Photo illustration: vote manipulation vs censorship
Social media platforms face challenges balancing vote manipulation risks with concerns about censorship, impacting the integrity of online democratic processes. Discover how these issues influence digital governance and public discourse in this article.
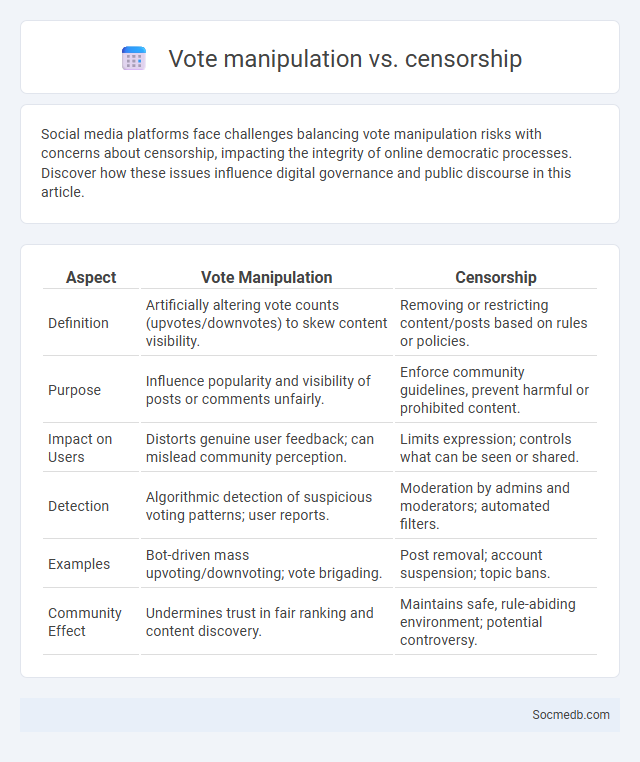
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Vote Manipulation | Censorship |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificially altering vote counts (upvotes/downvotes) to skew content visibility. | Removing or restricting content/posts based on rules or policies. |
| Purpose | Influence popularity and visibility of posts or comments unfairly. | Enforce community guidelines, prevent harmful or prohibited content. |
| Impact on Users | Distorts genuine user feedback; can mislead community perception. | Limits expression; controls what can be seen or shared. |
| Detection | Algorithmic detection of suspicious voting patterns; user reports. | Moderation by admins and moderators; automated filters. |
| Examples | Bot-driven mass upvoting/downvoting; vote brigading. | Post removal; account suspension; topic bans. |
| Community Effect | Undermines trust in fair ranking and content discovery. | Maintains safe, rule-abiding environment; potential controversy. |
Understanding Vote Manipulation: Definition and Examples
Vote manipulation refers to artificially inflating or deflating the number of likes, shares, or upvotes on social media platforms to distort public perception and influence decision-making. Common examples include the use of bots to generate fake engagement, coordinated campaigns to sway poll results, and purchasing votes or clicks to boost content visibility. Recognizing these tactics is crucial for maintaining the integrity of online interactions and ensuring authentic user feedback.
The Mechanics of Online Censorship
Online censorship operates through automated algorithms and human moderators that analyze content for violations of platform policies, often targeting hate speech, misinformation, or politically sensitive topics. These mechanisms employ keyword detection, user reporting, and machine learning models to identify and remove or restrict posts, which can sometimes result in over-censorship or bias against certain viewpoints. Understanding these processes empowers You to navigate social media more critically and advocate for transparent content moderation policies.
Key Differences Between Vote Manipulation and Censorship
Vote manipulation on social media involves artificially altering user engagement metrics, such as likes or votes, to skew popularity or visibility, while censorship involves the deliberate removal or suppression of content to restrict information flow. Manipulation targets the perception of consensus or popularity, affecting your ability to gauge genuine public opinion accurately. Censorship controls what content you can access by blocking or hiding posts based on specific criteria or policies enforced by platforms or authorities.
Vote Manipulation: Methods and Impact on Platforms
Vote manipulation on social media platforms involves tactics such as fake accounts, bots, and coordinated voting rings designed to artificially inflate or deflate content popularity. These methods can distort algorithmic rankings, leading to misinformation spread and reduced user trust. Understanding how your interactions may be influenced by manipulated votes helps maintain platform integrity and authentic engagement.
Censorship: Motivations and Mechanisms
Social media platforms enforce censorship to regulate content that violates community standards, addresses misinformation, hate speech, or illegal activities, protecting users and advertisers. Algorithms and human moderators work together to detect and remove harmful posts, while policies vary across platforms and regions based on legal and cultural norms. Understanding these mechanisms helps you navigate content visibility and engage responsibly within these digital ecosystems.
How Vote Manipulation Skews Digital Discourse
Vote manipulation on social media platforms distorts digital discourse by artificially inflating certain opinions, leading to a misleading representation of public sentiment. Algorithms prioritize content with high engagement, so manipulated votes can amplify misinformation and suppress genuine viewpoints, creating filter bubbles that limit diverse perspectives. Your online interactions become less reflective of true consensus, undermining the credibility of discussions and democratic decision-making online.
The Legal and Ethical Dimensions of Moderation
Social media platforms face complex legal and ethical challenges in content moderation, balancing free speech with the need to prevent harm such as hate speech, misinformation, and harassment. Your responsibility as a user involves understanding platform policies and reporting violations while respecting others' rights to expression. Compliance with legal standards like the Digital Services Act and ethical principles ensures safer, more inclusive online communities.
Case Studies: Real-World Instances of Voting Abuse and Censorship
Case studies reveal how social media platforms have been manipulated through voting abuse and targeted censorship, impacting election outcomes and public opinion. Examples include coordinated bot campaigns skewing poll results and suppression of dissenting voices during major political events. Understanding these instances helps you recognize the significance of transparency and accountability in digital democracy.
Preventing Manipulation and Censorship: Platform Strategies
Social media platforms employ advanced algorithms and transparent content moderation policies to prevent manipulation and censorship, ensuring the authenticity and diversity of online discourse. These strategies include real-time monitoring for coordinated inauthentic behavior, deploying AI-driven detection tools for misinformation, and implementing clear appeals processes to protect free expression. Collaboration with independent fact-checkers and user education initiatives further enhance platform integrity and democratic participation.
Building Transparent and Trustworthy Online Communities
Building transparent and trustworthy online communities requires clear communication, honest content sharing, and consistent moderation policies. Your engagement should foster openness by addressing concerns promptly and promoting authentic interactions among members. Establishing reliable guidelines and demonstrating accountability enhances trust and strengthens social media relationships.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com