social networks leveraging blockchain technology also promise greater user control over personal information and transparent data transactions.
Conclusion: Who Wins the Privacy War?
Tech companies continue to dominate the social media landscape, often prioritizing data monetization over user privacy. Despite increasing regulatory pressures and growing public awareness, individuals face significant challenges in safeguarding their personal information. The ongoing privacy war reveals a persistent imbalance, with corporations largely maintaining control over user data.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com