Photo illustration: Clickbait vs fake news
Clickbait uses sensational headlines to attract clicks, while fake news spreads false information with intent to deceive. Learn how to identify and combat both in this article.
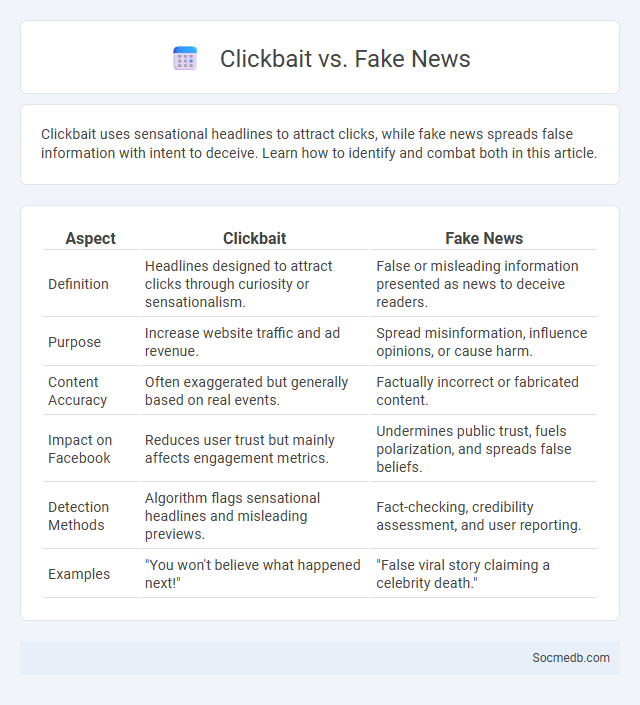
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Clickbait | Fake News |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Headlines designed to attract clicks through curiosity or sensationalism. | False or misleading information presented as news to deceive readers. |
| Purpose | Increase website traffic and ad revenue. | Spread misinformation, influence opinions, or cause harm. |
| Content Accuracy | Often exaggerated but generally based on real events. | Factually incorrect or fabricated content. |
| Impact on Facebook | Reduces user trust but mainly affects engagement metrics. | Undermines public trust, fuels polarization, and spreads false beliefs. |
| Detection Methods | Algorithm flags sensational headlines and misleading previews. | Fact-checking, credibility assessment, and user reporting. |
| Examples | "You won't believe what happened next!" | "False viral story claiming a celebrity death." |
Understanding Clickbait: Definition and Purpose
Clickbait is a social media strategy that uses sensationalized headlines and thumbnails to attract clicks and increase engagement. Its primary purpose is to drive traffic by exploiting curiosity gaps, often at the expense of accurate or valuable content. Understanding clickbait helps Your social media experience become more discerning and less susceptible to misleading information.
What Constitutes Fake News?
Fake news consists of false information deliberately created to mislead and manipulate public opinion, often spreading through social media channels where rapid sharing amplifies its reach. Key indicators include fabricated headlines, lack of credible sources, and emotionally charged content designed to provoke reactions rather than inform. Protecting Your social media experience requires critical evaluation of news sources, cross-verifying facts, and being cautious before sharing unverified information.
Key Differences Between Clickbait and Fake News
Clickbait headlines prioritize enticing users to click on content by exaggerating or misleading without necessarily presenting false information, while fake news deliberately fabricates or distorts facts to misinform readers. Clickbait often relies on sensational language and emotional triggers to drive traffic and engagement, whereas fake news aims to manipulate public opinion or spread disinformation. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for identifying misleading content on social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Psychological Triggers Behind Clickbait
Clickbait exploits psychological triggers such as curiosity, fear of missing out (FOMO), and emotional arousal to compel users to click on links, often by creating sensationalized or ambiguous headlines. This tactic manipulates Your brain's reward system by promising quick, valuable information, which can lead to repeated engagement despite potential disappointment from low-quality content. Understanding these triggers helps You recognize and critically evaluate clickbait, reducing its influence on your social media behavior.
How Fake News Spreads Online
Fake news spreads rapidly on social media through algorithms that prioritize engagement, amplifying sensational or emotionally charged content regardless of accuracy. Users often share misinformation without verification, propelled by confirmation bias and echo chambers where similar views are reinforced. Automated bots and coordinated disinformation campaigns further accelerate the distribution of false information, undermining public trust and complicating efforts to promote factual content.
The Overlap: When Clickbait Becomes Fake News
Clickbait headlines often exploit sensationalism to attract clicks, blurring the line between engaging content and misinformation. When these exaggerated or misleading titles evolve into fake news, they distort public perception and erode trust in social media platforms. Your ability to critically evaluate sources and verify facts is essential to navigate this intersection and combat the spread of false information online.
Impact of Clickbait Headlines on Reader Trust
Clickbait headlines often distort information to attract clicks, significantly eroding reader trust in social media platforms. Studies reveal that audiences exposed to sensationalized or misleading headlines report lower credibility ratings for the source. Maintaining transparent, accurate headlines boosts engagement while preserving long-term trust among digital users.
Identifying Fake News in the Digital Age
Identifying fake news in the digital age requires advanced algorithms that analyze content authenticity, user behavior patterns, and source credibility. Social media platforms increasingly deploy machine learning models to detect misinformation by cross-referencing facts with trusted databases and flagging suspicious accounts. Enhanced digital literacy campaigns emphasize critical evaluation skills, empowering users to discern false information amid the vast online ecosystem.
Combating Clickbait and Fake News: Practical Strategies
You can combat clickbait and fake news by critically evaluating sources and verifying information before sharing. Implementing fact-checking tools and promoting media literacy helps identify misleading headlines and false content. Encouraging transparency and accountability on social media platforms strengthens the reliability of the information you consume.
The Future of Online Media: Ethics and Accountability
Emerging regulations worldwide emphasize ethical standards and accountability in social media to combat misinformation and protect user privacy. Platforms are increasingly adopting transparent algorithms and content moderation policies driven by artificial intelligence to ensure responsible online discourse. The future of online media hinges on integrating ethical frameworks that prioritize digital well-being and foster trust between users and technology providers.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com