Photo illustration: 1st degree vs mutual connection
First-degree connections on social media are direct contacts, while mutual connections are shared links between two users through a common contact. Explore this article to understand how leveraging both can enhance your networking strategy.
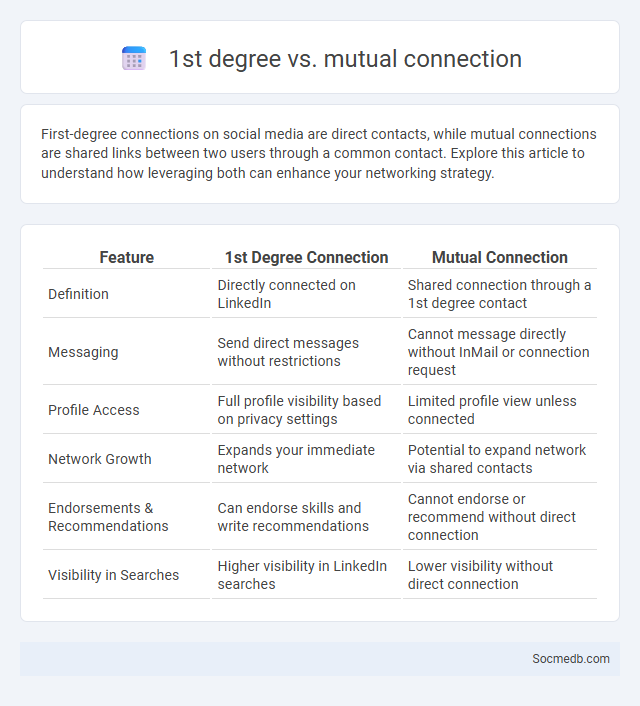
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 1st Degree Connection | Mutual Connection |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Directly connected on LinkedIn | Shared connection through a 1st degree contact |
| Messaging | Send direct messages without restrictions | Cannot message directly without InMail or connection request |
| Profile Access | Full profile visibility based on privacy settings | Limited profile view unless connected |
| Network Growth | Expands your immediate network | Potential to expand network via shared contacts |
| Endorsements & Recommendations | Can endorse skills and write recommendations | Cannot endorse or recommend without direct connection |
| Visibility in Searches | Higher visibility in LinkedIn searches | Lower visibility without direct connection |
Understanding Connection Degrees: An Overview
Understanding connection degrees on social media reveals how users are linked through varying levels of relationships, such as first-degree connections representing direct contacts, second-degree involving friends of friends, and third-degree extending to acquaintances within broader networks. This hierarchical structure influences content visibility, engagement rates, and networking potential, shaping the dynamics of information flow and community building. Platforms utilize algorithms that prioritize interactions based on these connection degrees to enhance personalized user experiences and targeted content delivery.
What is a 1st Degree Connection?
A 1st Degree Connection on social media platforms like LinkedIn refers to a direct connection between you and another user, meaning you have mutually accepted each other's invitations. This level of connection allows you to message each other directly without restrictions and often serves as the foundation for building professional relationships. Understanding your 1st Degree Connections helps optimize your networking strategy and expand your reach effectively.
Exploring Mutual Connections Explained
Exploring mutual connections on social media reveals common acquaintances that can strengthen your network and increase trust between you and new contacts. By identifying shared connections, you gain valuable insights into others' interests and professional backgrounds, facilitating more meaningful interactions. Your ability to leverage these mutual ties enhances relationship-building and opens opportunities for collaboration or social engagement.
2nd Degree Connections: Definition and Value
Second degree connections on social media refer to individuals who are connected to your direct contacts but not to you personally, expanding your extended network. These connections offer valuable opportunities for networking, business growth, and information sharing by bridging gaps between different social circles. Leveraging your second degree connections effectively can enhance your influence and open doors to new professional relationships.
3rd Degree Connections: Broadening Your Network
Third-degree connections on social media expand your network by linking you to friends of friends of friends, increasing your reach exponentially. Engaging with these connections can lead to new professional opportunities and diverse perspectives, enhancing your online presence. Leveraging features like mutual interests and groups helps bridge gaps and fosters meaningful interactions beyond direct contacts.
Key Differences: 1st Degree vs. Mutual Connections
1st Degree connections on social media platforms refer to individuals directly connected to You, typically through friend requests or follow approvals, enabling immediate interactions such as messaging and content sharing. Mutual connections represent shared contacts between two users, often highlighting potential networking opportunities by revealing common relationships without direct linkage. Understanding the distinctions between these connection types can optimize Your social media strategy for networking, engagement, and growth.
Advantages of 1st Degree Connections
First-degree connections on social media provide direct access to your network, enabling personalized interactions and fostering trust. These connections allow you to share content instantly and receive immediate feedback, enhancing engagement and collaboration opportunities. Leveraging your first-degree network can significantly boost your professional visibility and open doors to new career advancements.
Leveraging Mutual Connections for Networking
Leveraging mutual connections on social media platforms enhances networking opportunities by fostering trust and credibility between you and new contacts. Utilizing shared connections helps create personalized introductions, increasing the likelihood of meaningful professional relationships. Your engagement with these mutual contacts can accelerate networking growth and open doors to valuable collaborations.
Why Connection Degrees Matter on LinkedIn
Connection degrees on LinkedIn determine how closely you're linked to other professionals, influencing your network's reach and visibility. Your 1st-degree connections allow direct communication, while 2nd and 3rd-degree connections expand your access to industry opportunities and referrals. Understanding these connection levels helps optimize your networking strategy for career growth and business development.
Best Practices for Expanding Connection Degrees
Expanding connection degrees on social media requires consistent engagement through meaningful interactions such as commenting, sharing valuable content, and participating in relevant groups or discussions. Utilizing targeted hashtags and geo-tagging can enhance visibility and attract users interested in similar topics or locations. Regularly updating profiles with clear, optimized keywords improves discoverability, fostering authentic network growth and deeper connection levels.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com