Photo illustration: Twitter echo chamber vs academic research
Twitter echo chambers often reinforce user biases by limiting exposure to diverse perspectives, contrasting academic research that emphasizes critical analysis and evidence-based discourse. Explore this article to understand the implications of these differences on public opinion and knowledge dissemination.
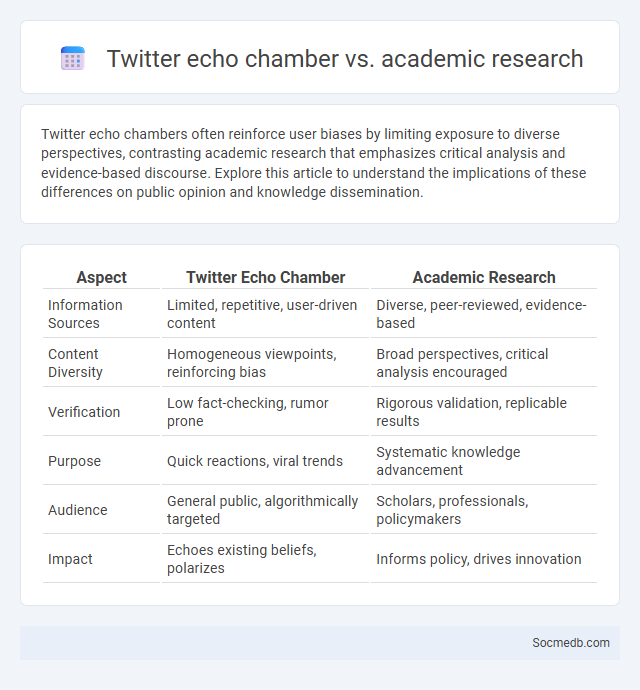
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Twitter Echo Chamber | Academic Research |
|---|---|---|
| Information Sources | Limited, repetitive, user-driven content | Diverse, peer-reviewed, evidence-based |
| Content Diversity | Homogeneous viewpoints, reinforcing bias | Broad perspectives, critical analysis encouraged |
| Verification | Low fact-checking, rumor prone | Rigorous validation, replicable results |
| Purpose | Quick reactions, viral trends | Systematic knowledge advancement |
| Audience | General public, algorithmically targeted | Scholars, professionals, policymakers |
| Impact | Echoes existing beliefs, polarizes | Informs policy, drives innovation |
Understanding the Concept of Echo Chambers
Echo chambers on social media refer to environments where users are exposed predominantly to information that reinforces their existing beliefs, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. Algorithms prioritize content similar to users' previous interactions, intensifying ideological segregation and polarization. This phenomenon impacts public discourse by creating feedback loops that hinder open, balanced discussions and critical thinking.
Twitter Echo Chambers: Mechanisms and Dynamics
Twitter echo chambers form through algorithmic curation that amplifies similar viewpoints, reinforcing users' existing beliefs by filtering out opposing perspectives. This dynamic creates polarized communities where information circulates within a closed loop, limiting exposure to diverse opinions and fostering confirmation bias. Your engagement within these echo chambers influences the spread of information, shaping public discourse and social polarization on the platform.
How Academic Research Defines and Studies Echo Chambers
Academic research defines echo chambers as environments where individuals encounter information reinforcing their existing beliefs, often through algorithmic filtering and selective exposure. Studies use network analysis, content analysis, and experimental methods to examine how social media platforms facilitate the formation and persistence of echo chambers by promoting homophily and reducing exposure to diverse viewpoints. Research highlights the impact of echo chambers on polarization, misinformation spread, and the reinforcement of cognitive biases in online communities.
Comparing Online and Offline Echo Chambers
Online echo chambers intensify your exposure to homogeneous viewpoints through algorithm-driven content tailored to reinforce personal beliefs, often amplifying misinformation and polarization. Offline echo chambers rely on physical social networks like family, friends, and local communities, which may limit diversity but tend to offer more nuanced and context-rich interactions. Comparing both, digital platforms accelerate the speed and breadth of echo chamber effects, while offline environments exert a slower, more localized influence on your worldview.
Influence of Twitter Algorithms on Echo Chamber Formation
Twitter algorithms prioritize showing users content similar to their interactions, reinforcing existing beliefs and perspectives within your feed. This selective exposure amplifies echo chamber effects, limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints and increasing polarization. Understanding how algorithmic curation shapes information flow is essential to navigating and mitigating the impact of social media echo chambers.
Academic Research: Methodologies for Studying Echo Chambers
Academic research on echo chambers employs methodologies such as network analysis, content analysis, and survey-based experiments to examine information flow and user behavior on social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook. Researchers utilize machine learning algorithms to detect homophily and polarization patterns within digital communities, quantifying the degree of ideological echoing. Experimental designs often include randomized controlled trials to assess interventions aimed at reducing algorithmic bias and promoting exposure to diverse viewpoints.
Common Myths and Facts About Echo Chambers
Echo chambers on social media are often believed to only reinforce existing beliefs, but research shows users are also exposed to diverse viewpoints through algorithmic recommendations. Contrary to the myth that echo chambers universally increase polarization, some studies indicate that selective exposure varies widely based on user behavior and platform design. Understanding these dynamics helps debunk oversimplified views and promotes more effective strategies for reducing misinformation and enhancing digital literacy.
Real-World Impacts of Echo Chambers on Public Opinion
Echo chambers on social media amplify selective information, reinforcing your existing beliefs and limiting exposure to diverse perspectives. This phenomenon distorts public opinion by creating polarized communities that resist factual correction and encourage misinformation spread. Understanding the real-world impact of echo chambers helps address societal division and promotes more informed, balanced discourse.
Twitter Echo Chamber vs Academic Perspectives: Key Differences
Twitter echo chambers often amplify homogeneous viewpoints by limiting exposure to diverse opinions, resulting in polarized communities driven by algorithms prioritizing engagement. Academic perspectives emphasize the importance of cognitive diversity and critical thinking, advocating for exposure to varied sources to mitigate confirmation bias and foster informed discourse. Research highlights that while Twitter reinforces ideological segregation, academic frameworks promote balanced knowledge acquisition through interdisciplinary dialogue and evidence-based analysis.
Future Directions in Echo Chamber Research and Social Media Policy
Future directions in echo chamber research emphasize analyzing algorithmic personalization and user behavior patterns to understand how misinformation and ideological segregation intensify. Social media policy must prioritize transparency in content curation algorithms, enforce stricter regulations on misinformation, and enhance digital literacy to mitigate echo chamber effects. Your engagement with platforms that adopt these policies can foster a more diverse and informed online environment.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com