Photo illustration: 3rd connection vs follower
Third connection in social media refers to individuals connected through two intermediaries, offering broader network reach than direct followers who are personally connected. Explore this article to understand the strategic impact of engaging third connections versus followers.
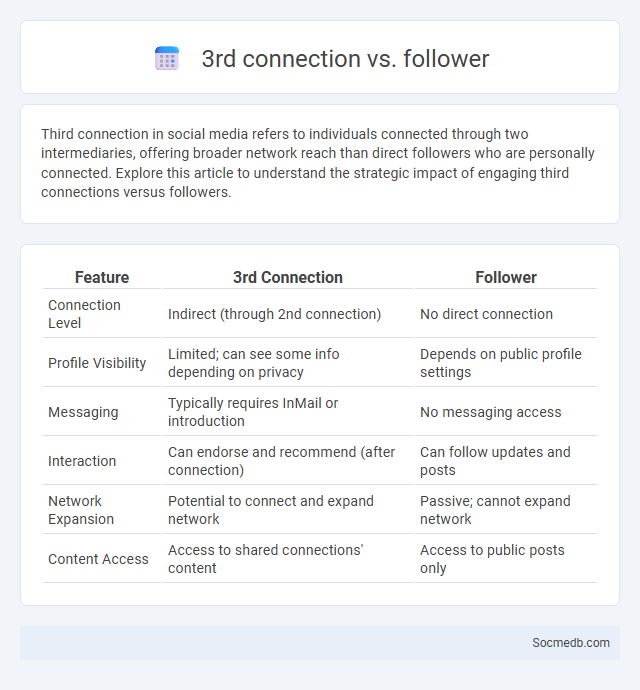
Table of Comparison
| Feature | 3rd Connection | Follower |
|---|---|---|
| Connection Level | Indirect (through 2nd connection) | No direct connection |
| Profile Visibility | Limited; can see some info depending on privacy | Depends on public profile settings |
| Messaging | Typically requires InMail or introduction | No messaging access |
| Interaction | Can endorse and recommend (after connection) | Can follow updates and posts |
| Network Expansion | Potential to connect and expand network | Passive; cannot expand network |
| Content Access | Access to shared connections' content | Access to public posts only |
Understanding LinkedIn Connection Types
LinkedIn connection types include first-degree, second-degree, and third-degree connections, defining the network's reach and potential engagement. First-degree connections allow direct messaging, while second-degree connections enable introductions through mutual contacts. Understanding these connection tiers enhances networking strategies and maximizes professional opportunities on the platform.
What is a 3rd-Degree Connection?
A 3rd-degree connection on social media platforms like LinkedIn represents a user who is connected to your 2nd-degree connections but not directly linked to you. This type of connection expands your network reach, enabling potential interactions with individuals who share indirect associations through mutual contacts. Understanding 3rd-degree connections helps optimize networking strategies by targeting broader audiences beyond immediate contacts.
Difference Between Followers and Connections
Followers on social media represent users who choose to receive updates and content from a particular account without requiring mutual approval, commonly seen on platforms like Instagram and Twitter. Connections, often found on professional networks like LinkedIn, imply a mutual agreement where both parties acknowledge the relationship, enabling two-way interaction and networking. Understanding the distinction between followers and connections helps optimize engagement strategies tailored to the platform's unique social dynamics.
The Significance of Connection Degrees on LinkedIn
Connection degrees on LinkedIn critically shape your professional network's reach, influencing the visibility of your profile and opportunities. First-degree connections enable direct messaging and endorsements, while second and third-degree connections expand your potential for introductions and collaborations. Understanding these connection levels empowers you to strategically grow your network and leverage LinkedIn for career advancement.
How 3rd Connections Impact Network Reach
Third connections on social media greatly extend network reach by bridging gaps between direct connections and new audiences. These extended links amplify content visibility, fostering increased engagement and potential collaborations beyond immediate circles. Leveraging third connections strategically enhances brand awareness and drives organic growth across platforms.
Followers vs. Connections: Engagement Potential
Followers on social media represent a one-way relationship, allowing content creators to broadcast messages to a wide audience and increase visibility, while connections imply a mutual relationship often found on platforms like LinkedIn, fostering deeper interaction and trust. Engagement potential tends to be higher with connections due to personalized communication and reciprocal interest, which can lead to meaningful conversations and business opportunities. Understanding the balance between followers and connections helps optimize social media strategies for both broad reach and high-quality engagement.
Building Stronger Networks Through Connection Degrees
Building stronger networks through connection degrees enhances social media effectiveness by leveraging first, second, and third-degree relationships to expand reach and influence. Focusing on strategic engagement within these layers increases trust and collaboration opportunities, driving both personal and professional growth. Understanding the dynamics of connection degrees allows users to optimize content sharing, resulting in higher interaction rates and network value amplification.
When to Follow vs. When to Connect
Follow on social media when you want to stay updated with content from thought leaders, brands, or influencers without requiring direct interaction. Connect when building a professional relationship or networking is your goal, allowing for private messaging and more personalized engagement. You should balance following and connecting to grow your network strategically and maintain meaningful interactions.
Leveraging 3rd Connections for Career Growth
Leveraging third connections on social media platforms like LinkedIn expands professional networks beyond immediate contacts, unlocking hidden job opportunities and industry insights. Engaging with second- and third-degree connections through targeted messaging or group interactions increases visibility and credibility within specific career fields. Utilizing these extended networks strategically accelerates career growth by fostering mentorship, collaboration, and access to exclusive professional resources.
Best Practices for Managing LinkedIn Connections and Followers
Effective management of LinkedIn connections and followers involves regularly engaging with your network by sharing relevant industry content and personalized messages to build trust. Organize connections using LinkedIn tags and notes to segment contacts for targeted communication and relationship nurturing. Consistently reviewing follower analytics helps identify key audiences, optimize content strategy, and expand professional influence on the platform.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com