Photo illustration: Facebook Group vs Workplace Group
Facebook Groups offer diverse community-building tools and vast user reach for personal and interest-based networking. Workplace Groups prioritize professional collaboration with integrated productivity features designed for business communication. Discover detailed comparisons in this article.
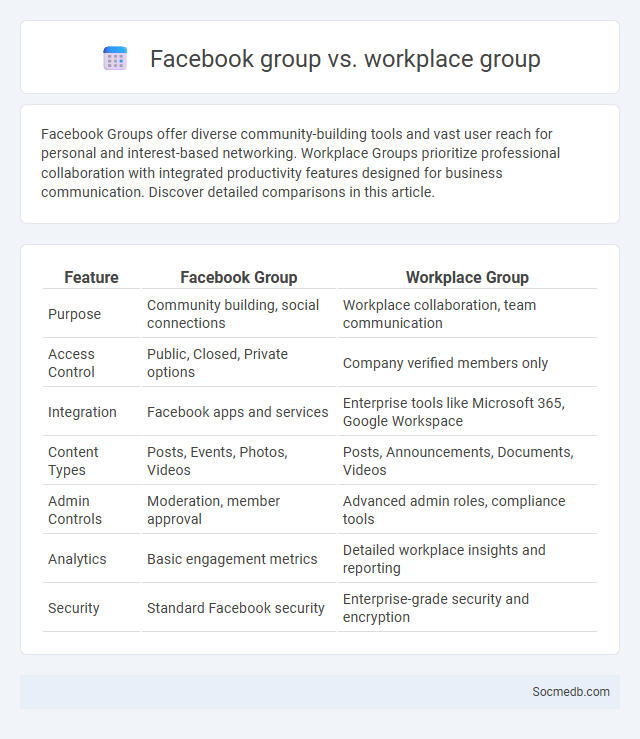
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facebook Group | Workplace Group |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Community building, social connections | Workplace collaboration, team communication |
| Access Control | Public, Closed, Private options | Company verified members only |
| Integration | Facebook apps and services | Enterprise tools like Microsoft 365, Google Workspace |
| Content Types | Posts, Events, Photos, Videos | Posts, Announcements, Documents, Videos |
| Admin Controls | Moderation, member approval | Advanced admin roles, compliance tools |
| Analytics | Basic engagement metrics | Detailed workplace insights and reporting |
| Security | Standard Facebook security | Enterprise-grade security and encryption |
Understanding Facebook Groups: Purpose and Features
Facebook Groups provide a dedicated space for communities to connect, share interests, and collaborate around specific topics or causes. Your participation in a Facebook Group allows you to engage with tailored content, access exclusive resources, and build relationships with like-minded individuals. Features such as privacy settings, event planning, and moderation tools enhance group interactions and ensure a focused, secure environment.
What Is a Workplace Group? Key Differences
A workplace group is a collection of employees collaborating within an organization to achieve specific goals, often formed around projects or shared functions. Unlike social media groups, workplace groups prioritize professional tasks, confidentiality, and productivity, ensuring secure communication tailored to business needs. Your engagement in a workplace group enhances teamwork by providing structured channels for feedback, resource sharing, and aligned objectives.
Defining General Groups: Scope and Usage
Social media platforms categorize users into general groups based on demographic, behavioral, and interest-based criteria to enhance targeted content delivery and advertising effectiveness. These groups encompass various segments such as age, location, profession, and online activity patterns, allowing marketers to tailor campaigns and optimize user engagement. Understanding the scope and usage of these general groups is crucial for businesses seeking to leverage social media analytics for strategic decision-making and audience expansion.
Membership and Access Control Comparison
Membership and access control in social media platforms vary significantly, with some platforms using invite-only groups to enhance privacy and exclusivity, while others implement tiered access levels based on user roles such as admins, moderators, and members. You benefit from these mechanisms by controlling who can view content, participate in discussions, or contribute, ensuring secure interaction within your social networks. Comparing Facebook groups, LinkedIn communities, and Discord servers reveals different strategies in managing member permissions effectively to balance engagement and privacy.
Communication Tools and Collaboration Features
Social media platforms offer advanced communication tools such as instant messaging, video calls, and group chats that enhance real-time interaction and information sharing. Collaboration features like file sharing, co-editing documents, and task management enable teams to work cohesively regardless of geographic location. These integrated tools streamline project workflows, boost productivity, and foster community engagement across various industries.
Privacy and Security Considerations
Social media platforms collect vast amounts of personal data, making privacy protection critical to safeguard users from identity theft and unauthorized data exploitation. Robust security measures like end-to-end encryption, two-factor authentication, and regular security audits are essential to prevent data breaches and cyberattacks. Users must also be educated on privacy settings and safe online behaviors to minimize risks associated with oversharing and phishing attempts.
Content Moderation and Administration
Content moderation on social media platforms involves filtering user-generated content to ensure compliance with community guidelines and legal standards, thereby reducing harmful, misleading, or inappropriate material. Effective administration employs AI-driven algorithms combined with human moderators to identify and remove content related to hate speech, misinformation, and explicit material while balancing freedom of expression. Robust content moderation strategies enhance user safety, trust, and platform integrity, driving sustainable social media engagement.
Use Cases: Social, Professional, and Community
Social media platforms enable you to connect with friends and family, share personal updates, and engage in entertainment content, enhancing your social interactions. Professional networks like LinkedIn facilitate career development, job hunting, and industry-specific networking, supporting your professional growth. Community-focused platforms create spaces for interest-based groups, local initiatives, and support networks, fostering meaningful connections around shared passions and causes.
Integration with Other Platforms and Apps
Seamless integration with other platforms and apps enhances the efficiency of your social media strategy by synchronizing content sharing, data analytics, and audience engagement. Tools like Hootsuite and Zapier enable automatic cross-posting and unified management across networks such as Instagram, Facebook, and Twitter. Leveraging these integrations amplifies your brand presence and streamlines workflow, driving consistent communication and measurable results.
Choosing the Right Group Type for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate social media group type depends on your specific objectives, whether fostering close-knit communities, facilitating professional networking, or promoting public discussions. Private groups offer controlled environments ideal for exclusive content sharing and member engagement, while public groups maximize visibility and growth potential. Understanding platform-specific features and member preferences ensures optimal group functionality and meaningful interaction.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com