Photo illustration: Fair Use vs Satire
Fair Use protects limited social media content reuse for commentary, criticism, and parody, while Satire uses humor and exaggeration to comment on broader societal issues. Explore this article to understand the legal boundaries and examples of Fair Use vs Satire on social media platforms.
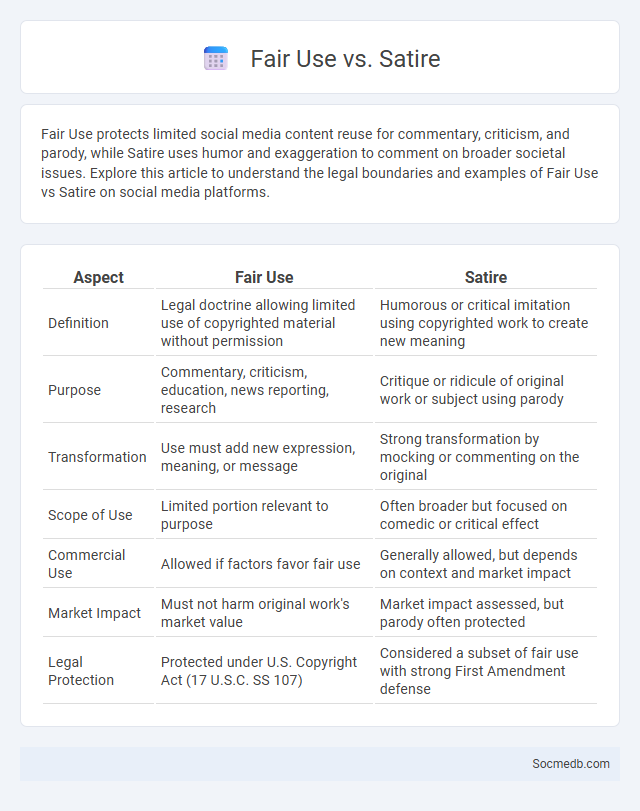
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Use | Satire |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal doctrine allowing limited use of copyrighted material without permission | Humorous or critical imitation using copyrighted work to create new meaning |
| Purpose | Commentary, criticism, education, news reporting, research | Critique or ridicule of original work or subject using parody |
| Transformation | Use must add new expression, meaning, or message | Strong transformation by mocking or commenting on the original |
| Scope of Use | Limited portion relevant to purpose | Often broader but focused on comedic or critical effect |
| Commercial Use | Allowed if factors favor fair use | Generally allowed, but depends on context and market impact |
| Market Impact | Must not harm original work's market value | Market impact assessed, but parody often protected |
| Legal Protection | Protected under U.S. Copyright Act (17 U.S.C. SS 107) | Considered a subset of fair use with strong First Amendment defense |
Understanding Fair Use: Legal Foundations
Understanding fair use is essential for navigating social media, as it allows you to share copyrighted content legally under specific conditions such as commentary, criticism, or education. The legal foundations of fair use hinge on factors like the purpose of use, the nature of the original work, the amount used, and the effect on the market value. Your ability to apply fair use principles can help avoid copyright infringement while fostering creative expression on social media platforms.
Satire Defined: Characteristics and Purpose
Satire in social media employs humor, irony, and exaggeration to critique and expose societal flaws, often targeting politics, culture, and current events. Its key characteristics include wit, sarcasm, and the use of parody to provoke thought and entertain while fostering critical reflection among audiences. The primary purpose of satire on social media is to challenge prevailing norms and encourage awareness and dialogue through engaging and accessible content.
Key Differences Between Fair Use and Satire
Fair use allows limited use of copyrighted material for purposes such as criticism, comment, news reporting, education, and research, often evaluated based on factors like purpose, nature, amount used, and market effect. Satire uses humor, irony, or exaggeration to criticize or mock, often transforming the original content to provide social or political commentary, which can sometimes qualify as fair use. On social media platforms, distinguishing between fair use and satire is crucial, as satire relies heavily on creative expression and transformative use, while fair use depends on legal criteria and context.
Fair Use: Criteria and Case Studies
Fair Use in social media hinges on four key criteria: purpose and character of use, nature of the copyrighted work, amount and substantiality of the portion used, and effect on the market value. Notable case studies like Campbell v. Acuff-Rose Music illustrate transformative use as a crucial factor, while Blanch v. Koons highlights parody and critique protections. Understanding these benchmarks ensures content creators navigate copyright laws effectively, fostering innovation without infringement risks.
Satire as a Defense to Copyright Infringement
Satire serves as a powerful defense against copyright infringement by transforming original work to critique or mock its subject, thereby qualifying as fair use under copyright law. Social media platforms often host satirical content that relies on copyrighted material to engage audiences while providing commentary or humor that adds new expression and meaning. When creating or sharing such content, your awareness of legal boundaries ensures both creative freedom and respect for the original creator's rights.
Overlapping Areas: Fair Use and Satirical Works
Social media platforms frequently host content that intersects fair use and satirical works, where creators transform copyrighted material to provide commentary or humor without explicit permission. This overlap is critical for protecting freedom of expression, as satire often relies on recognizable references to deliver its message effectively. Understanding the nuances of fair use in the context of online satire helps balance intellectual property rights with creative innovation.
Legal Precedents: Landmark Rulings Explained
Landmark legal precedents shape the landscape of social media regulation by establishing clear guidelines on privacy, content moderation, and user rights. Significant rulings, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) enforcement and the Supreme Court's decisions on Section 230 protections, influence how platforms manage user data and liability. Understanding these precedents helps you navigate your online presence while respecting legal boundaries and platform policies.
Practical Examples: Fair Use vs. Satirical Use
Fair use on social media often involves sharing copyrighted content for commentary, criticism, or educational purposes without permission, such as reposting news clips with added analysis. Satirical use transforms original content to mock or critique social behavior, exemplified by parody videos or memes exaggerating public figures to highlight societal flaws. Platforms like YouTube and Instagram enforce policies distinguishing factual commentary from satire, balancing creators' rights with freedom of expression.
Common Misconceptions in Fair Use and Satire
Many people misunderstand fair use, often assuming that any parody or satire automatically qualifies without considering factors like purpose, nature, and market impact. Social media platforms frequently see misuse of copyrighted content under the guise of satire, but You must evaluate whether your usage transforms the original work sufficiently. Proper knowledge of fair use criteria helps protect your content and respects creators' rights while enabling legitimate satirical expression.
Best Practices for Content Creators
Consistently delivering high-quality, engaging content tailored to Your target audience increases visibility and loyalty across social media platforms. Utilizing data analytics to understand audience behavior enables content optimization for maximum reach and interaction. Leveraging trends authentically and maintaining a clear brand voice fosters trust and encourages meaningful community engagement.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com