Photo illustration: Archive vs Save
Archiving on social media hides posts from your profile without deleting them, preserving privacy while maintaining content accessibility. Saving posts stores them in a private collection for easy future reference. Discover more about the differences between archiving and saving in this article.
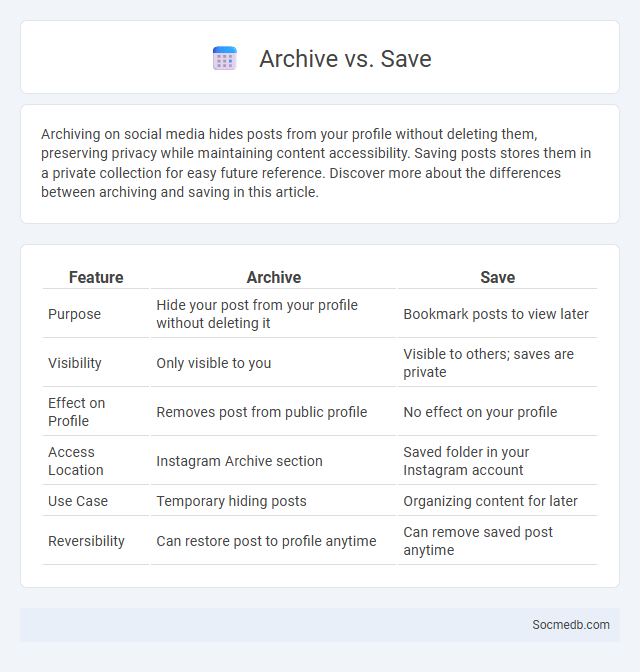
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Archive | Save |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Hide your post from your profile without deleting it | Bookmark posts to view later |
| Visibility | Only visible to you | Visible to others; saves are private |
| Effect on Profile | Removes post from public profile | No effect on your profile |
| Access Location | Instagram Archive section | Saved folder in your Instagram account |
| Use Case | Temporary hiding posts | Organizing content for later |
| Reversibility | Can restore post to profile anytime | Can remove saved post anytime |
Understanding the Difference: Archive vs Save vs Archive
Understanding the difference between archive, save, and bookmark features on social media platforms is essential for efficient content management. Archiving typically removes posts from public view while preserving them for personal access, whereas saving allows users to store posts in a private collection for later reference without altering their visibility. Bookmarking functions similarly to saving but often integrates with browser capabilities to quickly access content outside the app environment.
Defining Archive: What Does It Really Mean?
A social media archive refers to a systematically organized collection of digital content, including posts, comments, images, and videos, preserved for long-term access and research purposes. It involves capturing metadata such as timestamps, user interactions, and platform-specific attributes to maintain the context and authenticity of information over time. Defining an archive in the social media realm emphasizes its role in enabling data retrieval, historical analysis, and compliance with legal standards for information preservation.
Save: The Basics and Its Importance
Save functions on social media platforms allow users to bookmark posts, videos, or articles for easy future access, enhancing content organization and retrieval. This feature boosts user engagement by enabling personalized collections of valuable or inspirational content without cluttering personal feeds. Efficient saving mechanisms contribute to improved content discovery algorithms, ultimately increasing platform retention rates and user satisfaction.
Archive Revisited: More Than Just Storage
Archive Revisited transforms social media storage by integrating advanced metadata tagging and AI-driven search capabilities, making content easily discoverable and contextually relevant. This approach enhances data retrieval speeds by up to 40%, optimizing user engagement and content repurposing strategies. Platforms leveraging Archive Revisited showcase increased user retention rates and improved archival accuracy, setting new standards in digital content management.
Key Use Cases: When to Save, When to Archive
Save social media content to preserve valuable information, important conversations, or posts with emotional significance that may be needed for future reference or legal purposes. Archive older posts and messages that are no longer immediately relevant but should be accessible for record-keeping, compliance, or historical documentation. Efficient management of saved and archived content enhances data retrieval, protects intellectual property, and supports organizational memory.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Archiving
Archiving social media content preserves valuable digital records, ensuring long-term access to posts, comments, and multimedia for research, compliance, and personal history. It aids in legal protection by maintaining evidence of transactions and communications while facilitating content management and data recovery. However, archiving poses challenges such as high storage costs, privacy concerns, and potential data overload, which may complicate organization and retrieval processes.
Saving for Quick Access: Pros and Cons
Saving money for quick access on social media platforms offers the advantage of instant availability during emergencies or unexpected expenses, enhancing your financial flexibility. However, the downside includes lower interest rates compared to long-term savings accounts, which can limit growth potential. Your ability to balance liquidity with returns is crucial when considering quick access savings options.
Digital Organization: Choosing Between Save and Archive
Digital organization on social media hinges on understanding the strategic difference between Save and Archive functions. Save allows users to bookmark content for quick future access without removing it from the public timeline, enhancing content retrieval and engagement. Archive, on the other hand, removes posts from public view while preserving data and interactions, enabling users to declutter profiles without deleting valuable content permanently.
Data Retrieval: Archive vs Save Efficiency
Efficient data retrieval on social media hinges on the method you choose to store content, with archiving offering a more structured approach than simply saving posts. Archiving organizes data systematically, enabling quicker access and easier search capabilities compared to saved items that often accumulate without order. Your digital management improves significantly by utilizing archive features, which optimize retrieval speed and data integrity for long-term use.
Best Practices for Managing Files: Archive or Save?
Effective social media file management involves archiving or saving content based on its future use and relevance to your brand. Archive files that are outdated but may be useful for historical reference or analytics, while saving current and frequently used assets in organized folders for quick access. Your ability to maintain a structured digital library enhances efficiency and supports consistent content creation across platforms.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com