Photo illustration: Archive vs Block
Archiving on social media hides a post from your profile without deleting it, preserving content for later reference, while blocking restricts specific users from interacting with you or viewing your profile. Discover more about managing your online presence effectively in this article.
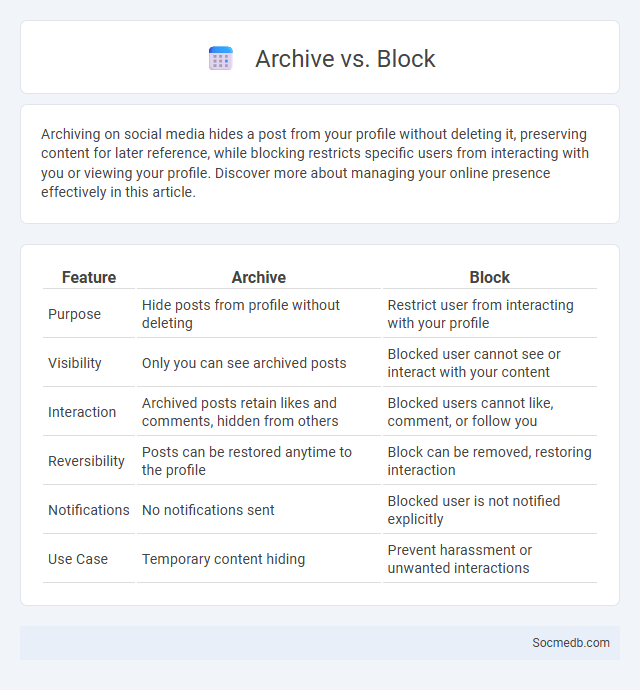
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Archive | Block |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hide posts from profile without deleting | Restrict user from interacting with your profile |
| Visibility | Only you can see archived posts | Blocked user cannot see or interact with your content |
| Interaction | Archived posts retain likes and comments, hidden from others | Blocked users cannot like, comment, or follow you |
| Reversibility | Posts can be restored anytime to the profile | Block can be removed, restoring interaction |
| Notifications | No notifications sent | Blocked user is not notified explicitly |
| Use Case | Temporary content hiding | Prevent harassment or unwanted interactions |
Introduction to Data Storage Types
Data storage types essential for social media platforms include relational databases, NoSQL databases, and cloud storage solutions, each optimized for handling massive volumes of user-generated content and interactions. Relational databases efficiently manage structured data such as user profiles and friend lists, while NoSQL databases are ideal for unstructured data like posts, images, and videos, offering scalability and flexible schema design. Understanding these storage types helps you optimize the management and retrieval of social media data, ensuring faster performance and enhanced user experience.
Understanding Archive Storage
Archive storage in social media platforms involves preserving vast amounts of user-generated content such as posts, images, and videos for long-term access and compliance purposes. Efficient archive storage solutions utilize cloud-based technologies with scalable capacity and robust indexing to ensure quick retrieval and secure data management. Understanding these storage mechanisms is essential for optimizing data retention policies and maintaining user privacy while supporting platform analytics and regulatory requirements.
Explaining Block Storage
Block storage is a data storage method crucial for social media platforms to efficiently manage vast amounts of user-generated content such as images, videos, and posts. Each file is divided into fixed-size blocks stored separately, allowing faster read/write operations and improved data retrieval performance. This technology supports scalability and high availability, ensuring seamless user experiences in social networking and real-time content delivery.
Archive Storage vs Block Storage: Key Differences
Archive storage in social media platforms is designed for long-term data retention with infrequent access, offering cost-effective and durable solutions for storing large volumes of user-generated content such as old posts, multimedia files, and backups. Block storage, on the other hand, provides high-performance, low-latency access to data and is ideal for real-time applications like feed updates, user interactions, and transactional data handling. The key differences lie in access speed, cost, and use case suitability, with archive storage optimizing for durability and economy, while block storage emphasizes speed and flexibility for active data management.
Use Cases for Archive Storage
Archive storage in social media platforms efficiently preserves massive volumes of user-generated content, including photos, videos, and messages, ensuring long-term availability and compliance with data retention policies. Your archived data supports advanced analytics for trend analysis, user behavior insights, and content recovery during audits or legal requests. Leveraging cloud-based archive storage solutions optimizes cost, scalability, and data security for sustained social media operations.
Use Cases for Block Storage
Block storage enhances social media platforms by enabling high-performance data management for user-generated content, such as photos, videos, and messages. It supports scalable, low-latency access to large volumes of unstructured data crucial for real-time content delivery and interactive features. Enterprises leverage block storage for efficient backup, disaster recovery, and seamless integration with analytics tools to improve user engagement and platform reliability.
Performance Comparison: Archive vs Block
Archive preserves social media content for long-term access and analysis, maintaining post visibility and engagement metrics without disruption. Block restricts user interactions by preventing content visibility, leading to a significant drop in engagement and reducing overall account reach. Performance analysis shows archived content sustains audience interest and data retention, whereas blocked content halts user interaction and diminishes social media influence.
Cost Considerations: Archive vs Block
Archiving social media content incurs lower costs by preserving data while allowing future access, making it ideal for long-term storage without immediate deletion. Blocking content involves higher operational expenses due to ongoing moderation, legal compliance, and potential user support efforts. You should weigh the balance between upfront archive savings and the continuous costs associated with maintaining blocked content.
Security and Compliance in Archive and Block Storage
Social media platforms implement advanced encryption and multi-factor authentication to ensure data security in archive and block storage systems, protecting user information from unauthorized access and breaches. Compliance with regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA is enforced through automated data retention policies and secure access controls, maintaining data integrity and privacy. Continuous monitoring and regular audits of archived data help identify vulnerabilities and ensure adherence to industry standards and legal requirements.
Choosing the Right Storage Solution for Your Needs
Selecting the right storage solution for your social media content ensures efficient management of large volumes of photos, videos, and metadata. Cloud-based storage offers scalability and remote access, while local storage provides faster retrieval and enhanced security for sensitive data. Your choice should balance cost, accessibility, and data backup options to optimize performance and protect valuable social media assets.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com