Photo illustration: Facebook vs Google
Facebook dominates social media with over 2.9 billion active users, offering personalized advertising and robust community engagement, while Google integrates social features through YouTube and Google My Business, emphasizing search-driven content and local business connections. Explore this article to understand the strategic differences and marketing advantages of Facebook versus Google.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | ||
|---|---|---|
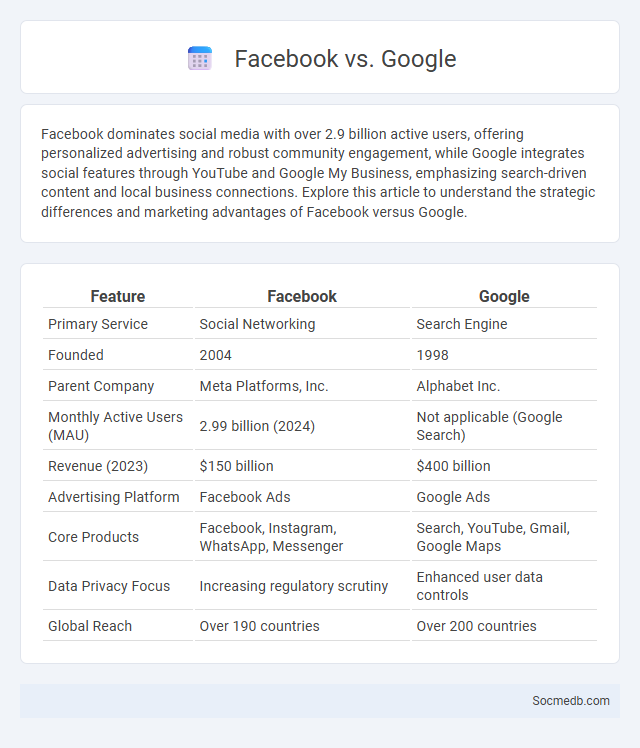
| Primary Service | Social Networking | Search Engine |
| Founded | 2004 | 1998 |
| Parent Company | Meta Platforms, Inc. | Alphabet Inc. |
| Monthly Active Users (MAU) | 2.99 billion (2024) | Not applicable (Google Search) |
| Revenue (2023) | $150 billion | $400 billion |
| Advertising Platform | Facebook Ads | Google Ads |
| Core Products | Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp, Messenger | Search, YouTube, Gmail, Google Maps |
| Data Privacy Focus | Increasing regulatory scrutiny | Enhanced user data controls |
| Global Reach | Over 190 countries | Over 200 countries |
Understanding the Fake News Dilemma
Fake news on social media spreads rapidly, leveraging sensational headlines and emotional content to capture attention and mislead audiences. Algorithms prioritize engagement, often amplifying false information and making it difficult for You to discern credible sources from unreliable ones. Developing critical thinking skills and verifying facts through multiple trustworthy channels is essential to navigate the fake news dilemma effectively.
Facebook’s Role in Fake News Proliferation
Facebook's algorithms prioritize engagement, often amplifying sensational and misleading content, which significantly contributes to the spread of fake news. Studies reveal that false information on Facebook spreads faster and reaches more people than truthful news, exacerbating misinformation crises. Efforts to combat fake news include fact-checking partnerships, algorithm adjustments, and content removal policies, yet challenges persist due to the platform's vast user base and content volume.
Google’s Influence on Online Information
Google dominates online information access by processing over 90% of global search queries, directly shaping what you see on social media platforms. Its algorithms prioritize content based on relevance, authority, and user behavior, influencing trends, news dissemination, and advertising strategies across networks like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram. This control over digital visibility impacts public opinion, marketing, and even social interactions in the digital landscape.
Comparing News Algorithms: Facebook vs Google
Facebook's news algorithm prioritizes content based on user interactions such as likes, comments, and shares to personalize your news feed, emphasizing social engagement. Google News uses machine learning to aggregate and rank news stories from multiple sources, considering factors like relevance, freshness, and diversity to deliver unbiased, comprehensive coverage. Understanding these differences helps you choose the platform best suited for staying informed with tailored content or broader perspectives.
Fact-Checking Initiatives by Facebook and Google
Facebook and Google have implemented robust fact-checking initiatives to combat misinformation on their platforms, partnering with third-party organizations to verify the accuracy of shared content. These companies use advanced AI algorithms combined with human reviewers to identify and flag false information, promoting credible sources in search results and news feeds. Their commitment significantly reduces the spread of fake news, enhancing the overall trustworthiness of social media environments.
Social Impact: Echo Chambers and Misinformation
Social media platforms contribute significantly to the formation of echo chambers, where users are exposed predominantly to information that reinforces their existing beliefs, intensifying social polarization. This environment facilitates the rapid spread of misinformation and fake news, undermining public trust in credible sources and complicating fact-based decision making. Algorithms designed to maximize engagement often prioritize sensational or misleading content, exacerbating the challenges of verifying accuracy and maintaining informed discourse.
Advertising Revenue and the Spread of Fake News
Social media platforms generate billions in advertising revenue annually, driven by targeted ads that leverage user data for personalized marketing campaigns. This massive influx of ad spending incentivizes algorithms to prioritize engaging content, often amplifying sensational or misleading information. The widespread distribution of fake news on social media not only undermines public trust but also poses significant challenges for content moderation and regulatory frameworks worldwide.
Policy Responses and Platform Accountability
Effective policy responses to social media emphasize transparency, data privacy, and user protection regulations. Governments worldwide are enforcing stricter platform accountability measures, including content moderation standards and algorithmic transparency mandates. These initiatives aim to mitigate misinformation, safeguard digital rights, and ensure ethical platform behavior.
User Responsibility and Media Literacy
User responsibility on social media encompasses ethical behavior, critical evaluation of content, and respectful communication to prevent misinformation and cyberbullying. Media literacy equips users with the skills to analyze sources, recognize biases, and understand digital footprints, enhancing their ability to navigate complex online environments. Promoting these competencies reduces harmful impacts and fosters a safer, more informed digital community.
The Future of News in the Digital Age
Social media platforms are transforming the future of news by enabling real-time updates and personalized content tailored to Your interests. Advances in AI-driven algorithms ensure that news delivery becomes increasingly efficient and relevant, shifting away from traditional media outlets. This digital evolution allows for greater engagement, interactive storytelling, and the rapid spread of information across global communities.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com