Photo illustration: 2nd degree vs mutual connection
Second-degree connections on social media refer to friends of your friends, extending your network beyond direct contacts. Understanding the difference between second-degree and mutual connections can enhance your networking strategy; discover more insights in this article.
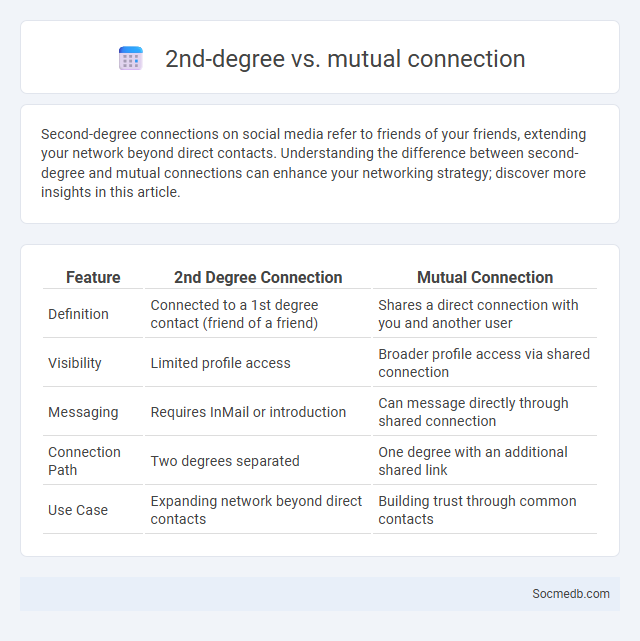
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 2nd Degree Connection | Mutual Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Connected to a 1st degree contact (friend of a friend) | Shares a direct connection with you and another user |
| Visibility | Limited profile access | Broader profile access via shared connection |
| Messaging | Requires InMail or introduction | Can message directly through shared connection |
| Connection Path | Two degrees separated | One degree with an additional shared link |
| Use Case | Expanding network beyond direct contacts | Building trust through common contacts |
Understanding LinkedIn Connection Degrees
LinkedIn connection degrees define the relationship strength between users, categorized as 1st-degree (direct connections), 2nd-degree (connections of 1st-degree contacts), and 3rd-degree (connections of 2nd-degree contacts). Understanding these connection levels is crucial for optimizing networking strategies, expanding professional reach, and leveraging mutual contacts for introductions. Effective use of LinkedIn's connection degrees enhances visibility and opens opportunities for career growth and business development.
What is a 1st Degree Connection?
A 1st Degree Connection on social media platforms like LinkedIn refers to individuals you have directly connected with, indicating a mutual acceptance of connection requests. These connections allow you to communicate freely, share content, and access each other's full profiles, fostering stronger networking opportunities. Understanding your 1st Degree Connections helps you leverage your immediate professional network effectively to enhance your career growth.
Defining 2nd Degree Connections
Second-degree connections on social media refer to individuals who are connected to your direct contacts but not directly linked to you. These connections represent the extended network of friends or followers, often accessible through mutual acquaintances. Leveraging second-degree connections enhances networking opportunities and potential outreach by tapping into shared relationships and interests.
The Meaning of Mutual Connections
Mutual connections on social media represent shared relationships that bridge your network to others, enhancing trust and credibility. Leveraging these overlapping contacts can expand your influence and foster meaningful interactions within professional and personal communities. Your ability to identify and engage with mutual connections strengthens networking opportunities and deepens relational bonds.
How Connection Degrees Differ on LinkedIn
Connection degrees on LinkedIn represent the levels of proximity between users: 1st-degree connections are direct contacts, 2nd-degree connections connect through mutual contacts, and 3rd-degree connections extend beyond immediate networks. These hierarchical distinctions influence networking opportunities, message privileges, and visibility within the platform's algorithm. Understanding how LinkedIn categorizes these connection degrees enables professionals to strategically expand their network and optimize engagement.
Advantages of 2nd Degree Connections
2nd degree connections on social media significantly expand your networking potential by introducing you to a wider audience beyond your immediate circle. These connections increase opportunities for collaboration, job referrals, and knowledge exchange, enhancing your professional growth. Leveraging 2nd degree connections allows you to build trust through mutual acquaintances, making outreach more effective and personalized.
The Role of Mutual Connections in Networking
Mutual connections serve as crucial trust bridges in social media networking, enabling users to form authentic relationships through shared acquaintances. Platforms like LinkedIn leverage these connections to facilitate introductions and expand professional networks, increasing opportunities for career advancement. The presence of mutual contacts often boosts credibility and fosters engagement, making networking more effective and efficient.
Expanding Your Network Through Connection Degrees
Social media platforms leverage connection degrees to expand your network exponentially, enabling access to friends of friends and beyond. Engaging actively with second- and third-degree connections increases visibility and fosters meaningful relationships across diverse professional and personal circles. Utilizing targeted outreach and personalized interactions accelerates network growth and opportunities for collaboration within your industry.
Connection Degrees: Privacy and Accessibility
Connection degrees on social media platforms determine the level of privacy and accessibility of your shared content, allowing control over who can view your posts based on whether they are close friends, acquaintances, or public followers. By customizing connection tiers, you enhance your privacy settings, ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to trusted contacts while maintaining broader engagement opportunities. Understanding and managing these connection degrees empowers you to balance social interaction with personal security effectively.
Connection Strategy: Leveraging 2nd Degree and Mutual Connections
Leveraging 2nd degree and mutual connections enhances social media connection strategies by expanding network reach through trusted relationships. Focusing on these connections increases the likelihood of engagement and trust, as introductions often come from familiar contacts. Utilizing platform features like LinkedIn's mutual connections tool enables targeted outreach and personalized communication, driving more effective relationship building.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com