Photo illustration: Network Effects vs Economies of Scale (LinkedIn)
LinkedIn leverages strong network effects by increasing user value as more professionals join, creating a self-reinforcing growth cycle. Its economies of scale reduce costs per user, amplifying profitability and service efficiency; explore how these dynamics shape LinkedIn's market dominance in this article.
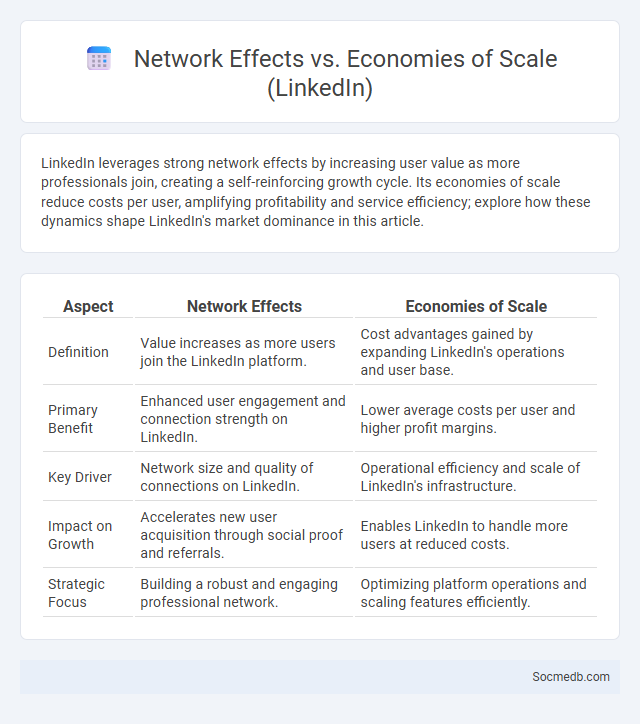
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Network Effects | Economies of Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Value increases as more users join the LinkedIn platform. | Cost advantages gained by expanding LinkedIn's operations and user base. |
| Primary Benefit | Enhanced user engagement and connection strength on LinkedIn. | Lower average costs per user and higher profit margins. |
| Key Driver | Network size and quality of connections on LinkedIn. | Operational efficiency and scale of LinkedIn's infrastructure. |
| Impact on Growth | Accelerates new user acquisition through social proof and referrals. | Enables LinkedIn to handle more users at reduced costs. |
| Strategic Focus | Building a robust and engaging professional network. | Optimizing platform operations and scaling features efficiently. |
Understanding Network Effects: Definition and Types
Network effects occur when the value of a social media platform increases as more users join, enhancing Your overall experience and engagement. Direct network effects arise when each new user adds value by expanding connections, while indirect network effects stem from complementary services or products that grow alongside the platform. Understanding these types helps optimize strategies for user growth and platform development.
What Are Economies of Scale?
Economies of scale refer to the cost advantages that social media companies achieve as their platforms grow and user bases expand, allowing them to spread fixed costs like infrastructure, development, and content moderation over a larger number of active users. As social media platforms scale up, advertising revenues increase while the marginal cost per user decreases, boosting profitability and competitive advantage. Major networks like Facebook and Instagram leverage economies of scale through advanced algorithms and global server networks to efficiently handle massive data traffic and user engagement.
Key Differences: Network Effects vs. Economies of Scale
Network effects in social media occur when each new user increases the platform's value for existing users, driving exponential growth and engagement. Economies of scale reduce the average cost per user as the platform expands, enhancing operational efficiency and profitability. Understanding these key differences helps you leverage social media strategies that maximize both user connectivity and cost advantages.
How LinkedIn Harnesses Network Effects
LinkedIn harnesses network effects by continuously expanding its user base, increasing the value of the platform as more professionals join and interact. Your connections create exponential opportunities for job referrals, content sharing, and collaboration, making the platform indispensable for career growth. The platform's algorithms amplify engagement by promoting relevant content and connections, driving user retention and platform value.
The Role of Economies of Scale in LinkedIn’s Growth
LinkedIn's growth has been significantly fueled by economies of scale achieved through its expanding user base, which enhances network effects and increases the platform's value to both professionals and advertisers. The scaling of data analytics and targeted advertising capabilities reduces per-user costs, driving higher revenue while improving user engagement. By leveraging large-scale infrastructure and user data, LinkedIn optimizes personalized content delivery and recruitment solutions, reinforcing its competitive advantage in the social media market.
User Acquisition Strategies: Network Effects in Action
User acquisition strategies thrive on network effects by leveraging the exponential growth of social connections to increase platform value and attract new users. As your social media network expands, each additional user enhances the experience for everyone, encouraging organic growth and boosting engagement rates. Maximizing these network effects creates a self-sustaining cycle that significantly reduces customer acquisition costs and accelerates market penetration.
Market Dominance: Economies of Scale Compared to Network Effects
Social media platforms achieve market dominance primarily through network effects, where the value of the platform increases as more users join, creating a self-reinforcing cycle of user growth and engagement. Economies of scale contribute by reducing operational costs per user, but these cost advantages are secondary to the exponential benefits generated by large, interconnected user bases. Platforms like Facebook and Instagram exemplify how dominant network effects create significant barriers to entry, surpassing the competitive edge provided by economies of scale alone.
Challenges and Risks of Relying on Network Effects
Social media platforms face significant challenges and risks when relying heavily on network effects, including user saturation and decreased growth potential once a critical mass is reached. The dominance of major platforms like Facebook and Twitter can create barriers to entry for new competitors, limiting innovation and diversity. Privacy concerns and misinformation also escalate as network size increases, amplifying the impact of harmful content and data breaches.
Building Competitive Advantages: Layering Network Effects and Economies of Scale
Social media platforms achieve competitive advantages by layering strong network effects with economies of scale, attracting more users as the value of the network increases exponentially. As user growth amplifies data generation and engagement, these platforms lower marginal costs while enhancing personalized content delivery and advertising precision. This synergy creates barriers to entry for rivals and drives sustainable market dominance.
Future Trends: Maximizing Value Through Network Effects
Social media platforms will increasingly leverage network effects to boost user engagement and maximize value, as interconnected user bases generate exponential growth in content sharing and interactions. Enhanced algorithms and AI-driven personalization will amplify these network effects by delivering more relevant content, fostering stronger community ties, and increasing time spent on platforms. Innovations such as decentralized social networks and integration with the metaverse will further extend these network effects, creating immersive and value-rich social experiences.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com