Photo illustration: Carousel post vs swipe post
Carousel posts on social media display multiple images or videos within a single post, encouraging swipe interactions for detailed storytelling. Swipe posts enhance user engagement by offering a seamless way to explore content; discover the benefits and best practices in this article.
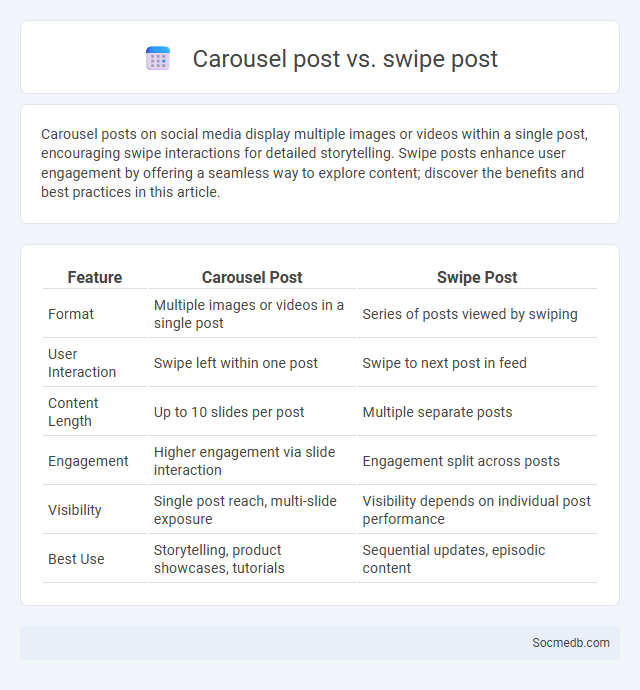
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Carousel Post | Swipe Post |
|---|---|---|
| Format | Multiple images or videos in a single post | Series of posts viewed by swiping |
| User Interaction | Swipe left within one post | Swipe to next post in feed |
| Content Length | Up to 10 slides per post | Multiple separate posts |
| Engagement | Higher engagement via slide interaction | Engagement split across posts |
| Visibility | Single post reach, multi-slide exposure | Visibility depends on individual post performance |
| Best Use | Storytelling, product showcases, tutorials | Sequential updates, episodic content |
What is a Carousel Post?
A carousel post on social media is a multi-image or video format that allows Your audience to swipe through a series of visuals within a single post. This format boosts engagement by providing interactive content that delivers a comprehensive story or showcases multiple products effectively. Leveraging carousel posts can significantly enhance your content strategy by increasing time spent on your profile and encouraging user interaction.
What is a Swipe Post?
A swipe post is a type of social media content designed for platforms like Instagram and Facebook, where users can swipe horizontally to view multiple images or slides within a single post. This interactive format enhances user engagement by allowing creators to share detailed information, storytelling elements, or product features in a visually appealing sequence. Swipe posts increase time spent on content and improve algorithm performance by encouraging viewers to interact with each slide.
Carousel Post vs Swipe Post: Key Differences
Carousel posts enable your audience to view multiple images or videos within a single Instagram or Facebook post, enhancing engagement through sequential storytelling. Swipe posts, often in the form of Instagram Stories or TikTok sequences, allow users to navigate through content by swiping left or right, offering a more interactive and immersive user experience. Both formats increase content visibility but cater to different interaction styles and platform algorithms, making your choice crucial for maximizing reach and engagement.
Advantages of Carousel Posts
Carousel posts on social media enhance user engagement by allowing brands to showcase multiple images or videos in a single post, increasing content richness and storytelling opportunities. They improve click-through rates and drive higher interaction by encouraging viewers to swipe through a sequence, making it ideal for product demonstrations, tutorials, and detailed narratives. Platforms like Instagram and Facebook report that carousel posts generate up to 1.4 times more reach and engagement compared to single-image posts, offering marketers a powerful tool to boost visibility and conversion rates.
Benefits of Swipe Posts
Swipe posts on social media enhance user engagement by offering interactive, multi-content experiences that keep viewers on a profile longer. They enable brands to convey detailed stories, product features, or tutorials without overwhelming the audience in a single image or caption. This format increases visibility in feed algorithms, boosting reach and fostering stronger connections with followers.
Engagement Rates: Carousel vs Swipe Posts
Engagement rates often differ between carousel and swipe posts on social media, with carousel posts typically generating higher interaction due to their multiple-slide format that encourages users to spend more time on your content. Swipe posts enhance engagement by promoting active user participation through interactive storytelling or sequential information presentation. To maximize your social media strategy, focus on creating carousel content that balances visual appeal and informative value, ultimately boosting your overall engagement rates.
Use Cases: When to Choose Carousel Posts
Carousel posts excel in showcasing multiple products or features within a single post, increasing engagement and user interaction. You can leverage them for tutorials, step-by-step guides, or storytelling to maintain audience interest and boost content retention. Brands aiming to highlight diverse offerings or complex narratives benefit significantly from choosing carousel formats over single-image posts.
Use Cases: When to Use Swipe Posts
Swipe posts are ideal for sharing step-by-step tutorials, product demonstrations, or in-depth storytelling that requires multiple visuals or pieces of information. You can leverage these posts to boost user engagement by encouraging swipes, increasing time spent on your content, and delivering value through sequential insights. Use swipe posts to showcase collections, highlight features, or break down complex topics in easily digestible chunks.
Best Practices for Carousel and Swipe Posts
Effective carousel and swipe posts on social media leverage high-quality, visually cohesive images that tell a compelling story or showcase a step-by-step process to enhance user engagement. Optimal post length ranges from 3 to 10 slides, balancing detailed content without overwhelming viewers, while clear calls-to-action on the final slide drive interaction or conversions. Using consistent branding elements, engaging captions with strategic hashtags, and analyzing performance metrics ensures continuous improvement and maximizes reach and impact.
Which Format Suits Your Content Strategy?
Choosing the right format for your social media content strategy depends on your target audience, platform algorithms, and content goals. Visual formats like videos and images tend to drive higher engagement on platforms such as Instagram and TikTok, while articles and infographics perform well on LinkedIn and Facebook. You should analyze your content type and audience behavior to ensure maximum reach and interaction.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com