Photo illustration: Twitter Bot vs Botnet
A Twitter bot is an automated account designed to post content or interact with users, while a botnet consists of multiple bots controlled simultaneously to amplify reach or conduct coordinated activities. Explore this article to understand how Twitter bots differ from complex botnets and their impact on social media dynamics.
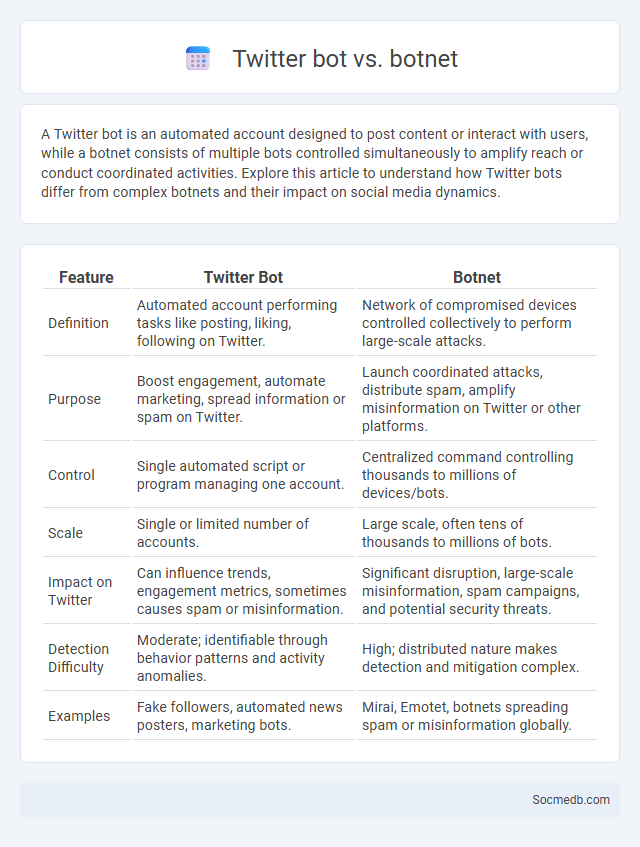
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Twitter Bot | Botnet |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated account performing tasks like posting, liking, following on Twitter. | Network of compromised devices controlled collectively to perform large-scale attacks. |
| Purpose | Boost engagement, automate marketing, spread information or spam on Twitter. | Launch coordinated attacks, distribute spam, amplify misinformation on Twitter or other platforms. |
| Control | Single automated script or program managing one account. | Centralized command controlling thousands to millions of devices/bots. |
| Scale | Single or limited number of accounts. | Large scale, often tens of thousands to millions of bots. |
| Impact on Twitter | Can influence trends, engagement metrics, sometimes causes spam or misinformation. | Significant disruption, large-scale misinformation, spam campaigns, and potential security threats. |
| Detection Difficulty | Moderate; identifiable through behavior patterns and activity anomalies. | High; distributed nature makes detection and mitigation complex. |
| Examples | Fake followers, automated news posters, marketing bots. | Mirai, Emotet, botnets spreading spam or misinformation globally. |
Defining Twitter Bots: Purpose and Functionality
Twitter bots are automated accounts programmed to perform specific tasks such as posting tweets, retweeting, liking, and following users based on predefined algorithms. Their primary purposes include enhancing user engagement, disseminating information rapidly, and executing marketing campaigns or customer service interactions. These bots operate by analyzing trends and keywords to simulate human-like behavior, influencing conversations and amplifying content across the Twitter platform.
Understanding Botnets: Architecture and Usage
Botnets consist of a network of compromised devices controlled by a central command-and-control server, enabling coordinated large-scale operations such as distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, spam campaigns, and credential theft. The architecture typically follows a hierarchical or peer-to-peer model, allowing attackers to efficiently manage and update compromised machines while evading detection. Understanding botnet infrastructure is crucial for cybersecurity professionals to develop effective mitigation strategies against social media exploitation and misinformation propagation.
What is a Bot? General Overview
A bot is an automated software application designed to perform tasks on social media platforms, such as posting content, liking posts, or following accounts. These programs often mimic human behavior to engage with users, amplify messages, or manage large volumes of interactions efficiently. Bots play a crucial role in marketing strategies, customer service, and information dissemination, but can also contribute to misinformation and spam.
Key Differences Between Bots, Botnets, and Twitter Bots
Bots are automated software programs that execute specific tasks on social media platforms, such as liking posts or sending messages. Botnets consist of interconnected bots controlled by a single entity to amplify spam, misinformation, or coordinated campaigns on sites like Twitter. Twitter bots specifically mimic human behavior on Twitter by tweeting, retweeting, and following users to influence trends or manipulate public opinion.
Common Applications of Twitter Bots
Twitter bots commonly automate customer service by responding to inquiries and providing real-time support, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction. They also play a significant role in marketing by scheduling posts, amplifying brand messages, and tracking campaign performance through analytics. Furthermore, Twitter bots facilitate news dissemination by curating and sharing timely updates, helping users stay informed on trending topics efficiently.
Malicious Intent: How Botnets Differ from Social Bots
Botnets consist of interconnected compromised devices controlled by malicious actors to execute large-scale cyberattacks, including spam distribution and data theft. Unlike social bots that simulate human behavior on social media platforms for marketing or information dissemination, botnets operate with a clear malicious intent to disrupt services or exploit users. The semantic distinction lies in botnets' coordination and purpose, emphasizing cybersecurity threats over the relatively benign or promotional roles of individual social bots.
Identifying and Detecting Bots on Twitter
Identifying and detecting bots on Twitter involves analyzing patterns such as unusually high tweet frequency, repetitive content, and network behavior that deviates from typical human users. Machine learning algorithms leverage features like account age, follower-to-following ratio, and linguistic anomalies to enhance bot detection accuracy. Advanced tools like Botometer and Twitter's internal API enable real-time monitoring and classification, aiding in the mitigation of misinformation and automated spam campaigns.
The Impact of Bots and Botnets on Social Media Ecosystems
Bots and botnets significantly distort social media ecosystems by amplifying misinformation and manipulating public opinion through automated content generation and interaction. These malicious entities inflate engagement metrics, creating artificial popularity that misleads users and undermines authentic user experiences. Their presence challenges platform algorithms designed to prioritize genuine interactions, complicating efforts to maintain trust and integrity in digital communication spaces.
Ethical and Legal Considerations of Bot Usage
Social media platforms face complex ethical and legal challenges regarding bot usage, including concerns about misinformation, data privacy, and user manipulation. Regulatory frameworks like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) impose strict guidelines on automated data collection and user consent to protect personal information. Ethical bot deployment mandates transparency, ensuring users are aware of automated interactions to maintain trust and uphold platform integrity.
Future Trends in Bot, Botnet, and Twitter Bot Technologies
Future trends in social media bot technologies emphasize the integration of advanced AI and machine learning to create more sophisticated Twitter bots capable of mimicking human interactions with higher precision and subtlety. Emerging botnets leverage decentralized blockchain frameworks to enhance resilience, evade detection, and amplify coordinated influence campaigns across multiple platforms. Innovations in detection algorithms increasingly use behavioral analytics and natural language processing to identify and mitigate the impact of these evolving automated agents on digital discourse and user engagement.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com