Photo illustration: Troll vs Faker
Trolls deliberately provoke and disrupt conversations on social media, spreading negativity to elicit emotional responses, while fakers create false identities or misleading content to deceive and manipulate audiences. Explore this article to understand the distinct behaviors and impacts of trolls versus fakers on social platforms.
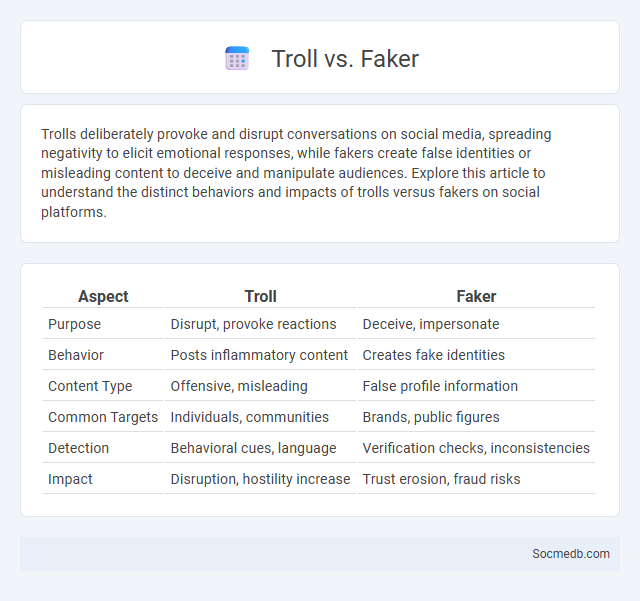
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Troll | Faker |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Disrupt, provoke reactions | Deceive, impersonate |
| Behavior | Posts inflammatory content | Creates fake identities |
| Content Type | Offensive, misleading | False profile information |
| Common Targets | Individuals, communities | Brands, public figures |
| Detection | Behavioral cues, language | Verification checks, inconsistencies |
| Impact | Disruption, hostility increase | Trust erosion, fraud risks |
Introduction: The Mythos of Troll and Faker Rivalry
The mythos of troll and faker rivalry often clouds the reality of social media dynamics, where misinformation and disruptive behavior coexist yet serve different purposes. Trolls thrive on provoking emotional reactions to derail conversations, while fakers manipulate information to deceive and influence perceptions strategically. Your ability to discern these nuances can enhance critical thinking and improve online interactions.
Origins: Defining Trolls and Fakers in Online Culture
Trolls originated as internet users who deliberately provoke or disrupt online communities by posting inflammatory or off-topic messages to elicit emotional responses. Fakers, on the other hand, create false identities or spread misinformation to manipulate opinions and deceive others in digital spaces. Both phenomena emerged in the early days of social media platforms, shaping the challenges of trust and authenticity in online culture.
Key Characteristics: What Makes a Troll vs a Faker
Trolls thrive on provoking emotional reactions by posting inflammatory or off-topic messages designed to disrupt conversations and incite conflict, often hiding behind anonymity. Fakers, on the other hand, create deceptive or misleading profiles and content to manipulate perceptions, often aiming to gain trust or spread false information. Understanding these key characteristics helps you identify and mitigate the impact of negative online behavior effectively.
Motivations: Why Trolls and Fakers Exist
Trolls and fakers thrive on social media primarily due to motivations such as seeking attention, exerting control, or disrupting online communities. Psychological factors including anonymity, lack of immediate consequences, and the desire for power or entertainment drive these behaviors. Understanding these motivations is essential for developing effective moderation strategies and fostering healthier digital environments.
Strategies Employed: Tactics of Trolls vs Fakers
Trolls often use provocative language and inflammatory comments to incite conflict and disrupt online communities, while fakers create fake profiles or spread misinformation to manipulate opinions and gain trust. Both employ psychological tactics to exploit emotional reactions, but trolls thrive on chaos and engagement, whereas fakers aim to deceive and influence targeted audiences systematically. Your awareness of these distinct methods can help you identify and avoid falling victim to their manipulative strategies on social media platforms.
Impact on Communities: Social Consequences
Social media platforms significantly shape community dynamics by facilitating faster information exchange and enhancing social connectivity across diverse groups. These digital interactions can foster a sense of belonging and collective identity, yet they also contribute to polarization and the spread of misinformation. Understanding the dual impact on social cohesion and division is crucial for developing strategies to promote positive community engagement online.
Detection and Identification: Spotting Trolls and Fakers
Advanced algorithms leverage natural language processing and behavioral analysis to detect trolls and fakers on social media platforms by identifying patterns of malicious activity and inconsistent user behavior. Machine learning models analyze metadata, posting frequency, and sentiment shifts to differentiate genuine users from automated bots or deceptive accounts. Enhanced detection tools contribute to safer online communities by mitigating the spread of misinformation and disruptive content.
Response Tactics: How to Handle Trolls vs Fakers
Handling trolls effectively requires maintaining a calm, factual tone and avoiding emotional engagement to prevent escalation. For fakers, verifying information before responding and using platform tools to report or block deceptive accounts protects your reputation. Your best response tactic combines strategic silence with proactive moderation to ensure a positive social media environment.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples of Troll vs Faker Interactions
Case studies reveal how social media platforms combat interactions between trolls and fakers using advanced algorithms and user reporting systems. One notable example includes Twitter's deployment of machine learning models that identify and suspend fake accounts spreading misinformation, improving overall community trust. By examining these scenarios, you gain insight into the dynamics of online engagement and how platforms strive to maintain authentic user experiences.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned in Managing Online Deception
Effective management of online deception requires continuous monitoring of social media algorithms to detect and counteract false information swiftly. Leveraging artificial intelligence and machine learning enhances the identification of deceptive content patterns, reducing misinformation spread. Collaboration between platform developers, cybersecurity experts, and users fosters a resilient digital environment that upholds trust and authenticity in social networks.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com