Photo illustration: Deactivate vs Delete
Deactivating a social media account temporarily hides your profile and content, allowing you to reactivate later, while deleting permanently removes all data with no recovery option. Discover the detailed differences and implications of deactivating versus deleting your social media accounts in this article.
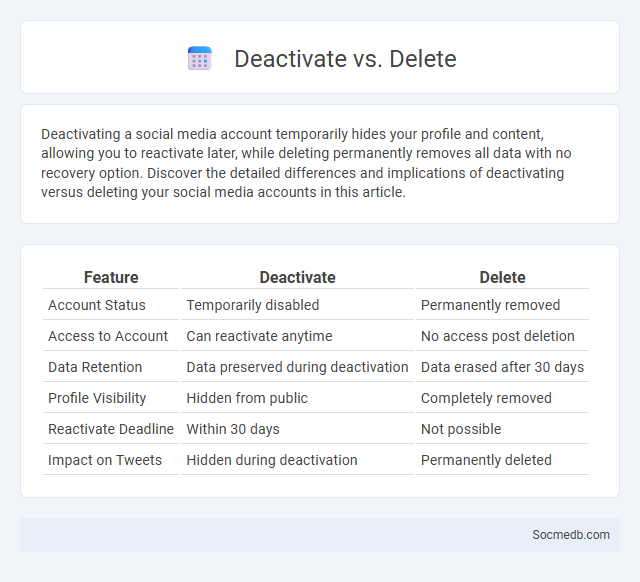
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Deactivate | Delete |
|---|---|---|
| Account Status | Temporarily disabled | Permanently removed |
| Access to Account | Can reactivate anytime | No access post deletion |
| Data Retention | Data preserved during deactivation | Data erased after 30 days |
| Profile Visibility | Hidden from public | Completely removed |
| Reactivate Deadline | Within 30 days | Not possible |
| Impact on Tweets | Hidden during deactivation | Permanently deleted |
Understanding Deactivate, Delete, and Deactivation
Understanding the differences between deactivate, delete, and deactivation on social media is essential for managing Your online presence effectively. Deactivate temporarily disables Your account, allowing you to reactivate it later without losing data, while delete permanently removes all Your information and cannot be reversed. Knowing these options helps you control privacy, data retention, and presence across platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter.
Key Differences Between Deactivate, Delete, and Deactivation
Deactivate temporarily disables your social media account, allowing you to reactivate and restore all data later. Delete permanently removes your account and all associated data, with no option for recovery. Deactivation often refers to the same temporary disabling process as deactivate, but some platforms may use the terms differently, so understanding each platform's specific policy is crucial for managing your online presence.
When Should You Deactivate an Account?
Deactivating a social media account is advisable when experiencing excessive time consumption, privacy concerns, or mental health challenges linked to online activity. Evaluating account usage patterns and the impact on personal well-being helps determine if a temporary or permanent deactivation is necessary. Users should also consider deactivation during digital detox periods or after data breaches to protect personal information.
The Process of Deleting: What Happens?
When a user deletes content on social media platforms, the data often moves to a temporary holding area where it remains recoverable for a limited period. During this retention phase, the platform's servers disassociate the content from the user's profile but maintain it for backup or legal compliance. After the retention window, the data undergoes secure deletion protocols, ensuring permanent removal from the platform's active and backup systems.
Deactivation Explained: Temporary vs Permanent Actions
Social media deactivation offers users two main options: temporary and permanent account suspension. Temporary deactivation allows users to pause their online presence, preserving data and enabling easy reactivation, while permanent deactivation results in total deletion of account data, posts, and connections, making recovery impossible. Choosing between these options depends on the user's intent to either take a short break or completely exit the platform.
Pros and Cons of Deactivating vs Deleting
Deactivating your social media account allows you to temporarily pause your online presence while preserving your data for future use, offering flexibility and privacy without permanent loss. Deleting your account results in permanent removal of all your content and connections, providing a fresh start but eliminating any chance of recovery. Both options impact your digital footprint and connectivity; you should weigh the benefits of privacy and control against the potential loss of social interactions and stored memories.
Data Retention: What Stays After Deactivation or Deletion?
When you deactivate or delete your social media account, platforms often retain certain data such as messages, shared content, and backups for varying periods depending on their privacy policies and legal requirements. Your profile may disappear from public view, but underlying information, including activity logs and metadata, can remain stored on servers. Understanding these retention practices helps you manage your digital footprint and safeguard your personal information effectively.
User Privacy: Deactivate vs Delete Outcomes
Deactivating a social media account temporarily suspends user visibility while retaining personal data for potential reactivation, preserving message history and friend connections. Deleting an account permanently removes all user data from the platform's servers, erasing posts, messages, and profile information with no recovery option. Understanding these outcomes helps users make informed decisions about controlling their digital footprint and protecting personal privacy online.
Reactivating After Deactivation: Is It Possible?
Reactivating a social media account after deactivation is generally possible within a specific timeframe set by the platform; for example, Facebook allows reactivation within 30 days, while Instagram permits it up to six months. Reactivation typically involves simply logging back in with your original credentials, which restores your profile, photos, and connections. However, permanent deletion of accounts, unlike temporary deactivation, usually cannot be reversed, emphasizing the importance of understanding platform policies before deactivation.
Choosing the Right Option: Deactivate, Delete, or Deactivation
Choosing the right option for managing your social media presence depends on your goals and needs. Deactivating your account temporarily hides your profile and content, allowing you to reactivate it later without losing data. Deleting your account permanently removes all your data and posts, making recovery impossible, so carefully consider if you want a temporary break or a complete exit from the platform.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com