Photo illustration: Lurker vs Spammer
Lurkers silently consume content without interaction, while spammers aggressively flood social media platforms with unsolicited messages, often harming user experience. Discover more insights on managing these user types in this article.
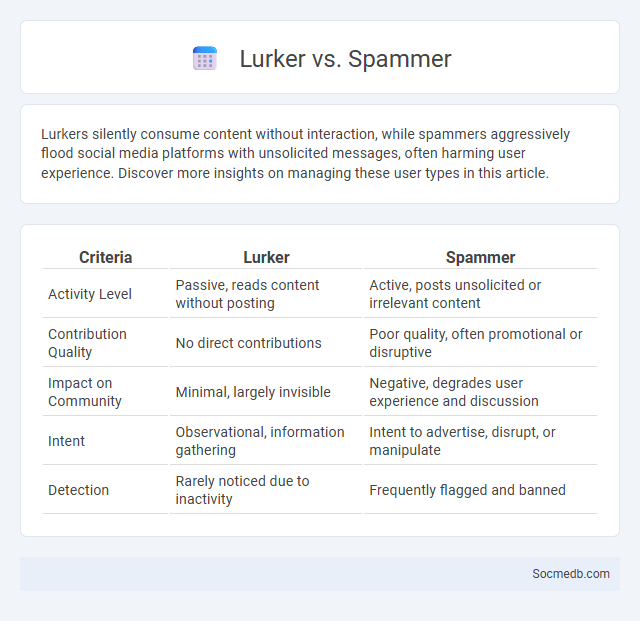
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Lurker | Spammer |
|---|---|---|
| Activity Level | Passive, reads content without posting | Active, posts unsolicited or irrelevant content |
| Contribution Quality | No direct contributions | Poor quality, often promotional or disruptive |
| Impact on Community | Minimal, largely invisible | Negative, degrades user experience and discussion |
| Intent | Observational, information gathering | Intent to advertise, disrupt, or manipulate |
| Detection | Rarely noticed due to inactivity | Frequently flagged and banned |
Introduction: Understanding Online Personas
Online personas shape how you present yourself across social media platforms, influencing perceptions and interactions. Crafting a consistent and authentic persona enhances your digital identity and builds trust with your audience. Effective management of your online presence helps control the narrative and supports personal or professional goals.
Defining the Lurker: Silent Observer
A lurker on social media is a silent observer who regularly consumes content without actively engaging through likes, comments, or shares. These users contribute to view counts and data analytics but remain invisible in interactive metrics. Understanding your lurkers helps tailor content strategies that encourage participation and foster community growth.
The Spammer: Disruptor of Digital Spaces
The Spammer floods your social media feeds with irrelevant or malicious content, disrupting authentic digital interactions and degrading user experience. This behavior compromises platform integrity by spreading misinformation, phishing links, and unwanted advertisements, which can lead to decreased engagement and trust. Effective spam detection algorithms are essential to safeguard online communities and maintain the quality of your digital spaces.
Lurker vs Spammer: Key Differences
Lurkers silently consume social media content without actively engaging, often representing a significant portion of the audience who prefer observation over participation. Spammers, in contrast, disrupt social platforms by posting unsolicited or irrelevant messages, aiming to promote products, scams, or malicious links. Understanding the behaviors of lurkers versus spammers helps improve community management and user experience by differentiating between passive users and harmful actors.
Motivations Behind Lurking
Social media lurking is often driven by the desire to gather information, maintain social connections, and avoid potential social risks by observing without participating. Users may lurk to monitor trending topics, stay informed about friends or communities, and manage their online presence cautiously. This passive engagement satisfies curiosity and social needs while minimizing exposure to negative interactions or privacy concerns.
Why Spammers Spam: Underlying Intentions
Spammers spam primarily to exploit social media platforms for financial gain through phishing, spreading malware, or generating fake traffic for advertising revenue. They also seek to manipulate public opinion, promote scams, and harvest personal data for identity theft. These malicious activities undermine user trust and degrade the overall social media experience.
Community Impact: Lurkers vs Spammers
Social media communities thrive when genuine interactions outweigh passive lurkers who consume content without engaging and harmful spammers who disrupt conversations with irrelevant posts. Your participation can strengthen these networks by fostering meaningful discussions and minimizing spam's negative effects. Platforms with active, engaged users see higher trust levels and more vibrant online ecosystems.
The Double Lurker Phenomenon
The Double Lurker Phenomenon describes social media users who silently consume content across multiple platforms without engaging through likes, comments, or shares, significantly impacting content visibility and algorithmic reach. Studies show that nearly 30% of users fall into this category, contributing to passive engagement trends and skewing typical user interaction metrics. Understanding this behavior is crucial for marketers aiming to optimize strategies for deeper audience interaction and accurate data analysis.
Managing Lurkers and Spammers in Forums
Effective management of lurkers and spammers in social media forums enhances community engagement and maintains content quality. Moderators utilize tools such as automated filters, activity monitoring, and user verification to identify and address disruptive behaviors promptly. Your proactive involvement in reporting suspicious activity helps sustain a healthy and interactive online environment.
Conclusion: Finding Balance in Online Communities
Maintaining a healthy balance in online communities requires users to engage mindfully, fostering positive interactions while limiting exposure to harmful content. Emphasizing digital well-being tools, such as screen time management and content moderation, supports sustainable social media use. Prioritizing authentic connections over passive scrolling enhances mental health and strengthens community trust on platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com