Photo illustration: LinkedIn Native Video vs Article Post
LinkedIn native videos generate 5x higher engagement than article posts, boosting visibility through autoplay and richer storytelling formats. Discover how to leverage these insights for maximum impact in this article.
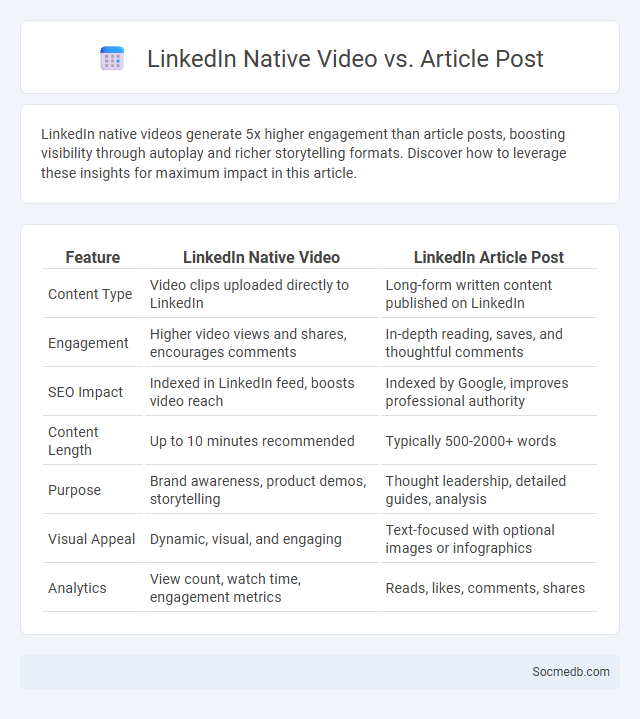
Table of Comparison
| Feature | LinkedIn Native Video | LinkedIn Article Post |
|---|---|---|
| Content Type | Video clips uploaded directly to LinkedIn | Long-form written content published on LinkedIn |
| Engagement | Higher video views and shares, encourages comments | In-depth reading, saves, and thoughtful comments |
| SEO Impact | Indexed in LinkedIn feed, boosts video reach | Indexed by Google, improves professional authority |
| Content Length | Up to 10 minutes recommended | Typically 500-2000+ words |
| Purpose | Brand awareness, product demos, storytelling | Thought leadership, detailed guides, analysis |
| Visual Appeal | Dynamic, visual, and engaging | Text-focused with optional images or infographics |
| Analytics | View count, watch time, engagement metrics | Reads, likes, comments, shares |
Introduction to LinkedIn Content Formats
LinkedIn offers a variety of content formats designed to enhance professional networking and engagement, including articles, posts, videos, and SlideShare presentations. Native videos and carousel posts capture attention with dynamic visuals while LinkedIn articles enable in-depth thought leadership. Understanding these formats helps optimize content strategy for increased visibility and audience interaction on the platform.
What is LinkedIn Native Video?
LinkedIn Native Video is a feature that allows users to upload and share videos directly on the LinkedIn platform, enhancing engagement through rich, visual content. It supports various formats and durations, enabling professionals and businesses to showcase expertise, company culture, and thought leadership effectively. Videos posted natively on LinkedIn tend to achieve higher organic reach and interaction compared to external video links.
What are LinkedIn Article Posts?
LinkedIn Article Posts are long-form content pieces published directly on LinkedIn, allowing users to share in-depth insights, industry knowledge, and professional experiences. These posts enhance your personal brand by establishing authority and boosting visibility within your professional network. Utilizing LinkedIn Article Posts effectively can increase engagement, attract potential employers or clients, and expand your influence on the platform.
Key Differences: Native Video vs Article Post
Native videos on social media platforms automatically play in users' feeds, capturing attention with dynamic visuals and sound, resulting in higher engagement rates compared to static article posts. Article posts provide detailed content through text and images, ideal for in-depth storytelling and SEO benefits, but may require users to click away from the feed, reducing immediate interaction. Your marketing strategy should leverage native video for brand visibility and quick impact, while utilizing article posts to enhance content depth and searchability.
Benefits of Publishing Native Videos on LinkedIn
Publishing native videos on LinkedIn significantly boosts your content's visibility by generating higher engagement rates compared to shared links or text posts. Native videos autoplay directly in users' feeds, capturing attention and encouraging longer viewing times, which improves your LinkedIn algorithm ranking. By sharing your expertise through native video, you strengthen professional connections and enhance your brand's authenticity on the platform.
Advantages of LinkedIn Article Posts
LinkedIn article posts enhance professional credibility by allowing users to showcase expertise through detailed, long-form content, increasing visibility within targeted industries. These posts foster stronger networking opportunities by encouraging meaningful interactions and discussions among professionals, boosting engagement and relationship-building. The platform's algorithm favors original articles, amplifying reach and driving more organic traffic to users' profiles or business pages.
Audience Engagement: Video vs Article
Video content drives higher audience engagement by combining visual and auditory stimuli, making your message more memorable and shareable. Articles offer detailed information and cater to readers seeking in-depth analysis but typically generate lower interaction rates compared to videos. For effective social media strategies, leveraging videos increases comments, likes, and shares, enhancing overall engagement with your target audience.
Analytics and Performance Metrics
Social media analytics provide critical insights into audience engagement, content reach, and conversion rates by measuring metrics such as impressions, click-through rates, and follower growth. Performance metrics like engagement rate, sentiment analysis, and share of voice help marketers assess campaign effectiveness and optimize content strategies. Advanced tools use data visualization and AI-driven predictive analytics to track trends and forecast social media ROI accurately.
Best Practices for Both Content Types
Effective social media strategies require tailoring content to suit both organic posts and paid advertisements, emphasizing authentic engagement and targeted messaging. High-quality visuals and clear calls-to-action enhance user interaction across platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and LinkedIn. Consistent posting schedules combined with audience analytics drive improved reach and conversion rates for both content types.
Choosing the Right Format for Your LinkedIn Strategy
Selecting the ideal format for your LinkedIn strategy significantly enhances engagement and professional networking outcomes. Utilize native video content to boost visibility by up to 5 times compared to text-only posts, while carousel posts facilitate storytelling and showcase multiple facets of your expertise. Incorporate LinkedIn articles to establish thought leadership, leveraging long-form content that attracts 3 times more comments and shares than regular updates.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com