Photo illustration: Fair Use vs Parody
Fair Use protects the limited use of copyrighted content for commentary, criticism, or parody without permission. Explore this article to understand the legal boundaries between Fair Use and parody on social media platforms.
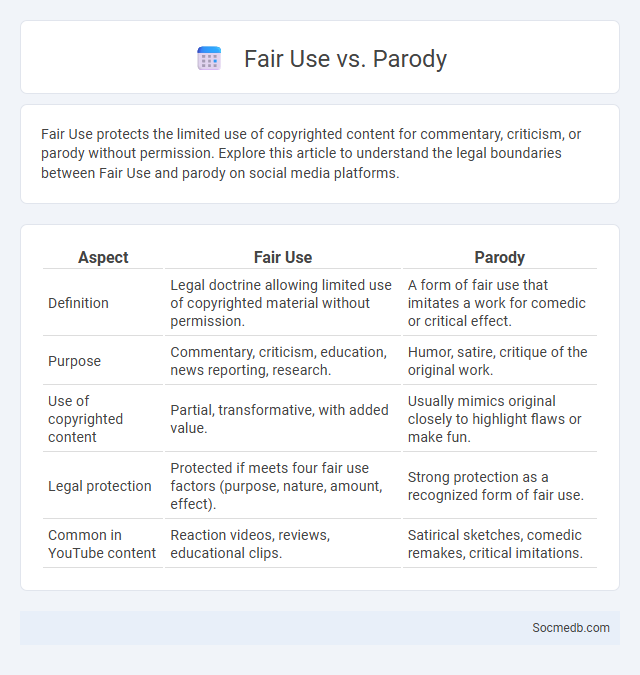
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Use | Parody |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal doctrine allowing limited use of copyrighted material without permission. | A form of fair use that imitates a work for comedic or critical effect. |
| Purpose | Commentary, criticism, education, news reporting, research. | Humor, satire, critique of the original work. |
| Use of copyrighted content | Partial, transformative, with added value. | Usually mimics original closely to highlight flaws or make fun. |
| Legal protection | Protected if meets four fair use factors (purpose, nature, amount, effect). | Strong protection as a recognized form of fair use. |
| Common in YouTube content | Reaction videos, reviews, educational clips. | Satirical sketches, comedic remakes, critical imitations. |
Understanding Fair Use: Definition and Purpose
Fair use allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes such as commentary, criticism, or education, protecting creative expression and innovation within social media. Understanding fair use helps You avoid infringement by recognizing factors like purpose, nature, amount used, and market effect when sharing content. This knowledge supports responsible content creation and sharing, fostering a legally compliant and respectful social media environment.
What Constitutes Parody? Legal and Creative Boundaries
Parody on social media involves the deliberate imitation of a work or style for humorous or satirical purposes, typically incorporating recognizable elements while transforming the original to convey new meaning. Legal boundaries hinge on fair use doctrine, requiring that the parody provides commentary or criticism, is non-commercial, and does not harm the original work's market value. Creatively, effective parodies balance originality with clear reference points, ensuring audiences can identify the source while appreciating the novel twist or message.
Key Differences Between Fair Use and Parody
Fair use allows limited use of copyrighted material for purposes such as criticism, commentary, or news reporting without permission, provided the use is transformative and does not harm the market value of the original. Parody specifically targets original works to humorously mimic or critique them, often protected under fair use but requiring a clear comedic or satirical element to distinguish it from direct copying. Key differences hinge on intent and context: fair use encompasses broader purposes with a focus on commentary, while parody relies on imitation for humor or social critique within social media platforms.
The Four Factors of Fair Use Explained
The four factors of fair use--purpose and character of the use, nature of the copyrighted work, amount and substantiality of the portion used, and effect on the market value--are critical when navigating social media content sharing. Using content for commentary, criticism, or educational purposes typically favors fair use, while using large or highly creative portions may not. Assessing whether the use impacts the original work's market or potential revenue is essential to determine fair use legitimacy on social media platforms.
Parody as a Form of Commentary and Criticism
Parody on social media serves as a powerful tool for commentary and criticism by humorously imitating popular content to highlight societal issues or cultural absurdities. This form of expression leverages satire and exaggeration to engage viewers, challenging norms and prompting reflection on current events or public figures. Your participation in sharing or creating parody can amplify important conversations, making complex topics more accessible and thought-provoking.
Legal Precedents: Notable Fair Use and Parody Cases
Fair use and parody cases such as Campbell v. Acuff-Rose Music and Cariou v. Prince have shaped social media content policies by establishing boundaries for transformative works and commentary. These legal precedents emphasize that your use of copyrighted material on platforms must add new expression or meaning to be protected. Understanding these rulings helps you navigate content creation within legal limits, balancing creativity with copyright law.
Common Misconceptions About Fair Use vs Parody
Social media often blurs the lines between fair use and parody, causing widespread confusion about copyright protections. Fair use permits limited use of copyrighted material for commentary or criticism, but parody requires transforming the original work to humorously critique it, establishing its distinct legal status. Misunderstanding these differences leads to frequent copyright infringement claims and can stifle creative expression on platforms like YouTube and Instagram.
Practical Examples: Fair Use vs Parody in Media
Fair use in social media allows creators to share copyrighted content for commentary, criticism, or educational purposes without permission, such as a YouTube reviewer analyzing a movie clip. Parody transforms original works for humor or satire, like popular Twitter accounts mimicking public figures with exaggerated traits to critique social behavior. Understanding the difference ensures legal protection while fostering creativity and critical discourse online.
Navigating Legal Risks: Tips for Creators
Social media creators must understand copyright laws, defamation risks, and privacy policies to protect their content and reputation. You should implement clear disclaimers, seek permissions for third-party material, and monitor comments to avoid legal pitfalls. Staying informed about changing regulations ensures your creative work remains compliant and secure.
Fair Use and Parody: Best Practices for Compliance
When using social media content under Fair Use, focus on commentary, criticism, or parody to ensure compliance with legal standards. Your posts should transform the original work by adding new expression or meaning, avoiding direct competition with the original content. Clearly labeling parodies and providing context helps safeguard your social media presence from copyright claims.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com