Photo illustration: Fair Use vs DMCA
Understanding the balance between Fair Use and the DMCA is essential for creators navigating copyright on social media platforms, as Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted content while the DMCA enforces takedown of infringing material. Explore this article to learn how to legally share content and protect your rights online.
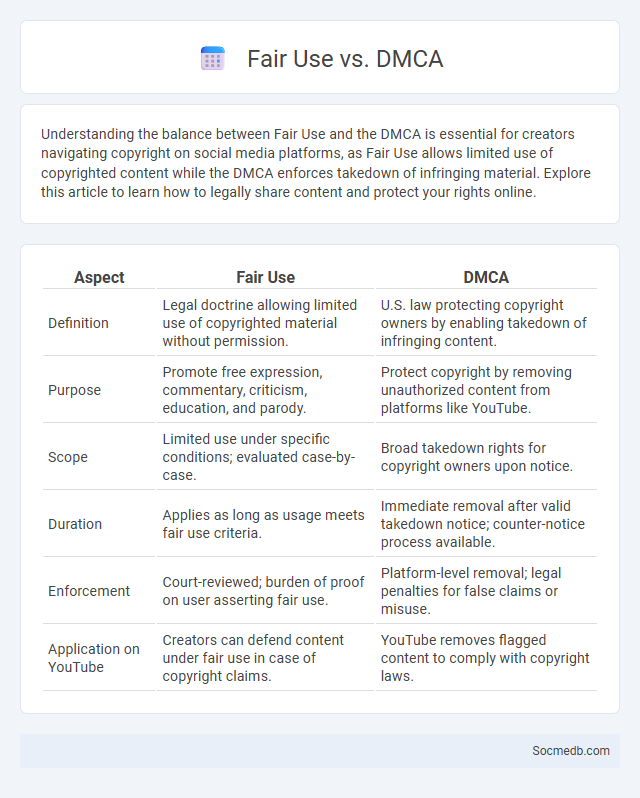
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Use | DMCA |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal doctrine allowing limited use of copyrighted material without permission. | U.S. law protecting copyright owners by enabling takedown of infringing content. |
| Purpose | Promote free expression, commentary, criticism, education, and parody. | Protect copyright by removing unauthorized content from platforms like YouTube. |
| Scope | Limited use under specific conditions; evaluated case-by-case. | Broad takedown rights for copyright owners upon notice. |
| Duration | Applies as long as usage meets fair use criteria. | Immediate removal after valid takedown notice; counter-notice process available. |
| Enforcement | Court-reviewed; burden of proof on user asserting fair use. | Platform-level removal; legal penalties for false claims or misuse. |
| Application on YouTube | Creators can defend content under fair use in case of copyright claims. | YouTube removes flagged content to comply with copyright laws. |
Understanding Fair Use: Definition and Scope
Fair use is a legal doctrine that allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission from the rights holders, especially in contexts like commentary, criticism, news reporting, education, and research. Social media users must navigate fair use by considering factors such as the purpose of use, nature of the copyrighted work, amount used, and effect on market value. Understanding these parameters helps prevent copyright infringement while enabling creative expression and content sharing on platforms like Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok.
What is the DMCA? An Overview
The DMCA (Digital Millennium Copyright Act) is a U.S. law enacted in 1998 to protect copyright holders by regulating the use of copyrighted material online, including on social media platforms. It provides a safe harbor for social media companies by allowing them to remove infringing content when notified, shielding them from liability. Understanding the DMCA helps you navigate copyright issues and safeguard your content from unauthorized use on social media.
Key Differences: Fair Use vs DMCA
Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted content without permission for purposes like commentary, criticism, or education, considering factors such as purpose, nature, amount, and market impact. The DMCA provides a legal framework to remove or block infringing content upon copyright holder requests, enforcing takedown notices and safe harbor provisions for service providers. Understanding these distinctions helps you navigate content sharing and protect your rights on social media platforms effectively.
Legal Foundations: Fair Use Explained
Fair use is a crucial legal doctrine that allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission, protecting your ability to share content on social media for commentary, criticism, or educational purposes. Key factors determining fair use include the purpose of use, the nature of the copyrighted work, the amount used, and the impact on the market value. Understanding these elements helps you navigate social media confidently while respecting intellectual property rights.
DMCA Takedown Notices: Process and Impact
DMCA takedown notices require copyright holders to submit a formal request to social media platforms to remove infringing content, initiating a strict review process. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter respond by promptly disabling access to the reported material to comply with the Digital Millennium Copyright Act. This enforcement not only protects intellectual property rights but also impacts user content, often leading to account penalties or restrictions when repeated violations occur.
Common Misconceptions about Fair Use and DMCA
Many users mistakenly believe that any content shared for educational or commentary purposes automatically qualifies as fair use under copyright law. The DMCA provides a strict framework for content removal, but fair use exceptions require nuanced legal interpretation considering factors like purpose, nature, and market impact. Misunderstanding these guidelines often leads to wrongful takedown notices or unauthorized usage disputes on social media platforms.
Content Creator Rights under Fair Use
Content creator rights under fair use protect individuals who produce original works, enabling them to use copyrighted material without permission in transformative ways such as commentary, criticism, or parody. Social media platforms must balance enforcing copyright policies while respecting creators' rights to utilize fair use for creative expression and audience engagement. Understanding fair use provisions empowers content creators to navigate copyright challenges and safeguard their intellectual property on digital platforms.
Copyright Protection under the DMCA
Social media platforms implement Copyright Protection under the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) to safeguard original content and prevent unauthorized use. You must submit a proper DMCA takedown notice when your copyrighted material is infringed upon to ensure swift removal. Compliance with these regulations helps maintain a fair environment for creators and promotes responsible content sharing online.
Navigating Disputes: Fair Use Claims vs DMCA Complaints
Navigating disputes on social media requires understanding the nuances between Fair Use claims and DMCA complaints, as each serves distinct legal purposes in content protection. You must assess whether your content qualifies for Fair Use, which allows limited use without permission under specific circumstances, or if a DMCA complaint has been legitimately filed, signaling a copyright infringement issue. Accurate evaluation helps prevent wrongful takedowns and ensures compliance with intellectual property laws while maintaining your digital presence.
Best Practices for Avoiding Copyright Infringement
Respecting intellectual property on social media requires you to use only original content or materials with clear licenses or permissions to avoid copyright infringement. Proper attribution, avoiding unauthorized use of images, music, or videos, and utilizing royalty-free or Creative Commons resources protect your brand from legal issues. Monitoring your posts regularly and promptly addressing any claims maintain your account's compliance and reputation.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com