Photo illustration: 1st connection vs group member
First connections on social media foster personalized interactions, while group memberships enable broader community engagement and shared interests. Explore how optimizing both can enhance your social networking strategy in this article.
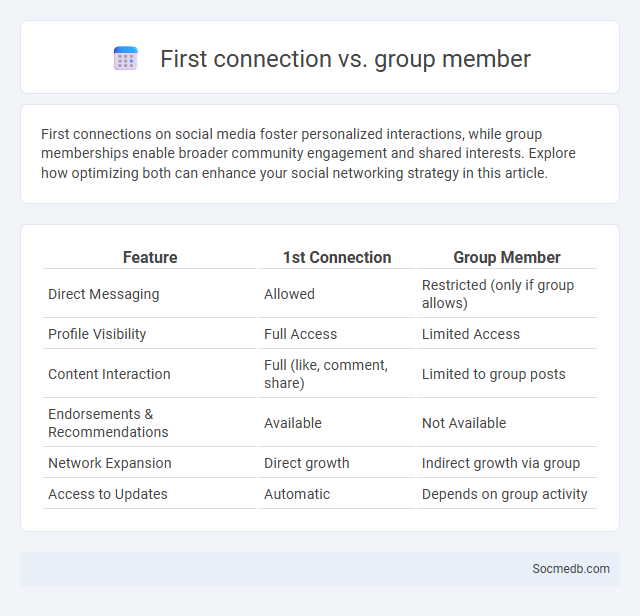
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 1st Connection | Group Member |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Messaging | Allowed | Restricted (only if group allows) |
| Profile Visibility | Full Access | Limited Access |
| Content Interaction | Full (like, comment, share) | Limited to group posts |
| Endorsements & Recommendations | Available | Not Available |
| Network Expansion | Direct growth | Indirect growth via group |
| Access to Updates | Automatic | Depends on group activity |
Understanding LinkedIn Connections: An Overview
Understanding LinkedIn connections involves recognizing the value of your professional network in expanding career opportunities and industry insights. Your LinkedIn connections serve as vital links for endorsements, referrals, and sharing relevant content, enhancing your visibility in targeted sectors. Optimizing these connections by engaging thoughtfully boosts your personal brand and strengthens professional relationships.
Defining 1st-Degree Connections
1st-degree connections on social media are direct relationships established when two users mutually agree to connect, such as following or befriending each other. These connections enable immediate interaction, messaging, and content sharing, forming the foundation of personalized networking. Platforms like LinkedIn and Facebook prioritize 1st-degree connections for targeted communication and trust-building among users.
What are Group Members on LinkedIn?
Group Members on LinkedIn are professionals who join specific LinkedIn Groups to network, share industry insights, and engage in discussions relevant to their field. These members contribute content, participate in conversations, and connect with like-minded individuals to expand their professional reach. LinkedIn Groups foster collaboration and enable targeted communication among members with shared interests or expertise.
Connection Degrees Explained: 1st, 2nd, and 3rd
Social media platforms categorize connections into 1st, 2nd, and 3rd degrees to define relationship proximity: 1st-degree connections are direct contacts, 2nd-degree connections are friends of friends, and 3rd-degree connections represent acquaintances beyond friends of friends. These connection degrees impact content visibility and networking opportunities by determining how information and requests can be shared across different network tiers. Understanding these degrees enhances social media strategies for networking, marketing, and personal engagement by targeting specific audience layers effectively.
Differences Between 1st Connection and Group Member
First connections on social media represent direct, personal links often based on mutual trust and familiar interactions, facilitating immediate and tailored communication. Group members, however, embody a broader network where engagement occurs within shared interests or communities, emphasizing collective discussions and diverse perspectives. Understanding this distinction helps you strategize your social interactions and content sharing more effectively for targeted networking outcomes.
How Connection Degree Impacts Networking Opportunities
The degree of connection on social media platforms directly influences networking opportunities by expanding access to diverse professional communities and potential collaborators. Higher connection degrees facilitate trust-building and information sharing, increasing the likelihood of referrals and partnerships. Platforms like LinkedIn demonstrate that users with extensive, well-maintained networks receive more job offers and business inquiries compared to those with limited connections.
Group Members vs. Connections: Communication Privileges
Group members on social media platforms often enjoy expanded communication privileges, such as posting, commenting, and accessing exclusive content within the group, unlike general connections who may have limited interaction capabilities. These groups facilitate targeted discussions, enabling members to share ideas and updates in a private or semi-private setting, fostering stronger engagement. Connections typically enable one-on-one interactions like messaging or commenting on public posts, whereas group membership unlocks collaborative functionalities essential for community building.
Building Value: Why Connection Degree Matters
The degree of connection on social media significantly influences user engagement and trust, directly impacting brand credibility and customer loyalty. Highly connected networks facilitate faster information dissemination and richer interactions, enhancing content visibility and driving organic growth. Platforms with strong connection degrees also boost algorithms' ability to deliver personalized experiences, increasing overall user satisfaction and retention.
Strategies to Move from Group Member to 1st Connection
Building meaningful relationships on social media requires strategic engagement by consistently interacting with targeted group members through comments and direct messages. Personalizing connection requests with relevant context or shared interests significantly increases acceptance rates and fosters trust. Leveraging mutual connections and participating in group discussions regularly positions you as an active, valuable contact, facilitating seamless transitions from group member to first connection.
Maximizing LinkedIn: Leveraging Connection Degrees and Groups
Maximizing LinkedIn involves strategically engaging with first, second, and third-degree connections to expand professional networks and access targeted opportunities. Joining and actively participating in relevant LinkedIn Groups enhances visibility and fosters valuable industry-specific discussions. Utilizing LinkedIn's advanced search filters and group memberships drives effective relationship building and lead generation.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com