Photo illustration: Fake News vs Disinformation
Fake news refers to fabricated information presented as true, while disinformation is deliberately false content spread to deceive. Explore this article to understand the differences, impacts, and strategies to combat misinformation in social media.
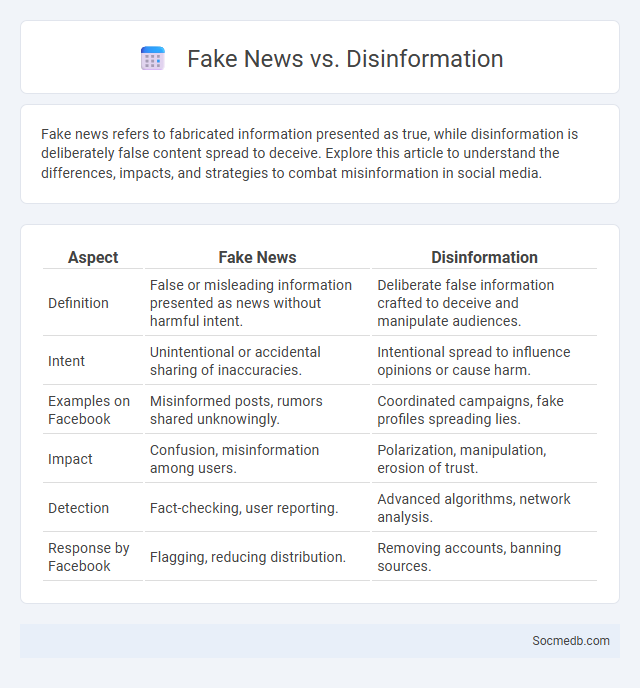
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fake News | Disinformation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | False or misleading information presented as news without harmful intent. | Deliberate false information crafted to deceive and manipulate audiences. |
| Intent | Unintentional or accidental sharing of inaccuracies. | Intentional spread to influence opinions or cause harm. |
| Examples on Facebook | Misinformed posts, rumors shared unknowingly. | Coordinated campaigns, fake profiles spreading lies. |
| Impact | Confusion, misinformation among users. | Polarization, manipulation, erosion of trust. |
| Detection | Fact-checking, user reporting. | Advanced algorithms, network analysis. |
| Response by Facebook | Flagging, reducing distribution. | Removing accounts, banning sources. |
Understanding the Terminology: Fake News, Disinformation, Misinformation
Fake news refers to deliberately fabricated content designed to deceive audiences, often mimicking legitimate news sources to spread falsehoods. Disinformation is intentionally false or misleading information spread to manipulate public opinion or obscure the truth, frequently associated with political or ideological agendas. Misinformation involves the unintentional sharing of incorrect or inaccurate information without harmful intent, which can still contribute to confusion and misunderstanding on social media platforms.
The Evolution of Fake News in the Digital Age
The evolution of fake news in the digital age has been propelled by the widespread use of social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram, which enable rapid dissemination of misinformation. Advances in AI-generated content and deepfake technology have further complicated detection efforts, increasing the challenge for fact-checkers and users alike. The rise of algorithm-driven echo chambers amplifies deceptive narratives, making digital literacy and platform accountability critical in combating the spread of fake news.
Disinformation: Intentional Deception Explained
Disinformation on social media involves the deliberate spread of false or misleading information designed to deceive and manipulate public perception. This intentional deception can influence opinions, disrupt social harmony, and undermine trust in legitimate sources. Understanding how disinformation operates empowers you to critically evaluate online content and protect your digital environment.
Differentiating Between Fake News and Disinformation
You can identify fake news by verifying the credibility of sources and cross-referencing information with reputable outlets. Disinformation involves the deliberate creation and sharing of false information to mislead or manipulate public opinion. Understanding these distinctions helps protect your online experience and supports critical evaluation of social media content.
Motives Behind Spreading False Information
False information on social media often spreads due to motives such as political influence, financial gain, and social manipulation. Malicious actors exploit algorithms designed to maximize engagement, using sensational content to trigger emotional responses and increase shares. Understanding these motives helps you critically evaluate the credibility of the information you encounter online.
Channels and Platforms for Fake News and Disinformation
Social media channels such as Facebook, Twitter, and WhatsApp are primary platforms where fake news and disinformation rapidly spread due to their vast user bases and algorithm-driven content distribution. These platforms often lack robust verification mechanisms, enabling the viral sharing of misleading information that influences public opinion and behavior. Protecting your digital literacy by critically evaluating sources and cross-referencing facts is essential to combat the influence of false content across social media networks.
The Impact on Public Opinion and Democracy
Social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram have transformed how public opinion is shaped, enabling rapid dissemination of information and fostering direct political engagement. The amplification of diverse voices and the spread of real-time news empower citizens but also lead to challenges such as misinformation, echo chambers, and polarization that can undermine democratic processes. Algorithms designed to maximize user engagement often prioritize emotionally charged content, influencing voter behavior and impacting the integrity of elections and public discourse.
Methods to Identify and Combat Disinformation
Advanced algorithms leveraging natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning analyze content patterns to detect disinformation on social media platforms. Fact-checking organizations collaborate with platforms by providing verified data and real-time alerts to flag misleading posts. User education programs emphasize critical thinking and digital literacy to empower audiences in recognizing and reporting false information effectively.
The Role of Media Literacy in Countering Fake News
Media literacy plays a crucial role in countering fake news by equipping individuals with critical thinking skills to evaluate the credibility of sources and identify misinformation. Platforms like Facebook and Twitter have integrated fact-checking tools and educational campaigns to promote media literacy among users. Enhancing media literacy reduces the spread of false information and fosters a more informed, discerning social media audience.
Future Challenges in the Fight Against Information Disorder
Future challenges in the fight against information disorder include the rapid evolution of deepfake technology and AI-generated content that complicate verification processes. Your ability to discern trusted sources will be increasingly tested as misinformation becomes more sophisticated and ubiquitous across emerging social media platforms. Addressing these issues requires advanced AI detection tools, cross-platform collaboration, and enhanced digital literacy initiatives.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com