Photo illustration: Haha vs Angry
Haha reactions on social media often indicate amusement or lightheartedness, while Angry reactions reveal strong disapproval or frustration. Explore the psychological impact and engagement trends behind these responses in this article.
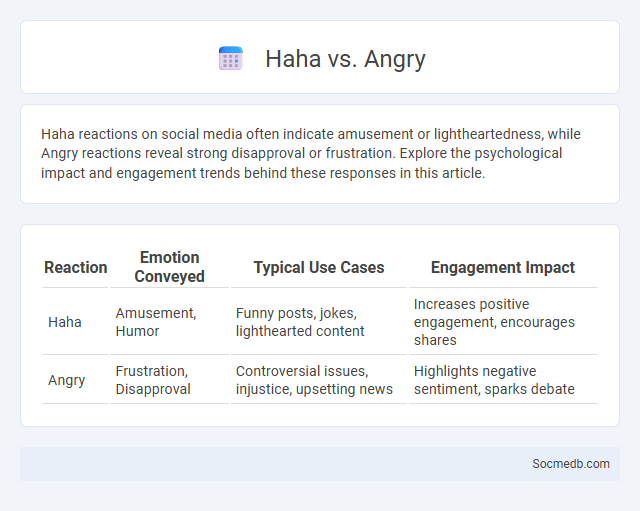
Table of Comparison
| Reaction | Emotion Conveyed | Typical Use Cases | Engagement Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Haha | Amusement, Humor | Funny posts, jokes, lighthearted content | Increases positive engagement, encourages shares |
| Angry | Frustration, Disapproval | Controversial issues, injustice, upsetting news | Highlights negative sentiment, sparks debate |
Understanding Facebook Reactions: Haha, Angry, and More
Facebook Reactions provide nuanced ways for your audience to express emotions beyond a simple Like, including Haha, Angry, Wow, Sad, and Love. Each reaction helps you gauge genuine sentiment, enabling better engagement analysis and tailored content strategies. Understanding the specific meanings behind these reactions enhances your ability to connect with your community and respond effectively.
Psychological Impact of Different Reactions
Social media reactions, such as likes, comments, and shares, significantly influence your psychological well-being by triggering dopamine releases that reinforce engagement behaviors. Positive reactions can enhance self-esteem and social validation, while negative or lack of responses may lead to feelings of rejection, anxiety, or depression. Understanding the psychological impact of these feedback mechanisms helps manage social media use and maintain mental health balance.
How "Haha" Reaction Shapes Online Interactions
The "Haha" reaction on social media platforms significantly influences user engagement by injecting humor and lightheartedness into online conversations, which can diffuse tension and foster positive community interactions. This reaction often signals amusement or sarcasm, guiding content creators and commenters to interpret posts with a playful tone, thus shaping the emotional dynamics of digital communication. Research shows that posts with "Haha" reactions tend to generate higher sharing rates and interactive responses, highlighting its role in amplifying viral content and enhancing social connectivity.
The Role of "Angry" in Digital Communication
The emotion "angry" plays a crucial role in digital communication by amplifying engagement and driving viral content across social media platforms like Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram. Studies show that posts expressing anger often receive higher interaction rates, as this emotion triggers strong reactions and prompts users to share or comment, influencing the spread of information. Understanding the function of anger in online discourse is essential for managing digital communities, mitigating conflict, and designing algorithms that balance user experience with content moderation.
Comparing Reactions: Expressing Humor vs Expressing Anger
Expressing humor on social media often generates positive reactions such as likes, shares, and supportive comments that foster community engagement and enhance your online presence. In contrast, expressing anger tends to provoke polarized responses, including heated debates, conflicts, and potential backlash, which may harm your reputation and reduce follower loyalty. Understanding these dynamics helps you tailor your content strategy to maximize engagement while managing risks.
Social Media Algorithms and Reaction Influence
Social media algorithms analyze user behavior, preferences, and engagement patterns to curate personalized content feeds that maximize user interaction and time spent on platforms. Reaction influence, such as likes, shares, and comments, plays a critical role in shaping algorithmic priorities, boosting the visibility of posts that generate significant user responses. This feedback loop intensifies content reach and drives trends by promoting posts with high engagement metrics across networks like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
Cultural Interpretations of "Haha" and "Angry
The cultural interpretations of "Haha" and "Angry" reactions on social media vary significantly across global communities, influencing online communication and emotional expression. In Western cultures, "Haha" often conveys genuine amusement or sarcasm, while the "Angry" reaction signifies frustration or disagreement. Conversely, in some Asian cultures, "Haha" may be used to mask discomfort or politeness, and "Angry" reactions can indicate social disapproval rather than personal anger, highlighting the importance of cultural context in digital interactions.
The Effect of Reactions on Post Engagement
Reactions on social media posts significantly impact your post engagement by influencing algorithm visibility and user interaction rates. Positive reactions such as likes, loves, and shares increase the likelihood of your content appearing on followers' feeds, driving higher reach and interaction. These engagement metrics serve as signals that boost content ranking, making user reactions crucial for expanding your audience and engagement levels.
Brands and Businesses: Leveraging Reactions Strategically
Brands and businesses leverage social media reactions to gauge audience engagement and sentiment, enabling targeted marketing strategies that enhance brand loyalty and customer retention. By analyzing reaction patterns, companies optimize content delivery, tailor campaigns, and improve customer interactions for maximum impact. Strategic use of reactions supports data-driven decisions that drive revenue growth and strengthen competitive advantage in digital markets.
Future Trends in Social Media Reactions
Future trends in social media reactions will increasingly leverage AI-driven sentiment analysis to deliver more personalized and context-aware engagement options. Platforms are expected to expand beyond traditional emojis to include dynamic and interactive reactions that reflect nuanced emotions and real-time expressions. Your social media experience will become more immersive as these advanced reaction features enhance communication and deepen connections with online communities.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com