Photo illustration: Fake News vs Satire
Fake news spreads misinformation by presenting false information as factual, while satire uses humor and exaggeration to critique or entertain. Explore this article to understand the differences and impact of fake news versus satire on social media.
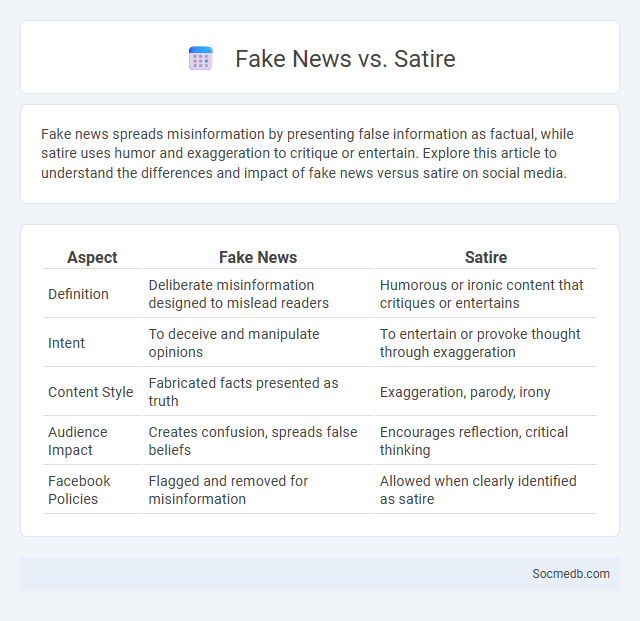
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fake News | Satire |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate misinformation designed to mislead readers | Humorous or ironic content that critiques or entertains |
| Intent | To deceive and manipulate opinions | To entertain or provoke thought through exaggeration |
| Content Style | Fabricated facts presented as truth | Exaggeration, parody, irony |
| Audience Impact | Creates confusion, spreads false beliefs | Encourages reflection, critical thinking |
| Facebook Policies | Flagged and removed for misinformation | Allowed when clearly identified as satire |
Understanding the Difference: Fake News vs Satire
Distinguishing between fake news and satire is crucial for navigating social media accurately. Fake news often spreads misinformation with the intent to deceive or manipulate public opinion, whereas satire uses humor and exaggeration to criticize or highlight real issues. When you analyze sources critically, you protect your online experience from being misled by false content and better appreciate the role of satire in digital communication.
Defining Fake News: Intent and Impact
Fake news involves deliberately fabricated information designed to mislead audiences and manipulate public perception. The intent behind fake news is often to create confusion, influence political outcomes, or generate financial gain through viral misinformation. Its impact includes undermining trust in legitimate sources, polarizing communities, and distorting reality in social media ecosystems.
What is Satire? Purpose and Techniques
Satire is a literary and artistic technique used on social media platforms to critique and expose societal flaws, politics, or human behavior through humor, irony, and exaggeration. Its primary purpose is to provoke thought, challenge norms, and inspire change by highlighting contradictions and absurdities in current events or cultural practices. Common techniques include parody, sarcasm, hyperbole, and caricature, effectively engaging audiences while delivering sharp social commentary.
Key Characteristics: Fake News
Social media platforms facilitate rapid information sharing, making them prime environments for the spread of fake news characterized by misinformation, sensationalism, and unverified claims. Algorithms prioritize engaging content, often amplifying false stories that exploit emotional triggers, which undermines public trust and disrupts informed discourse. Users' echo chambers and confirmation biases further entrench fake news, complicating efforts to promote accurate and reliable information.
Key Characteristics: Satire
Satire in social media leverages humor, irony, and exaggeration to critique societal issues, politics, and cultural norms effectively. It often uses memes, parody accounts, and viral videos to engage audiences while provoking thought and challenging mainstream narratives. This characteristic enables creators to communicate complex messages succinctly, fostering critical reflection and dialogue among users.
The Role of Intention in Fake News and Satire
The role of intention is crucial in distinguishing fake news from satire, as fake news deliberately aims to mislead and manipulate audiences for political or financial gain. Satire, by contrast, employs humor and exaggeration with the intended purpose of critiquing social and political issues, fostering awareness rather than deception. Understanding these intentions helps social media platforms develop more effective content moderation strategies to reduce misinformation without stifling freedom of expression.
Common Examples: Fake News and Satire in Media
Fake news spreads misinformation rapidly across social media platforms, often misleading Your perceptions with fabricated headlines and false claims. Satire in media uses humor and exaggeration to criticize or highlight social issues, but without clear context, it can be mistaken for genuine news. Understanding the difference is crucial for navigating digital content critically and avoiding the pitfalls of deceptive information.
Effects on Public Perception and Trust
Social media significantly influences public perception and trust by shaping the information people encounter daily. Misinformation and echo chambers can erode Your confidence in credible sources, while transparent communication and verified content help build trustworthiness. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for recognizing how social platforms affect societal beliefs and behaviors.
How to Distinguish Fake News from Satire
Identifying fake news from satire involves analyzing content for intent and credibility; genuine news aims to inform, while satire uses humor or exaggeration to entertain or critique. Check source reliability by verifying the publisher's reputation and cross-referencing with trustworthy news outlets. Examine language cues such as sensationalism, emotional manipulation, or absurd claims typical of fake news, contrasting with the exaggerated but humorous tone found in satire.
Combating Misinformation: Tools and Strategies
Effective tools and strategies for combating misinformation on social media include advanced AI-powered fact-checking algorithms that detect false content in real-time and user-reporting mechanisms that enable community-driven moderation. Platforms like Facebook and Twitter implement content labeling, warning users about disputed information, while partnerships with independent fact-checkers enhance credibility and accuracy. Educational campaigns promoting media literacy also empower users to critically evaluate sources, reducing the spread of misinformation across digital networks.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com