Photo illustration: Sockpuppet vs Lurker
Sockpuppets are fake online identities created to manipulate discussions or deceive users, while lurkers actively consume social media content without participating or posting. Discover the key differences and impacts of sockpuppets and lurkers in this article.
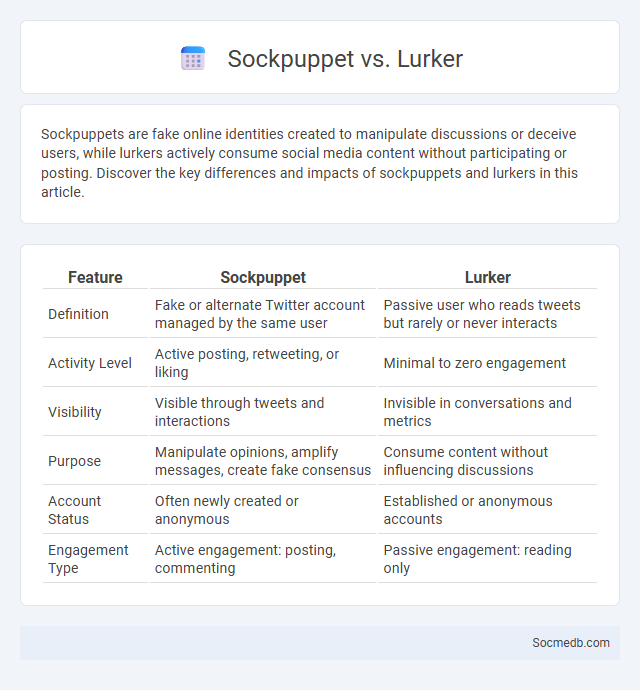
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sockpuppet | Lurker |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Fake or alternate Twitter account managed by the same user | Passive user who reads tweets but rarely or never interacts |
| Activity Level | Active posting, retweeting, or liking | Minimal to zero engagement |
| Visibility | Visible through tweets and interactions | Invisible in conversations and metrics |
| Purpose | Manipulate opinions, amplify messages, create fake consensus | Consume content without influencing discussions |
| Account Status | Often newly created or anonymous | Established or anonymous accounts |
| Engagement Type | Active engagement: posting, commenting | Passive engagement: reading only |
Introduction: Understanding Online Identities
Online identities shape how you present yourself across social media platforms, influencing personal branding and digital interactions. Social media profiles, including usernames, bios, and shared content, serve as extensions of your real-life persona, affecting perceptions and opportunities. Careful management of privacy settings and consistent messaging helps maintain authenticity and protect your reputation in the digital landscape.
What is a Sockpuppet?
A sockpuppet is a fake online identity created to deceive others, often used to manipulate social media discussions or inflate support for a topic artificially. These accounts disguise the true user's identity, enabling strategic interaction without accountability. Sockpuppets can distort public opinion, spread misinformation, and undermine trust in social media platforms.
Defining a Lurker in Online Communities
A lurker in online communities is an individual who regularly consumes content without actively participating through comments or posts. These users contribute to the overall traffic and engagement metrics but remain silent observers, often gathering information or entertainment. Understanding the behavior of lurkers can help you tailor social media strategies to encourage more active participation and foster community growth.
Key Differences: Sockpuppet vs Lurker
A sockpuppet is a fake online identity created to deceive others, manipulate opinions, or support a covert agenda, often engaging actively in discussions under false pretenses. In contrast, a lurker is an anonymous or passive social media user who observes content without interacting, posting, or revealing their identity. The key difference lies in intent and activity level: sockpuppets intentionally contribute misleading content, while lurkers remain silent consumers, influencing engagement metrics only through views.
Motivations Behind Sockpuppetry
Individuals engage in sockpuppetry on social media to manipulate public opinion, evade bans, and amplify their own viewpoints secretly. Motivations include spreading misinformation, creating artificial consensus, and bypassing platform restrictions. This deceptive behavior undermines authentic interactions and distorts online discourse dynamics.
The Role of Lurkers in Social Platforms
Lurkers play a crucial role in social media platforms by silently consuming content without actively engaging, which contributes significantly to the overall user base and content visibility. They influence platform algorithms through passive interactions such as views and time spent on posts, indirectly shaping content trends and community dynamics. Understanding lurker behavior helps social platforms optimize user experience and engagement strategies, enhancing content reach and retention.
Identifying Sockpuppets: Warning Signs
Sockpuppets on social media often exhibit synchronized posting patterns, including identical or highly similar content across multiple accounts. Warning signs include new accounts with minimal personal information and rapid engagement in niche discussions or heated debates. Analyzing IP addresses and behavioral inconsistencies can further help identify these deceptive profiles designed to manipulate perception or amplify certain viewpoints.
Ethical and Community Impacts
Social media platforms significantly influence ethical standards by shaping public discourse and privacy expectations through data handling practices. The community impact includes fostering connections and awareness while also presenting challenges like misinformation, cyberbullying, and echo chambers that can erode trust. Your responsible engagement with content and respect for diverse perspectives are crucial to maintaining a healthy online environment.
Preventing Sockpuppetry and Encouraging Authenticity
Social media platforms implement advanced algorithms and identity verification methods to prevent sockpuppetry, enhancing trust and credibility among users. Encouraging authenticity involves promoting transparent user profiles and fostering genuine engagement through community guidelines and content moderation. These measures collectively reduce fake accounts and support a more honest and secure digital environment.
Conclusion: Navigating Digital Personas
Navigating digital personas requires a strategic approach to balance authenticity and privacy while engaging meaningfully across platforms. Your online presence shapes perceptions, influences opportunities, and impacts mental well-being in the constantly evolving social media landscape. Mastering this balance empowers you to build a credible, impactful digital identity that resonates with your audience.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com