Photo illustration: Lurker vs Lurker (comparisons of different types)
Lurkers in social media vary from passive observers who consume content quietly to reactive lurkers who engage through likes or shares without posting. Discover detailed comparisons of different lurker types and their impacts on online communities in this article.
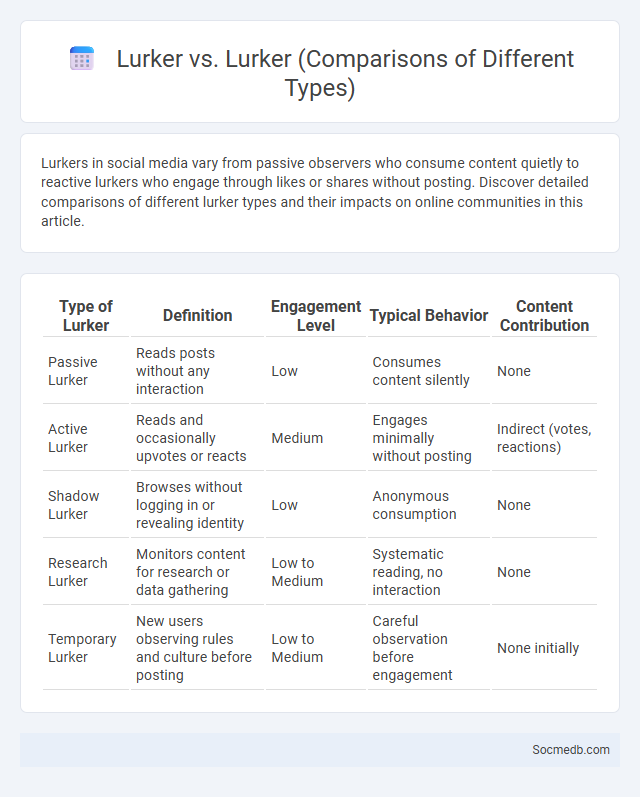
Table of Comparison
| Type of Lurker | Definition | Engagement Level | Typical Behavior | Content Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Passive Lurker | Reads posts without any interaction | Low | Consumes content silently | None |
| Active Lurker | Reads and occasionally upvotes or reacts | Medium | Engages minimally without posting | Indirect (votes, reactions) |
| Shadow Lurker | Browses without logging in or revealing identity | Low | Anonymous consumption | None |
| Research Lurker | Monitors content for research or data gathering | Low to Medium | Systematic reading, no interaction | None |
| Temporary Lurker | New users observing rules and culture before posting | Low to Medium | Careful observation before engagement | None initially |
Introduction to Lurkers: Defining the Term
Lurkers on social media are users who consume content without actively participating in discussions or creating their own posts. This group constitutes a significant portion of online communities, often representing around 70-90% of the audience on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Reddit. Understanding lurkers' behavior helps in tailoring content strategies to increase engagement and foster a more interactive digital environment.
Types of Lurkers in Online Communities
Social media platforms host various types of lurkers in online communities, including passive observers who consume content without interaction, selective participants who engage only with specific topics or users, and occasional contributors who post infrequently while predominantly remaining silent. These lurker profiles influence community dynamics by shaping content visibility and engagement patterns without direct participation in discussions. Understanding lurker behavior helps in designing strategies to increase active user involvement and foster a more vibrant online community.
Passive Lurker vs. Active Lurker: Key Differences
Passive lurkers consume social media content without engaging, often missing out on opportunities to build connections and influence conversations. Active lurkers, however, interact through comments, shares, or likes, enhancing their social presence and increasing content visibility. Your choice between passive and active engagement directly impacts your online influence and network growth.
Social Media Lurkers vs. Forum Lurkers
Social media lurkers primarily engage with content on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter without interacting, whereas forum lurkers typically observe discussions on specialized online communities without posting. Your presence as a lurker means you consume valuable information and trends silently, which can inform your interests and decisions without the need for active participation. Understanding these behaviors helps marketers tailor content strategies to convert passive users into engaged followers.
Motivations Behind Lurking: A Comparative Overview
Social media lurking is primarily driven by users' desire for information gathering, passive enjoyment, and social comparison without active participation. Research shows that lurkers seek to stay updated on trends, observe social dynamics, and avoid potential negative interactions while still maintaining a sense of community connection. This behavior contrasts with active engagement motives, highlighting the dual nature of online social experience where consumption often outweighs contribution.
Engagement Patterns: Different Lurker Behaviors
Social media engagement patterns reveal distinct lurker behaviors, including passive consumption, occasional interaction, and selective participation, which impact content visibility and community dynamics. Understanding these subtle variations helps optimize your content strategy to foster deeper connections and encourage more active involvement from hesitant users. Tailoring posts to address the interests and comfort levels of different lurker types maximizes audience reach and engagement.
Impact of Lurkers on Community Dynamics
Lurkers, who constitute a significant portion of social media communities, subtly influence community dynamics by absorbing content without active participation, thereby affecting engagement metrics and perceived community health. Your presence as an active member can encourage these silent observers to contribute, fostering richer interactions and diverse perspectives. Understanding the impact of lurkers helps in developing strategies to balance content creation and consumption, enhancing overall community vitality.
Lurker vs. Lurker: Case Studies and Examples
Social media lurkers are users who consume content without actively engaging, contrasting with active participants who comment and share posts. Case studies reveal that lurkers often exceed active users in number, influencing trends indirectly through passive data collection and content exposure. Examples from platforms like Reddit and Instagram highlight how lurkers contribute to community growth by silently observing discussions while shaping algorithm-driven content recommendations.
Benefits and Challenges of Lurker Diversity
Lurker diversity in social media enriches your online community by bringing varied perspectives and enhancing content engagement without immediate contributions. These silent participants contribute to the collective knowledge base and increase reach through passive interactions like views and shares. However, managing the balance between active users and lurkers presents challenges in fostering meaningful conversations and measuring true engagement levels.
Encouraging Participation: Turning Lurkers into Contributors
Encouraging participation in social media transforms passive lurkers into active contributors by fostering inclusive content and interactive features. Utilizing targeted prompts, personalized notifications, and community challenges increases user engagement and content generation. Platforms that prioritize user involvement see higher retention rates and more dynamic online communities.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com