Photo illustration: Licensed Use vs Transformation
Licensed use in social media allows the authorized sharing and display of content under specific terms, while transformation involves altering original content to create new, derivative works. Explore this article to understand the legal nuances and practical implications of licensed use versus transformation in social media.
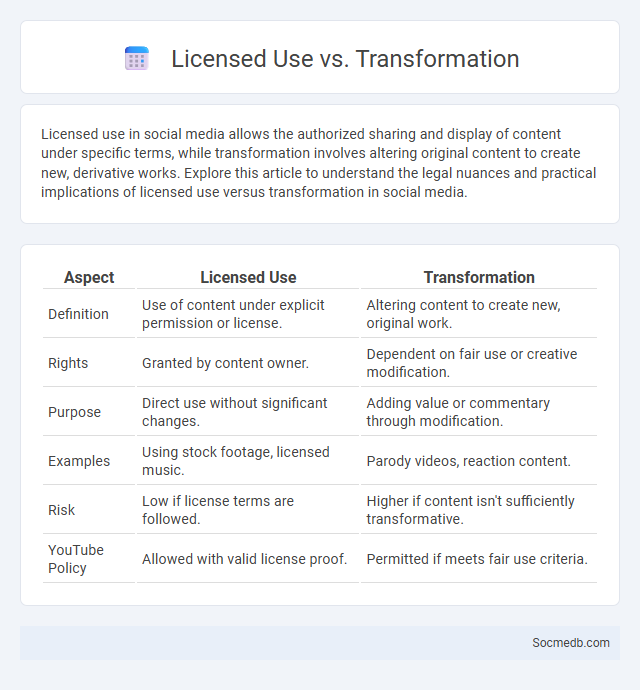
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Licensed Use | Transformation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of content under explicit permission or license. | Altering content to create new, original work. |
| Rights | Granted by content owner. | Dependent on fair use or creative modification. |
| Purpose | Direct use without significant changes. | Adding value or commentary through modification. |
| Examples | Using stock footage, licensed music. | Parody videos, reaction content. |
| Risk | Low if license terms are followed. | Higher if content isn't sufficiently transformative. |
| YouTube Policy | Allowed with valid license proof. | Permitted if meets fair use criteria. |
Understanding Licensed Use in Creative Works
Understanding licensed use in creative works on social media is crucial for content creators to avoid copyright infringement and maintain legal compliance. Licensed use involves obtaining explicit permission from the rights holder or using content under specific licenses such as Creative Commons, which clearly outline how the material can be used, shared, or modified. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok enforce strict guidelines on licensed content, emphasizing the need for creators to verify copyright status and adhere to licensing agreements to protect their accounts and intellectual property.
What Constitutes a Transformation in Copyright Law
A transformation in copyright law occurs when new technology or social media platforms significantly alter how copyrighted content is created, shared, or monetized, prompting legal adaptations to address user rights and content ownership. Key factors include changes in content creation methods, distribution channels, and user-generated content dynamics that challenge traditional copyright frameworks. Legal precedents often focus on whether the use is transformative enough to constitute fair use, balancing the interests of copyright holders with innovation in digital communication.
Differences Between Licensed Use and Transformation
Licensed use of social media content allows you to access and share media within the boundaries set by the original creator, typically involving permissions or licenses specifying how the content can be used. Transformation involves modifying or remixing the original content to create something new, which may fall under fair use or require additional approvals depending on the extent and nature of the changes. Understanding these differences is crucial for safeguarding your social media strategy from copyright infringements while maximizing creative opportunities.
Copyright Claims: Basics and Legal Framework
Copyright claims on social media protect your original content from unauthorized use, ensuring legal rights under the Copyright Act. Platforms enforce these claims through Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) procedures, allowing creators to report infringement and request content removal. Understanding how to file and respond to copyright claims safeguards your intellectual property while navigating platform-specific rules.
Scope and Limits of Licensed Permissions
Licensed permissions on social media define the specific scope of content use, including reproduction, distribution, and modification rights granted to platforms or third parties. These permissions often limit how, where, and for how long user-generated content can be exploited, ensuring original creators retain control over their intellectual property. Restrictions may include geographic boundaries, time constraints, and prohibited monetization, protecting users from unauthorized commercial use or content misuse.
Identifying Transformative Use in Content Creation
Transformative use in content creation involves reimagining existing social media material to add new meaning, insights, or value rather than merely replicating it. By integrating innovative storytelling techniques, remixing visuals, or blending diverse platforms, creators can produce fresh narratives that resonate uniquely with audiences. Understanding this concept empowers your content strategy, ensuring originality and legal compliance while engaging viewers effectively.
Common Grounds for Copyright Infringement Claims
Social media platforms often face copyright infringement claims due to the unauthorized sharing of copyrighted content such as images, videos, and music. Common grounds for these claims include the reposting of original works without permission, failure to credit creators, and the use of copyrighted materials in user-generated content. Protecting Your intellectual property requires understanding platform policies and promptly addressing infringement notices to avoid legal consequences.
Legal Precedents: Licensed Use vs. Transformation
Legal precedents in social media emphasize the distinction between licensed use and transformative use, with courts often scrutinizing whether content alteration constitutes fair use or infringement. Your ability to repurpose licensed material hinges on demonstrable transformation that adds new expression or meaning, avoiding mere replication. Understanding these precedents helps safeguard your content strategy while respecting intellectual property rights.
Protecting Your Work: Licensing and Transformative Defense
Protecting your work on social media requires a clear understanding of licensing options like Creative Commons, which define how others can legally use, share, or modify your content. Employing transformative defense involves demonstrating that new creations significantly transform original material, qualifying as fair use under copyright law. Regularly monitoring unauthorized use and issuing takedown notices further safeguards your intellectual property online.
Best Practices to Avoid Copyright Violation
To avoid copyright violation on social media, always ensure you have explicit permission or proper licenses before sharing any content created by others. Use royalty-free or Creative Commons-licensed images, videos, and music to protect your account from potential strikes or bans. Your best practice includes giving appropriate credit and creating original content to maintain compliance and uphold your brand's integrity.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com