Photo illustration: Facebook Group Admin vs Page Admin
Facebook Group Admins manage community interactions and membership controls, while Page Admins oversee brand presence and content promotion. Explore this article to understand the distinct roles and effective strategies for each admin type.
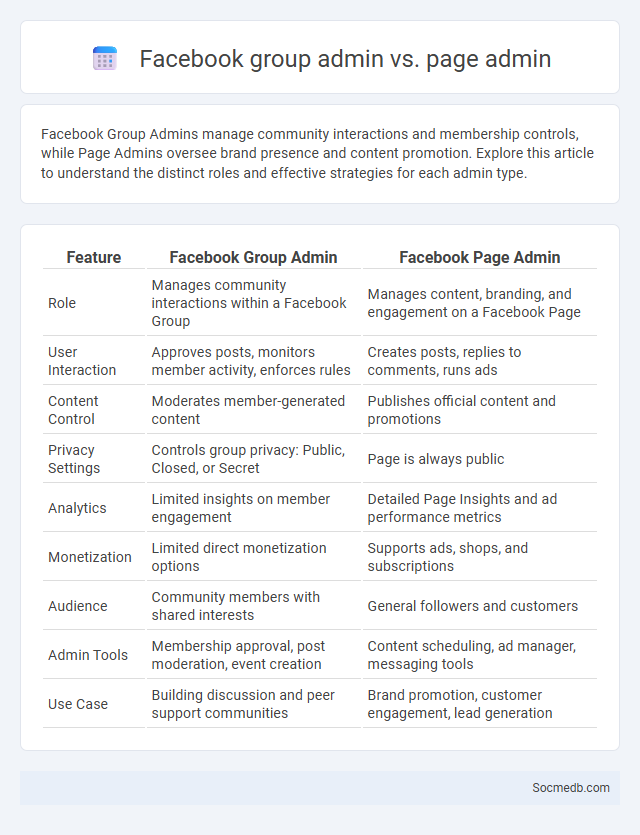
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facebook Group Admin | Facebook Page Admin |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Manages community interactions within a Facebook Group | Manages content, branding, and engagement on a Facebook Page |
| User Interaction | Approves posts, monitors member activity, enforces rules | Creates posts, replies to comments, runs ads |
| Content Control | Moderates member-generated content | Publishes official content and promotions |
| Privacy Settings | Controls group privacy: Public, Closed, or Secret | Page is always public |
| Analytics | Limited insights on member engagement | Detailed Page Insights and ad performance metrics |
| Monetization | Limited direct monetization options | Supports ads, shops, and subscriptions |
| Audience | Community members with shared interests | General followers and customers |
| Admin Tools | Membership approval, post moderation, event creation | Content scheduling, ad manager, messaging tools |
| Use Case | Building discussion and peer support communities | Brand promotion, customer engagement, lead generation |
Understanding Facebook Admin Roles
Facebook Admin roles define user permissions and access levels within a Facebook Page, essential for managing content, insights, and user interactions effectively. Key roles include Admin, Editor, Moderator, Advertiser, and Analyst, each with specific capabilities that help segment tasks and maintain page security. Proper understanding of these roles allows for efficient team collaboration and ensures that page management responsibilities are clearly assigned and controlled.
What is a Facebook Group Admin?
A Facebook Group Admin is an individual responsible for managing and moderating a Facebook Group, ensuring community guidelines are followed and content stays relevant. They have the authority to approve new members, remove inappropriate posts, and customize group settings to enhance member engagement. Your role as an admin is crucial for fostering a safe, active, and organized online community.
What is a Facebook Page Admin?
A Facebook Page Admin is a user with the highest level of control over a Facebook Page, enabling them to manage roles, edit page information, and create content. Admins can respond to messages, moderate comments, and access insights to track page performance and audience engagement. This role is essential for businesses and organizations aiming to maintain brand presence and interact with their community effectively on the platform.
General Definition of an Admin on Facebook
An admin on Facebook holds the highest level of control within a group or page, responsible for managing settings, approving members, and creating content. Your role as an admin includes moderating posts and comments to maintain community standards while ensuring the group's growth and engagement. Admins have access to insights and tools that help in analyzing member activity and optimizing the group's performance.
Key Responsibilities: Group Admin vs Page Admin
Group Admins manage member access by approving requests, enforcing group rules, and moderating posts to maintain community engagement and safety. Page Admins oversee content creation, schedule posts, respond to customer inquiries, and analyze page insights to enhance brand visibility. Both roles require strong communication skills but differ in focus: Groups prioritize member interaction, while Pages emphasize brand promotion and audience reach.
Access and Control Differences
Social media platforms exhibit significant access and control differences based on user roles, privacy settings, and regional regulations. Access to content can vary from public, friends-only, or restricted groups, while control mechanisms enable users to manage visibility, data sharing, and interaction permissions. These disparities influence user experience, data security, and the extent of information dissemination across networks.
Content Management: Groups vs Pages
Social media content management distinguishes between Groups and Pages by their purpose and audience interaction: Groups foster community engagement through member-driven discussion and exclusive content, ideal for niche interests and collaboration. Pages serve as official profiles for brands, organizations, or public figures to broadcast updates, promotions, and announcements to a broader, public audience. Effective content strategies leverage Groups for deeper community bonds and Pages for wider reach and brand visibility.
Community Engagement in Groups vs Pages
Community engagement in social media groups tends to be higher than in pages due to the interactive nature and sense of belonging fostered within groups. Groups enable members to share experiences, ask questions, and participate in discussions, creating a dynamic and authentic environment. Pages primarily serve as broadcasting platforms where content is pushed to followers, often resulting in less active interaction and lower engagement rates.
Privacy and Security Settings
Social media platforms offer a range of privacy and security settings to help you control who can see your posts, personal information, and activity online. Adjusting these settings regularly ensures protection against unauthorized access, cyber threats, and data breaches. Utilizing features like two-factor authentication and custom friend lists enhances your online safety and privacy management.
Choosing the Right Admin Role for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate admin role for your social media platform ensures effective management and security tailored to your needs. You must evaluate the responsibilities and permissions each role offers, such as content moderation, user management, or analytics access, to align with your team's strengths. Assigning roles thoughtfully enhances your social media strategy's efficiency and protects your account from unauthorized changes.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com