Photo illustration: X vs Mastodon
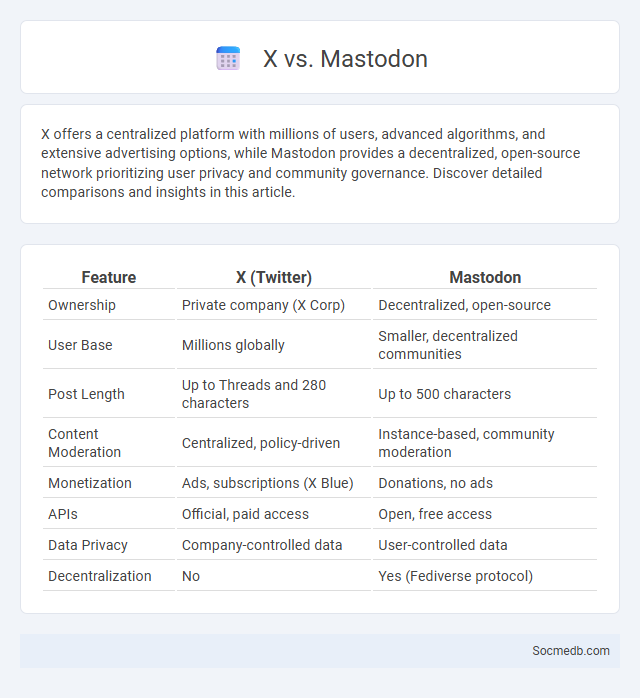
X offers a centralized platform with millions of users, advanced algorithms, and extensive advertising options, while Mastodon provides a decentralized, open-source network prioritizing user privacy and community governance. Discover detailed comparisons and insights in this article.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | X (Twitter) | Mastodon |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership | Private company (X Corp) | Decentralized, open-source |
| User Base | Millions globally | Smaller, decentralized communities |
| Post Length | Up to Threads and 280 characters | Up to 500 characters |
| Content Moderation | Centralized, policy-driven | Instance-based, community moderation |
| Monetization | Ads, subscriptions (X Blue) | Donations, no ads |
| APIs | Official, paid access | Open, free access |
| Data Privacy | Company-controlled data | User-controlled data |
| Decentralization | No | Yes (Fediverse protocol) |
Overview: X, Mastodon, and Disk Horse Compared
X, Mastodon, and Disk Horse represent distinct approaches to social media platforms emphasizing different paradigms for user interaction. X, formerly Twitter, focuses on real-time microblogging with a vast global user base and algorithm-driven content curation, enhancing visibility and engagement. Mastodon offers decentralized, open-source federated networks prioritizing user control and community moderation, while Disk Horse emphasizes privacy through encrypted, blockchain-based interactions that limit centralized data ownership.
Platform Purpose and Core Philosophy
Social media platforms are designed to facilitate communication, content sharing, and community building among users worldwide. Their core philosophy centers on fostering connectivity, enabling real-time interaction, and empowering individuals to express themselves authentically. Understanding these principles helps you engage more effectively and leverage social media's potential for personal or professional growth.
User Base and Demographics
Social media platforms boast a diverse user base, with Facebook exceeding 2.9 billion monthly active users predominantly aged 25-34, while TikTok attracts over 1 billion users, largely within the 18-24 age range. Instagram appeals to a younger demographic with 67% of users aged between 18 and 29, and LinkedIn primarily serves professionals aged 25-34, representing the largest user segment. Understanding these demographic insights helps marketers tailor content strategies to target specific audiences effectively across each platform.
Account Creation and Onboarding
Creating your social media account involves providing essential personal information, selecting a unique username, and setting a strong password to ensure security. The onboarding process guides you through profile customization, connecting with friends, and understanding platform features to maximize engagement. Efficient account creation and onboarding streamline your social media experience, enabling you to build a personalized digital presence quickly.
Content Moderation and Community Guidelines
Content moderation ensures that social media platforms maintain a safe and respectful environment by filtering harmful or inappropriate posts according to specific community guidelines. These guidelines define acceptable behavior, helping You understand what content is allowed and how to engage positively. Effective moderation enhances user experience and promotes trust within online communities.
Features and Customization
Social media platforms offer diverse features such as live streaming, story sharing, targeted advertising, and advanced analytics to enhance user engagement. Customization options include personalized feeds, privacy settings, and content filters that allow you to tailor your online experience to match your interests and comfort level. These tools collectively empower users to create a unique and controlled digital presence across various social networks.
Privacy and Data Security
Protecting Your privacy on social media involves managing account settings to control who can access your personal information and posts. Data security is enhanced by enabling two-factor authentication and regularly updating passwords to prevent unauthorized access. Being aware of each platform's data collection policies helps You make informed decisions about the information shared online.
Algorithmic vs Chronological Feeds
Algorithmic feeds prioritize content based on engagement metrics, user preferences, and behavior patterns, ensuring Your social media experience highlights posts relevant to Your interests. Chronological feeds display posts in the order they were published, offering a real-time update without personalization. Understanding the differences helps You optimize Your content strategy and enhances your interaction on platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and Facebook.
Monetization and Revenue Models
Social media platforms primarily generate revenue through advertising models, leveraging targeted ads based on user data to maximize engagement and advertiser ROI. Subscription services, such as premium memberships or ad-free experiences, offer alternative monetization channels by providing enhanced features and exclusive content. Affiliate marketing and in-app purchases also contribute to diversified revenue streams, increasing overall profitability for social networks.
Pros, Cons, and Best Use Cases
Social media platforms enhance communication by enabling instant connectivity, facilitating brand promotion, and supporting community building across diverse audiences. Risks include privacy breaches, misinformation spread, and potential mental health impacts such as anxiety and depression. Best use cases involve targeted marketing campaigns, customer engagement, real-time news dissemination, and educational content sharing to maximize social media's positive impact.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com