Photo illustration: Facebook OAuth vs SSO
Facebook OAuth enables secure user authentication by allowing apps to access specific user data without sharing passwords, while Single Sign-On (SSO) streamlines login across multiple platforms using a single set of credentials. Explore this article to understand the differences and benefits of Facebook OAuth versus SSO for seamless user experiences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facebook OAuth | Facebook SSO |
|---|---|---|
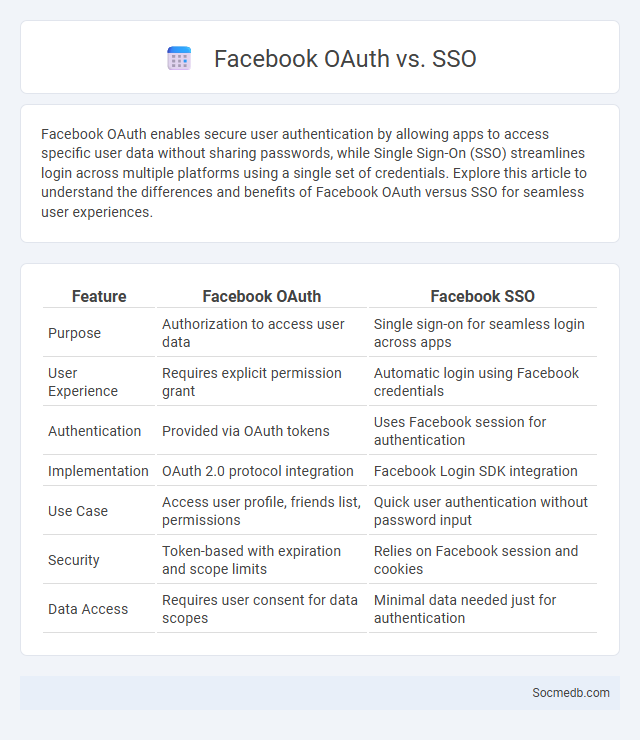
| Purpose | Authorization to access user data | Single sign-on for seamless login across apps |
| User Experience | Requires explicit permission grant | Automatic login using Facebook credentials |
| Authentication | Provided via OAuth tokens | Uses Facebook session for authentication |
| Implementation | OAuth 2.0 protocol integration | Facebook Login SDK integration |
| Use Case | Access user profile, friends list, permissions | Quick user authentication without password input |
| Security | Token-based with expiration and scope limits | Relies on Facebook session and cookies |
| Data Access | Requires user consent for data scopes | Minimal data needed just for authentication |
Introduction to Authentication Methods
Authentication methods in social media platforms ensure user identity verification to protect accounts from unauthorized access and fraudulent activities. Common techniques include multi-factor authentication (MFA), which combines passwords with additional verification steps like SMS codes or biometric data, and single sign-on (SSO) that enables users to access multiple services with one set of credentials. These security measures enhance trust, reduce account compromises, and maintain the integrity of user interactions across platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
Overview of Facebook OAuth
Facebook OAuth is an authorization protocol enabling users to grant third-party applications secure access to their Facebook data without sharing credentials. It utilizes access tokens to authenticate API requests, supporting scopes that define specific permissions such as email, profile information, and friend lists. This standardized OAuth 2.0 framework enhances user privacy while simplifying app integration and user login experiences across multiple platforms.
What is Single Sign-On (SSO)?
Single Sign-On (SSO) is an authentication process that allows you to access multiple social media platforms using a single set of login credentials. This technology enhances security by reducing password fatigue and minimizing the risk of credential theft across networks like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. Your seamless experience improves as SSO simplifies account management and streamlines user access to social media services.
Understanding Third-Party App Authentication
Third-party app authentication allows social media platforms to securely connect Your accounts with external applications, enabling seamless data sharing and enhanced functionality. This process uses standardized protocols like OAuth to grant limited access without exposing Your login credentials. Understanding these authentication mechanisms helps You manage permissions and protect Your personal information effectively.
Key Differences: Facebook OAuth vs SSO vs Third-Party App
Facebook OAuth enables users to log in using their Facebook credentials, streamlining authentication across multiple platforms with secure token-based access. Single Sign-On (SSO) allows users to authenticate once and gain entry to multiple independent applications or services without repeated logins, improving user convenience and security management. Third-party apps leverage either OAuth or SSO protocols to integrate with Facebook, but they differ in the level of access control and user data permissions, making OAuth more user-specific while SSO is broader across services.
Security Comparison of Authentication Methods
Biometric authentication, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, offers enhanced security for social media platforms by reducing the risk of password theft and unauthorized access. Two-factor authentication (2FA) involving SMS codes or authentication apps significantly strengthens account protection by requiring an additional verification step beyond passwords. Password-based methods remain vulnerable to phishing and brute-force attacks, making multi-factor approaches essential for robust social media security.
User Experience and Usability
Optimizing social media platforms for user experience and usability enhances engagement by providing intuitive navigation, fast loading times, and personalized content tailored to Your preferences. Key factors include responsive design, accessibility features, and seamless interaction flows that reduce cognitive load and frustration. Prioritizing these elements leads to higher user satisfaction, longer session durations, and increased platform loyalty.
Integration Complexity and Implementation
Integrating social media platforms into your business ecosystem often involves managing API compatibility, data synchronization, and security protocols to ensure seamless communication across channels. Implementation requires careful planning of workflows, authentication methods, and real-time content updates to maintain consistent user engagement and data integrity. Understanding platform-specific requirements and leveraging integration tools can significantly reduce complexity and accelerate deployment.
Use Cases and Industry Applications
Social media platforms drive targeted marketing strategies, enhance customer engagement, and facilitate real-time communication in diverse industries such as retail, healthcare, and finance. Brands use social media analytics to monitor consumer sentiment and improve product development, while healthcare providers employ these channels for patient education and community support. Your business can leverage these use cases to boost brand awareness, drive sales, and build stronger customer relationships.
Choosing the Right Authentication for Your Platform
Choosing the right authentication method for your social media platform ensures secure user access and protects personal data from unauthorized breaches. Implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA) or biometrics enhances security by verifying identity beyond just passwords. You must evaluate your platform's user base and security requirements to select the most effective authentication system.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com