Photo illustration: Pinterest Repin vs Repost
Pinterest repins allow users to share content within the platform while maintaining the original post's source and link, enhancing content discoverability and traffic attribution. Learn more about the differences between Pinterest repins and reposts in this article.
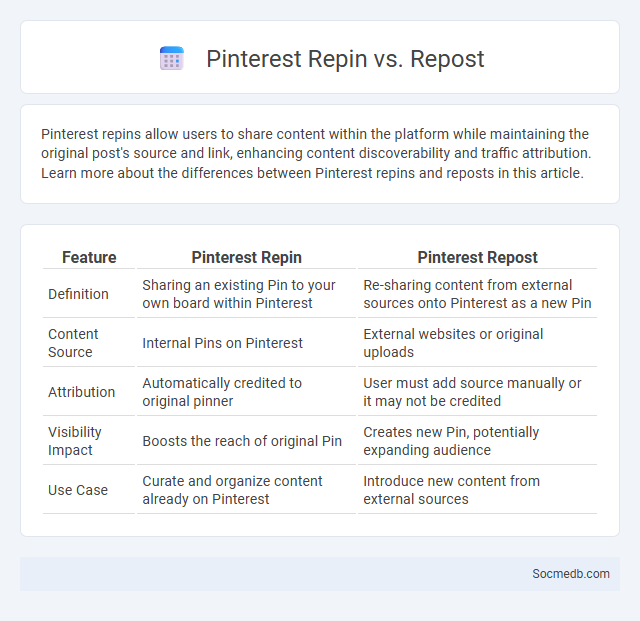
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Pinterest Repin | Pinterest Repost |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Sharing an existing Pin to your own board within Pinterest | Re-sharing content from external sources onto Pinterest as a new Pin |
| Content Source | Internal Pins on Pinterest | External websites or original uploads |
| Attribution | Automatically credited to original pinner | User must add source manually or it may not be credited |
| Visibility Impact | Boosts the reach of original Pin | Creates new Pin, potentially expanding audience |
| Use Case | Curate and organize content already on Pinterest | Introduce new content from external sources |
Understanding Pinterest: Repin, Repost, and Save Defined
Pinterest enables users to engage with content through key actions: repin, repost, and save, each serving distinct purposes for content discovery and organization. Repin allows users to share others' pins directly onto their boards, amplifying visibility within their network. Repost involves sharing content beyond Pinterest while save primarily denotes bookmarking pins for personal reference and curation.
What Is a Repin on Pinterest?
A repin on Pinterest is when you save someone else's pin to one of your own boards, effectively sharing that content with your followers. This action helps increase the visibility and reach of the original pin, making it a key metric for content engagement on the platform. Understanding how repins work can boost your social media strategy by driving more traffic and interaction to your pins.
The Concept of Repost on Pinterest
The concept of repost on Pinterest revolves around users sharing and redistributing existing pins to their own boards, effectively amplifying original content and increasing visibility across the platform. Reposting boosts engagement by allowing users to curate collections based on niches like fashion, recipes, or home decor while crediting the original creator. This practice enhances content discovery algorithms, driving more traffic and potential followers to both reposters and original posters.
Repin vs. Repost: Key Differences
Repin and repost are distinct social media actions primarily used on Pinterest and platforms like Instagram or Twitter, respectively. Repin involves saving another user's pin directly to one's own Pinterest board, preserving the original post's link and context. Repost, however, entails sharing someone else's content on your feed or story, often with attribution but sometimes without linking back to the original source, impacting content visibility and attribution differently.
The Evolution of the Pinterest Repin Feature
Pinterest revolutionized content sharing with its Repin feature, enabling users to effortlessly save and redistribute images to personalized boards, boosting visual discovery and engagement. Since its introduction, the Repin function has evolved to include enhanced categorization, improved algorithmic recommendations, and seamless integration with e-commerce platforms, allowing users to connect inspiration with actionable shopping experiences. This evolution has significantly contributed to Pinterest's identity as a powerful tool for creative expression, trendspotting, and driving traffic to original content sources.
How to Repin and Repost on Pinterest: Step-by-Step
To repin on Pinterest, find the desired pin, click the "Save" button, and select the relevant board to add it to your collection. For reposting content, download the image to your device, then upload it as a new pin, ensuring to credit the original source in your description. You can expand your reach by regularly repinning and reposting content relevant to your niche to keep your Pinterest profile active and engaging.
Best Practices for Repinning and Reposting Content
Repinning and reposting content on social media platforms like Pinterest and Instagram maximize engagement by sharing relevant, high-quality visuals that resonate with your target audience. Best practices include crediting original creators, adding personalized captions to enhance context, and maintaining consistent posting schedules to boost visibility and foster community trust. Leveraging trending hashtags and analyzing performance metrics ensures optimized reach and sustained content relevance.
Impact of Repins and Reposts on Pinterest Engagement
Repins and reposts on Pinterest significantly boost user engagement by amplifying content visibility across diverse boards and user networks. High repin rates signal valuable and relevant content to Pinterest's algorithm, improving the likelihood of content appearing in more users' feeds and search results. This increased exposure drives organic traffic and fosters community interaction, making repinning a critical metric for assessing content performance on Pinterest.
Copyright, Attribution, and Pinterest Sharing Ethics
Copyright laws protect original content shared on social media platforms, making it essential for users to respect creators' rights by avoiding unauthorized use or reproduction. Proper attribution on Pinterest involves crediting the original source or creator, enhancing transparency and respecting intellectual property. Ethical sharing on Pinterest requires obtaining permissions when necessary and refraining from misrepresenting content ownership to maintain integrity within the online community.
Choosing Between Repin and Repost: Which Is Best for You?
Choosing between Repin and Repost depends on your social media goals and platform preferences. Repinning on Pinterest boosts content visibility within niche communities, enhancing your board's engagement and follower growth. Reposting on platforms like Instagram or Twitter helps you share relevant content quickly, expanding your reach and maintaining an active presence to engage your audience effectively.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com