Photo illustration: vote manipulation vs vote fraud
Social media platforms face challenges distinguishing vote manipulation, which involves organizing misleading online campaigns, from vote fraud, the illegal alteration of ballots. Explore this article to understand the impact of both on electoral integrity.
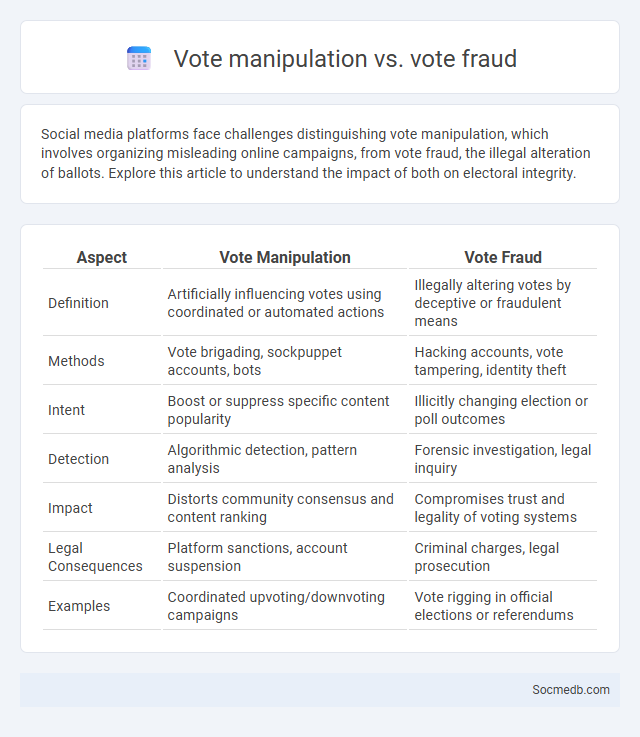
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Vote Manipulation | Vote Fraud |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Artificially influencing votes using coordinated or automated actions | Illegally altering votes by deceptive or fraudulent means |
| Methods | Vote brigading, sockpuppet accounts, bots | Hacking accounts, vote tampering, identity theft |
| Intent | Boost or suppress specific content popularity | Illicitly changing election or poll outcomes |
| Detection | Algorithmic detection, pattern analysis | Forensic investigation, legal inquiry |
| Impact | Distorts community consensus and content ranking | Compromises trust and legality of voting systems |
| Legal Consequences | Platform sanctions, account suspension | Criminal charges, legal prosecution |
| Examples | Coordinated upvoting/downvoting campaigns | Vote rigging in official elections or referendums |
Understanding Vote Manipulation: Definitions and Types
Vote manipulation on social media involves tactics designed to artificially influence the popularity or visibility of content, such as likes, shares, comments, or upvotes. Common types include vote buying, where individuals or groups pay for engagement; vote brigading, coordinated mass upvoting or downvoting by communities; and bot-driven manipulation, using automated accounts to skew results. Recognizing these practices is crucial for maintaining platform integrity and ensuring authentic user interactions.
What is Vote Fraud? Key Differences from Manipulation
Vote fraud involves illegal interference with the election process, such as casting multiple ballots or falsifying results, directly undermining the integrity of democratic systems. Social media manipulation, by contrast, refers to the spread of misleading information or coordinated campaigns to influence public perception without altering actual vote counts. Understanding these distinctions helps You recognize the different threats to fair elections and focus efforts on promoting transparency and accountability.
Common Methods of Vote Manipulation
Common methods of vote manipulation on social media include bot accounts that artificially inflate likes, shares, or votes, and coordinated campaigns using fake profiles to sway public opinion. You should be aware of astroturfing tactics, where organized groups create the illusion of widespread support to influence algorithms and decision-making. Detection often involves analyzing irregular activity patterns and cross-referencing user behavior to maintain platform integrity.
Tactics Used in Vote Fraud: A Closer Look
Social media platforms have become critical battlegrounds for election interference, with vote fraud tactics including coordinated misinformation campaigns, fake accounts, and automated bots designed to manipulate public opinion and suppress voter turnout. These tactics exploit algorithmic biases and spread divisive content rapidly, undermining trust in electoral processes. Advanced data analytics and AI-driven targeting enable perpetrators to identify and influence vulnerable demographics, amplifying the scale and impact of fraudulent activities.
Digital vs. Analog Vote Manipulation Techniques
Digital vote manipulation techniques leverage algorithms, bots, and deepfake technology to sway public opinion and distort election outcomes on social media platforms. Analog methods involve traditional tactics such as misinformation through print media, phone call campaigns, and physical disruption of voting processes. Understanding the interplay between digital algorithms and human-driven analog strategies is crucial for safeguarding electoral integrity in the digital age.
Impact of Vote Manipulation on Democratic Processes
Vote manipulation through social media platforms disrupts the integrity of democratic processes by spreading misinformation and influencing voter behavior unfairly. Coordinated disinformation campaigns exploit algorithmic biases to amplify divisive content, undermining public trust and skewing election outcomes. The resulting erosion of transparent and fair elections threatens the fundamental principles of democracy and civic participation.
Legal Frameworks Addressing Vote Fraud
Legal frameworks addressing vote fraud on social media include regulations that enforce transparency, such as the Honest Ads Act requiring disclosure of political ad sponsors. Platforms like Facebook and Twitter implement algorithms to detect and remove misleading content and coordinate with government agencies to identify foreign interference. Cybersecurity laws and election integrity acts further enhance protections against manipulation by mandating reporting of suspicious activities and penalizing fraudulent behavior.
Famous Cases of Vote Manipulation and Fraud
Famous cases of vote manipulation and fraud on social media highlight the vulnerability of digital platforms to coordinated disinformation campaigns and bot-driven influence. High-profile incidents like the 2016 U.S. presidential election interference involved widespread dissemination of fake news and fake accounts designed to sway voter opinions and suppress turnout. Protecting Your vote integrity requires heightened scrutiny of social media activities and advanced security measures to detect and prevent manipulation.
How to Detect and Prevent Vote Manipulation
Detecting vote manipulation on social media involves monitoring for unusual voting patterns such as rapid spikes in votes, repeated votes from the same IP address, and the use of bots or fake accounts. Implement CAPTCHA verification and implement machine learning algorithms to identify and block suspicious activity automatically. Protect Your platform's integrity by educating users on authentic engagement and regularly auditing voting data for anomalies.
Comparing Vote Manipulation, Vote Fraud, and Election Integrity
Vote manipulation undermines election integrity by artificially inflating or deflating candidate support through tactic-driven social media campaigns, while vote fraud involves illegal actions such as ballot tampering or multiple voting, directly violating election laws. Both practices degrade democratic processes, but vote manipulation exploits digital platforms to sway public opinion subtly, posing newer challenges for monitoring authorities. Protecting your right to a fair vote requires robust safeguards against these multifaceted threats to preserve the legitimacy and transparency of electoral outcomes.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com