Photo illustration: EdgeRank vs Algorithm
EdgeRank, Facebook's original ranking system, prioritized content visibility based on affinity, weight, and time decay, while modern social media algorithms use advanced machine learning to personalize user feeds dynamically. Explore this article to understand the evolution from EdgeRank to current algorithms and how it impacts social media engagement.
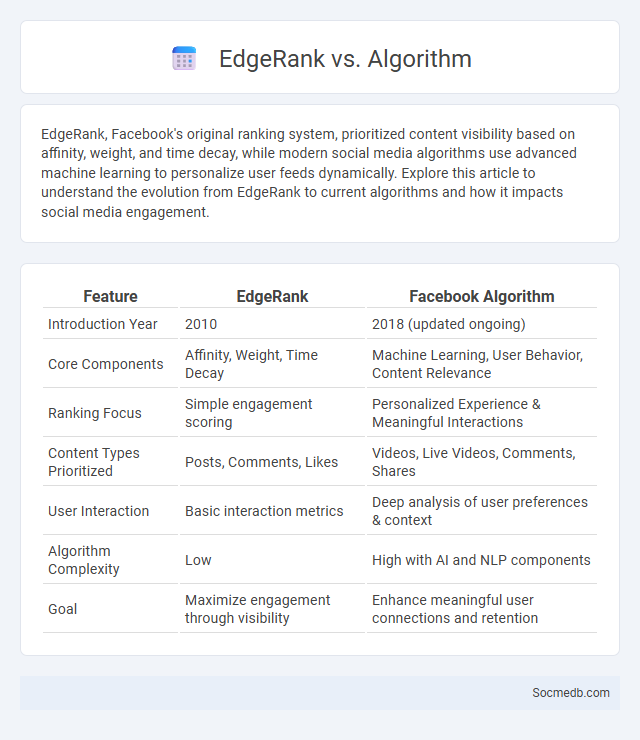
Table of Comparison
| Feature | EdgeRank | Facebook Algorithm |
|---|---|---|
| Introduction Year | 2010 | 2018 (updated ongoing) |
| Core Components | Affinity, Weight, Time Decay | Machine Learning, User Behavior, Content Relevance |
| Ranking Focus | Simple engagement scoring | Personalized Experience & Meaningful Interactions |
| Content Types Prioritized | Posts, Comments, Likes | Videos, Live Videos, Comments, Shares |
| User Interaction | Basic interaction metrics | Deep analysis of user preferences & context |
| Algorithm Complexity | Low | High with AI and NLP components |
| Goal | Maximize engagement through visibility | Enhance meaningful user connections and retention |
Understanding EdgeRank: A Historical Overview
EdgeRank, Facebook's original algorithm launched in 2011, determined the visibility of posts by analyzing user interactions, affinity, weight, and time decay. This ranking system prioritized meaningful content by evaluating likes, comments, and shares, thereby influencing user engagement and news feed curation. Over time, EdgeRank evolved into more complex algorithms integrating machine learning and AI to improve personalized content delivery across social media platforms.
What is an Algorithm in Social Media Context?
An algorithm in a social media context is a complex set of rules and data-driven processes that determine which content appears on your feed based on your behavior, preferences, and interactions. It analyzes factors such as likes, shares, comments, and time spent on posts to prioritize content that is most relevant and engaging for you. Understanding how these algorithms work can help optimize your social media strategies and improve your online visibility.
EdgeRank vs. Algorithm: Key Differences
EdgeRank, Facebook's original formula, prioritized content visibility based on affinity, weight, and time decay, influencing how posts appeared in users' News Feeds. Modern social media algorithms have evolved to include a broader range of signals such as user interaction patterns, content type, and relevancy to deliver personalized experiences. Understanding the key differences between EdgeRank's simpler scoring model and today's complex, AI-driven algorithms is essential for optimizing social media marketing strategies.
Evolution of Facebook's EdgeRank to Algorithm
Facebook's EdgeRank initially used a simple formula based on affinity, weight, and time decay to prioritize posts in users' news feeds, optimizing content visibility. Over time, this evolved into a complex AI-driven algorithm incorporating machine learning, user behavior, and content relevance signals like engagement likelihood and personal preferences. Facebook's algorithm now continuously adapts to maximize meaningful interactions while mitigating misinformation and clickbait, ensuring a tailored user experience.
How EdgeRank Worked: Core Components
EdgeRank operated using three core components: affinity, weight, and time decay. Affinity measured the relationship between You and the content creator, weight evaluated the significance of interactions like comments or likes, and time decay prioritized newer posts for relevance. These factors combined to determine which content appeared in Your Facebook News Feed, maximizing engagement based on personalized connections.
Modern Social Media Algorithms Explained
Modern social media algorithms analyze user interactions such as likes, shares, comments, and viewing time to personalize content feeds and maximize engagement. Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and TikTok employ machine learning models that prioritize relevant and trending content based on real-time behavior patterns. These algorithms continuously evolve to improve content recommendations, balancing user retention and advertiser interests through data-driven optimization.
Misconceptions: EdgeRank vs. Edgerank
Misconceptions about EdgeRank often confuse it with Edgerank, though they refer to the same Facebook algorithm that determines content visibility in news feeds. Your content's reach depends on factors like user engagement, relevancy, and timeliness, all elements within the EdgeRank system. Understanding this algorithm helps optimize your social media strategy effectively.
Current Relevance of EdgeRank in 2024
EdgeRank remains a crucial algorithm for determining content visibility on Facebook in 2024, influencing user engagement and reach by prioritizing posts based on affinity, weight, and time decay factors. Social media marketers optimize strategies around these elements to enhance organic reach amidst increasing platform competition and algorithm updates. Understanding the current nuances of EdgeRank supports effective content delivery and audience targeting in a dynamic digital marketing landscape.
Impact on Organic Reach and Engagement
Social media algorithms increasingly prioritize paid content, causing a significant decline in organic reach for brands and individual creators. To maintain Your visibility and boost engagement, consistent, high-quality posts tailored to audience preferences are essential. Leveraging interactive features such as polls, stories, and live videos enhances user interaction and helps counteract algorithm limitations.
Best Practices for Navigating Algorithm Changes
Mastering social media algorithm changes involves prioritizing authentic engagement, creating high-quality content tailored to your audience's interests, and monitoring performance metrics closely. You should diversify content formats such as videos, stories, and interactive posts to maintain visibility and adapt to evolving platform priorities. Staying informed about platform updates and leveraging data analytics will help optimize your strategy and sustain consistent reach.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com