Photo illustration: WhatsApp Web vs WhatsApp Desktop
WhatsApp Web offers convenient browser-based messaging accessible from any device, while WhatsApp Desktop provides a dedicated application with enhanced performance and offline capabilities. Discover the key differences and decide the best option for your communication needs in this article.
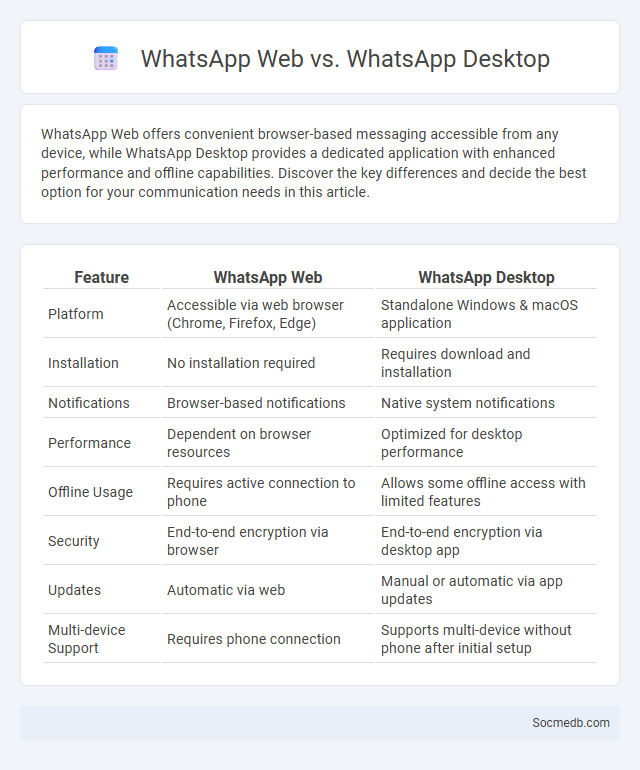
Table of Comparison
| Feature | WhatsApp Web | WhatsApp Desktop |
|---|---|---|
| Platform | Accessible via web browser (Chrome, Firefox, Edge) | Standalone Windows & macOS application |
| Installation | No installation required | Requires download and installation |
| Notifications | Browser-based notifications | Native system notifications |
| Performance | Dependent on browser resources | Optimized for desktop performance |
| Offline Usage | Requires active connection to phone | Allows some offline access with limited features |
| Security | End-to-end encryption via browser | End-to-end encryption via desktop app |
| Updates | Automatic via web | Manual or automatic via app updates |
| Multi-device Support | Requires phone connection | Supports multi-device without phone after initial setup |
Overview of WhatsApp Web, Desktop, and Linked Devices
WhatsApp Web and Desktop provide seamless synchronization with your smartphone, enabling users to send messages, share media, and manage chats directly from a computer without needing to unlock their phone. Linked Devices feature allows connection of up to four non-phone devices simultaneously while maintaining end-to-end encryption, ensuring secure communication across platforms. This integration enhances user convenience by offering a versatile, multi-device messaging experience that is consistent and reliable.
Key Features Comparison
Social media platforms differ primarily in content format, audience interaction, and algorithm design, with Instagram emphasizing visual content and Stories, Twitter focusing on real-time text updates and trending topics, and LinkedIn targeting professional networking with detailed profiles and endorsements. User engagement metrics vary, with Facebook offering diverse media sharing and community groups, while TikTok leverages short-form video and AI-driven content discovery for viral potential. Privacy controls and advertising options are also distinct, as Snapchat provides ephemeral messaging, and Pinterest centers on idea curation through pins and boards, catering to specific user intents and behaviors.
Device Compatibility and Requirements
Your social media experience depends heavily on device compatibility and technical requirements, including operating systems like iOS, Android, and Windows. Ensuring your smartphone, tablet, or computer supports the latest app versions, along with adequate RAM and internet speed, enhances performance and accessibility. Many platforms also require updated browser versions and specific screen resolutions to display content optimally.
Installation and Setup Process
Installing and setting up social media platforms involves downloading the official app from trusted sources like Google Play Store or Apple App Store, followed by creating a user account with a valid email or phone number. Verification processes, such as two-factor authentication and profile personalization, enhance security and user engagement. Optimizing privacy settings and connecting with contacts streamlines the onboarding experience and ensures a tailored social networking environment.
User Interface Differences
Social media platforms vary significantly in user interface designs, influencing how users interact with content and navigate features. You will notice differences in layout structure, such as feed orientation, menu placement, and content prioritization, impacting usability and engagement. Understanding these UI distinctions helps optimize your social media experience for efficiency and personalized interaction.
Performance and Speed Analysis
Social media platforms rely heavily on performance and speed analysis to ensure seamless user experiences and real-time content delivery. Your ability to track key metrics like load times, server response rates, and data throughput directly impacts engagement and retention. Optimizing these parameters enhances platform scalability and supports high-volume interactions without compromising quality.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Social media platforms collect vast amounts of personal data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks and data breaches that compromise user privacy. Implementing robust encryption protocols, multi-factor authentication, and regular security audits are critical to safeguarding sensitive information. Users must remain vigilant by managing privacy settings, avoiding suspicious links, and understanding platform data-sharing policies to minimize risks associated with social media use.
Notification Management
Effective notification management on social media platforms enhances your digital wellbeing by reducing distractions and improving focus. Customizing alert settings allows you to prioritize important messages and updates from key contacts or groups, minimizing unimportant interruptions. Leveraging features like "Do Not Disturb" modes and notification batching helps maintain productivity while staying connected to relevant social interactions.
File Sharing Capabilities
Social media platforms enhance collaboration through advanced file sharing capabilities, enabling users to upload, share, and access various file formats seamlessly. Features like cloud integration, real-time editing, and secure file transfer improve productivity and streamline communication across networks. High-capacity storage and cross-platform compatibility facilitate efficient distribution of multimedia content among global user bases.
Pros, Cons, and Best Use Cases
Social media platforms offer unparalleled connectivity, enabling individuals and businesses to engage with global audiences, promote brands, and foster community building effectively. However, challenges include privacy concerns, misinformation spread, and potential negative impacts on mental health due to excessive use. Best use cases involve targeted marketing campaigns, real-time customer service interactions, and social activism, where timely information dissemination and audience engagement are critical.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com