Photo illustration: public vs private
Public social media platforms enable wide content sharing visible to all users, while private social media emphasizes controlled access and user privacy through limited audience settings. Explore the key differences and benefits of public versus private social media in this article.
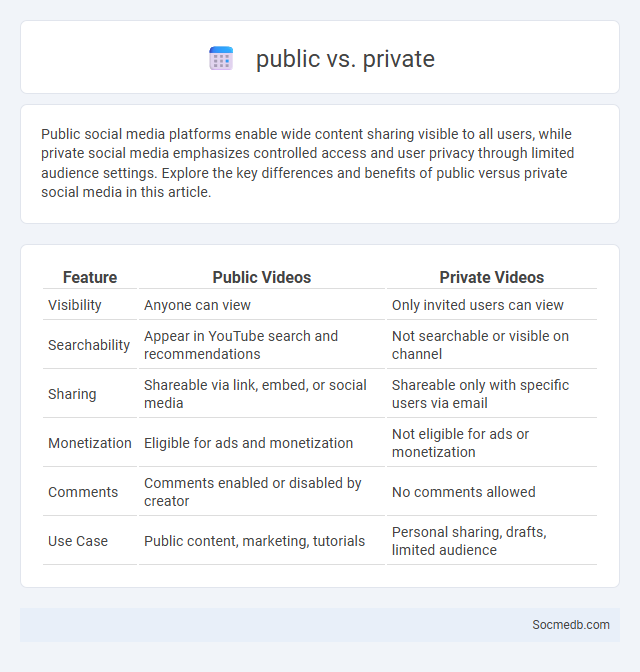
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Public Videos | Private Videos |
|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Anyone can view | Only invited users can view |
| Searchability | Appear in YouTube search and recommendations | Not searchable or visible on channel |
| Sharing | Shareable via link, embed, or social media | Shareable only with specific users via email |
| Monetization | Eligible for ads and monetization | Not eligible for ads or monetization |
| Comments | Comments enabled or disabled by creator | No comments allowed |
| Use Case | Public content, marketing, tutorials | Personal sharing, drafts, limited audience |
Understanding Public, Private, and Metadata
Understanding public, private, and metadata on social media is crucial for managing your online presence and protecting your personal information. Public data includes posts and profiles visible to anyone, while private data refers to content restricted to approved connections or specific groups. Metadata, such as timestamps, geolocation, and device information, can reveal more about your activities than you might realize, making it essential to review privacy settings carefully.
Key Differences Between Public and Private
Public social media platforms allow users to share content openly, resulting in wider audience reach and increased visibility, while private social media restricts access to approved connections, enhancing personal privacy and control. Public profiles often contribute to brand building and social influence, whereas private settings prioritize secure communication and limited sharing among trusted contacts. Privacy settings, audience targeting, and content visibility are fundamental factors distinguishing public social media from private networks.
The Role of Metadata in Data Management
Metadata plays a crucial role in social media data management by organizing and categorizing vast amounts of user-generated content, enabling efficient search and retrieval. Precise metadata tags such as timestamps, geolocation, and content type enhance data discoverability and facilitate targeted analytics. This structured information supports personalized user experiences and improves platform content moderation and recommendation algorithms.
Accessibility: Public vs Private Data
Social media platforms differentiate between public and private data to enhance user accessibility and control over personal information. Public data includes profiles, posts, and comments visible to everyone, enabling broader social interaction and content discovery. Private data remains restricted to authorized users, such as friends or followers, ensuring user privacy and safeguarding sensitive information.
Security Implications of Public and Private Information
Sharing personal details on social media platforms can expose your sensitive information to cyber threats and privacy breaches, increasing the risk of identity theft and unauthorized access. Publicly available data often becomes a target for phishing attacks, while private information shared within seemingly secure networks may be vulnerable due to insufficient security settings or platform vulnerabilities. Understanding these security implications helps you control your digital footprint and protect your personal and professional identity effectively.
Metadata: Importance and Use Cases
Metadata in social media enhances content discoverability by enabling precise categorization and efficient search through tags, timestamps, and geolocation data. It supports targeted advertising by providing insights into user demographics, preferences, and behavior patterns, improving campaign accuracy and ROI. Platforms leverage metadata for content moderation, trend analysis, and personalized user experiences, driving engagement and platform growth.
Real-World Examples: Public, Private, and Metadata
Social media platforms generate vast amounts of public data, including user posts, comments, and shares, which are often analyzed for trends and sentiment. Private data, such as direct messages and user settings, remain accessible only to individuals and authorized entities, emphasizing the importance of privacy controls. Metadata, including timestamps, geolocation tags, and device information, plays a crucial role in understanding user behavior and enhancing targeted advertising strategies.
Choosing Between Public, Private, and Metadata
Choosing the right social media privacy setting significantly impacts your online presence and data security. Public profiles maximize visibility and engagement but expose your personal information to a broad audience, while private settings restrict access and safeguard your content from unknown users. Understanding the metadata attached to your posts, such as location and timestamps, helps you control the granularity of your shared information and protect your digital footprint.
Best Practices for Managing Public, Private, and Metadata
Effective social media management requires clear strategies for handling public, private, and metadata to protect user privacy and enhance content discoverability. Employ strict access controls for private data and ensure compliance with privacy regulations like GDPR while optimizing metadata with relevant keywords and tags to improve search engine rankings. Regularly audit social media content and metadata to maintain data accuracy and prevent unauthorized access or misuse.
Future Trends in Data Classification
Future trends in data classification for social media emphasize the integration of advanced machine learning algorithms and AI-powered tools to enhance accuracy and speed. Your platforms will leverage real-time data analysis to categorize user interactions, content types, and sentiment, enabling more personalized experiences and targeted advertising. Privacy-preserving techniques such as federated learning will become crucial in maintaining user trust while handling vast amounts of sensitive information.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com