Photo illustration: Fact-Checking vs Facebook Moderation
Fact-checking on social media platforms involves verifying the accuracy of shared content to combat misinformation, whereas Facebook moderation includes enforcing community standards by removing harmful or inappropriate posts. Explore this article to understand the critical differences and impacts of fact-checking versus Facebook moderation.
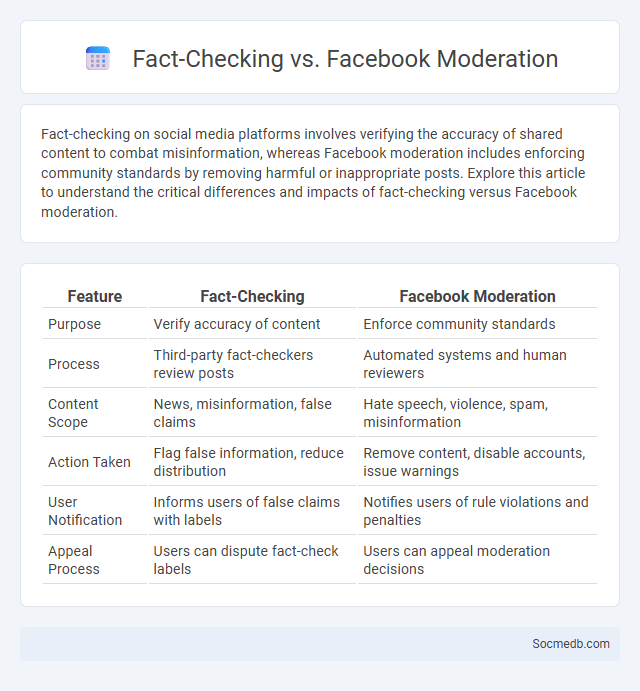
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Fact-Checking | Facebook Moderation |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Verify accuracy of content | Enforce community standards |
| Process | Third-party fact-checkers review posts | Automated systems and human reviewers |
| Content Scope | News, misinformation, false claims | Hate speech, violence, spam, misinformation |
| Action Taken | Flag false information, reduce distribution | Remove content, disable accounts, issue warnings |
| User Notification | Informs users of false claims with labels | Notifies users of rule violations and penalties |
| Appeal Process | Users can dispute fact-check labels | Users can appeal moderation decisions |
Understanding Fact-Checking: Definitions and Purpose
Fact-checking involves verifying the accuracy of information shared on social media platforms to combat the spread of misinformation and disinformation. Its purpose is to help users discern credible content from false claims, thereby promoting informed decision-making and trust in online communication. Understanding fact-checking empowers you to critically evaluate posts and avoid sharing misleading information.
The Mechanics of Facebook Moderation
Facebook moderation relies on advanced AI algorithms combined with human reviewers to detect and remove harmful content such as hate speech, misinformation, and graphic violence. The platform employs machine learning models trained on vast datasets to flag posts automatically, while human moderators assess context and enforce community standards. To protect Your experience, Facebook continuously updates its moderation policies and technologies to address emerging threats and maintain a safe online environment.
What Constitutes Fake News?
Fake news consists of intentionally fabricated or misleading information designed to deceive readers, often disguised as credible journalism. It thrives on emotional manipulation, sensational headlines, and the lack of verifiable sources, making it challenging to distinguish from legitimate news. Social media platforms amplify fake news through rapid sharing, contributing to misinformation and public confusion.
Fact-Checking vs Automated Moderation: Key Differences
Fact-checking involves human experts analyzing content for accuracy and providing verified information to combat misinformation. Automated moderation relies on algorithms and machine learning to detect and remove harmful or policy-violating content based on preset criteria. The key difference lies in fact-checking's emphasis on content verification by humans, while automated moderation prioritizes rapid, large-scale enforcement through technology.
The Role of Human Review in Curbing Misinformation
Human review plays a critical role in curbing misinformation on social media by identifying context and nuances that automated algorithms often miss. Content moderators analyze posts for accuracy, relevance, and intent, helping to flag false information and prevent its spread. Integrating human judgment with AI tools enhances the overall effectiveness of misinformation detection and improves platform credibility.
How Facebook Identifies and Flags Fake News
Facebook utilizes advanced AI algorithms combined with human fact-checkers to identify and flag fake news across its platform. The system analyzes content for misleading information, checks against verified sources, and evaluates user reports to determine the credibility of posts. Flagged posts are either labeled with warnings, reduced in distribution, or removed to limit the spread of false information.
The Impact of Fact-Checking on Social Media Discourse
Fact-checking on social media plays a crucial role in shaping public discourse by reducing the spread of misinformation and promoting accurate information. Your engagement with fact-checked content encourages critical thinking and supports the accountability of information sources. This process enhances the overall quality of conversations and fosters a more informed online community.
Limitations and Challenges of Facebook Moderation
Facebook moderation faces significant limitations and challenges due to the platform's vast content volume, making it difficult to monitor every post effectively. Automated systems often struggle with context, resulting in false positives or negatives, while human moderators face ethical and psychological burdens. Your online experience may be impacted by inconsistent enforcement, delayed responses, and ongoing debates over censorship versus free expression.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Fake News Prevention Strategies
Evaluating the effectiveness of fake news prevention strategies on social media involves analyzing data from fact-checking tools, user engagement metrics, and algorithmic content filtering. Your ability to identify patterns in misinformation spread and the impact of educational campaigns helps refine these strategies. Continuous assessment using AI-driven analytics ensures that interventions adapt to evolving tactics of misinformation.
Toward a Balanced Approach: Collaboration for Information Integrity
Promoting information integrity on social media requires a balanced approach that engages platform developers, policymakers, and users in cooperative efforts. Implementing advanced algorithms alongside human oversight enhances content accuracy while respecting free expression. Collaborative frameworks foster transparency, accountability, and shared responsibility to mitigate misinformation effectively.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com