Photo illustration: 2nd degree vs 3rd degree
Second-degree social media connections refer to friends of your friends, expanding your network beyond direct contacts, while third-degree connections include friends of those second-degree contacts, further extending your reach. Explore this article to understand how leveraging these connection layers can enhance your social networking strategy.
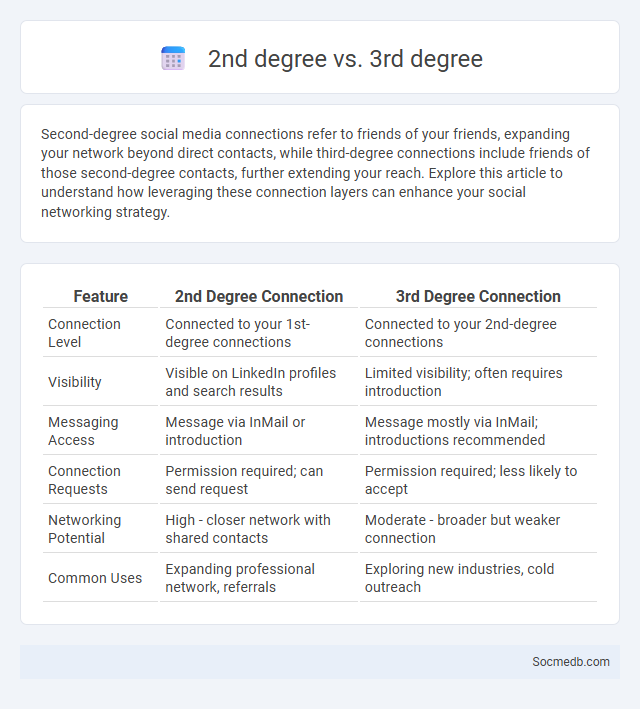
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 2nd Degree Connection | 3rd Degree Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Level | Connected to your 1st-degree connections | Connected to your 2nd-degree connections |
| Visibility | Visible on LinkedIn profiles and search results | Limited visibility; often requires introduction |
| Messaging Access | Message via InMail or introduction | Message mostly via InMail; introductions recommended |
| Connection Requests | Permission required; can send request | Permission required; less likely to accept |
| Networking Potential | High - closer network with shared contacts | Moderate - broader but weaker connection |
| Common Uses | Expanding professional network, referrals | Exploring new industries, cold outreach |
Understanding Degree Classifications
Degree classifications on social media platforms often use influencer tiers such as micro, macro, and mega to categorize users based on their follower count and engagement rates. Your understanding of these classifications can help optimize marketing strategies, ensuring you target the appropriate audience size and maximize content reach. Accurate recognition of these tiers allows for more effective collaborations and resource allocation in social media campaigns.
What is a 2nd Degree Relationship?
A 2nd degree relationship on social media refers to the connection between two users who are linked through a mutual friend but do not know each other directly. This level of connection expands networking opportunities by allowing access to contacts just one step removed from direct friends. Platforms like LinkedIn and Facebook use 2nd degree relationships to suggest potential connections and facilitate introductions.
Defining 3rd Degree Connections
Third-degree connections on social media refer to the contacts that are connected to your friends' friends, representing a network two steps removed from your direct connections. These connections expand your reach, enabling access to potential opportunities, contacts, or information available within a broader network. Understanding and leveraging third-degree connections can enhance your social visibility and professional networking efficiency.
Exploring the Concept of Connection Degree
The connection degree on social media measures the number of direct and indirect interactions between users, reflecting how closely individuals are linked within a network. Understanding your connection degree helps optimize your social reach and engagement potential, revealing pathways to expand influence and foster meaningful relationships. Platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn utilize this metric to suggest new contacts or content, enhancing the interconnectedness of your digital community.
Key Differences: 2nd vs 3rd Degree
Second-degree social media connections involve interactions between friends of friends, creating a wider but still somewhat familiar network that influences content visibility and engagement through mutual connections. Third-degree connections extend further to friends of friends of friends, significantly broadening the potential audience but reducing the likelihood of direct interaction or trust. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing social media strategies, targeting, and viral content spread.
Practical Examples of Each Degree
Social media impact varies across degrees of engagement, from passive scrolling to active content creation. Observing a brand's posts without interaction represents first-degree exposure, while liking or sharing content shows second-degree involvement, enhancing visibility and reach. Creating original content or managing community interactions exemplifies third-degree engagement, strengthening Your online presence and influence.
How Connection Degree Impacts Networking
Connection degree significantly influences networking efficiency by determining the reach and diversity of social media interactions. First-degree connections offer direct communication and trust, while second and third-degree connections enable access to broader networks and potential opportunities. Higher connection degrees amplify information flow, collaboration potential, and discovery of new contacts essential for professional and personal growth on social platforms.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Degree
Social media offers significant benefits including enhanced connectivity, real-time communication, and targeted marketing opportunities, but it also presents challenges such as privacy concerns, misinformation, and digital addiction. You must navigate each platform's degree of engagement carefully to maximize outreach while minimizing risks like data breaches and algorithmic biases. Understanding these nuances ensures effective and responsible use of social media for both personal and business growth.
Choosing the Right Degree for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate social media degree requires evaluating programs that emphasize digital marketing, content creation, and data analytics to align with your career goals. Degrees in communications, marketing, or media studies equipped with hands-on experience in social media platforms offer practical skills for managing online engagement and analytics. Identifying curricula that focus on current social media strategies and technologies ensures you gain relevant knowledge for roles like social media strategist, digital marketer, or content manager.
Frequently Asked Questions About Connection Degrees
Connection degrees on social media define the levels of relationship between users, such as first-degree (direct connections), second-degree (friends of friends), and third-degree (friends of friends of friends). Understanding these degrees helps optimize networking, content visibility, and targeted advertising by identifying how closely users are linked within a platform. Many platforms provide tools to visualize and measure these connections, enabling users to expand their network strategically.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com