Photo illustration: Deepfake vs Face Swap
Deepfake technology uses AI to create highly realistic fake videos by manipulating faces and voices, while face swap simply replaces one face with another in images or videos without altering expressions or speech. Explore this article to understand the differences, risks, and detection methods of deepfake versus face swap technologies.
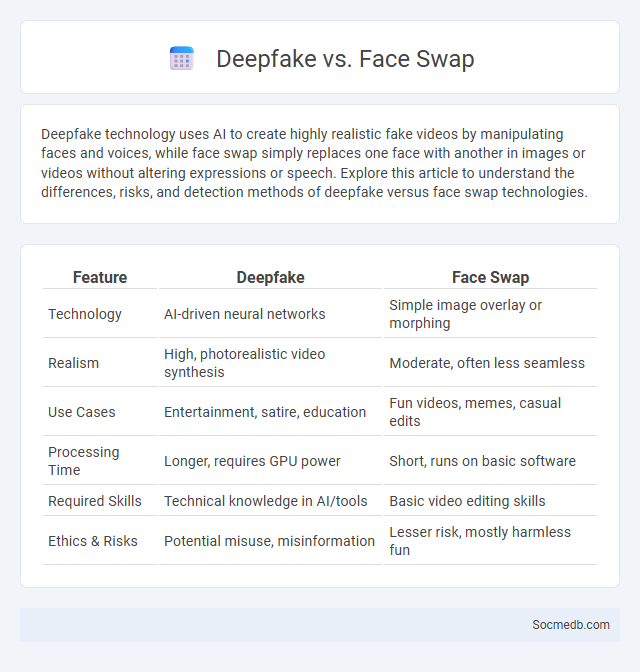
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Deepfake | Face Swap |
|---|---|---|
| Technology | AI-driven neural networks | Simple image overlay or morphing |
| Realism | High, photorealistic video synthesis | Moderate, often less seamless |
| Use Cases | Entertainment, satire, education | Fun videos, memes, casual edits |
| Processing Time | Longer, requires GPU power | Short, runs on basic software |
| Required Skills | Technical knowledge in AI/tools | Basic video editing skills |
| Ethics & Risks | Potential misuse, misinformation | Lesser risk, mostly harmless fun |
Understanding Deepfake Technology
Deepfake technology leverages artificial intelligence algorithms, particularly deep learning and neural networks, to create hyper-realistic synthetic videos and images that manipulate reality by replacing or altering faces and voices convincingly. The proliferation of deepfakes on social media platforms poses significant risks including misinformation, identity theft, and erosion of trust in digital content, necessitating advanced detection tools powered by machine learning and forensic analysis. Awareness and understanding of deepfake technology are critical for users, content moderators, and policymakers to implement effective countermeasures and maintain the integrity of online information ecosystems.
What is Face Swap?
Face swap is a digital technique that replaces one person's face with another in images or videos, using artificial intelligence and deep learning algorithms. This technology leverages facial recognition and mapping to seamlessly merge features, creating realistic or humorous content often used in social media apps like Snapchat and Instagram. Face swap enhances user engagement by allowing creative expression and entertainment through instant transformation of faces.
Key Differences: Deepfake vs Face Swap
Deepfake technology uses artificial intelligence and machine learning to create highly realistic videos or images by manipulating facial expressions and movements, making it difficult to distinguish fabricated content from genuine media. Face swap involves exchanging faces between two images or videos, typically using simpler algorithms, resulting in less convincing and often more easily identifiable altered visuals. While deepfakes pose significant risks for misinformation and privacy invasion due to their sophistication, face swaps are commonly used for entertainment and social media filters with minimal malicious intent.
How Deepfakes are Created
Deepfakes are created using advanced artificial intelligence techniques such as deep learning and neural networks that analyze and manipulate video and audio data to produce hyper-realistic synthetic content. These algorithms require large datasets of images, voice samples, or videos of the target individual to generate seamless face swaps or voice impersonations. Understanding how deepfakes are crafted can help you recognize manipulated social media content and protect your digital identity.
Face Swap Techniques Explained
Face swap techniques utilize deep learning algorithms and convolutional neural networks to seamlessly replace one person's face with another in images or videos. These methods rely on facial landmark detection, texture mapping, and generative adversarial networks (GANs) to ensure realistic blending and preservation of facial expressions. Advances in AI-driven face swapping enable applications in entertainment, augmented reality, and privacy-focused content creation while raising important ethical considerations.
Real-World Applications of Deepfakes
Deepfake technology transforms social media content by enabling hyper-realistic video and audio manipulation, impacting areas such as viral marketing, political campaigns, and entertainment. You can leverage deepfakes to create compelling storytelling and personalized advertising that captivate audiences with unprecedented authenticity. However, ethical considerations and detection tools remain crucial to prevent misinformation and protect digital trust.
Common Uses of Face Swap Tools
Face swap tools are commonly used on social media platforms for entertainment, allowing users to create humorous or surprising images by swapping faces between people or celebrities. These tools also enhance content creation by enabling influencers and marketers to produce engaging visuals that attract audience attention. Privacy concerns arise as these tools can be misused for creating deepfakes or misleading content, prompting social media sites to implement stricter regulations.
Security Risks: Deepfake vs Face Swap
Social media platforms face increasing security risks from deepfake technology, which uses AI to create highly realistic but fabricated videos, posing threats to personal identity and misinformation. Face swap applications, while often seen as harmless entertainment, can also be exploited to manipulate images and deceive viewers, compromising your privacy and trustworthiness online. Protecting your digital identity requires awareness of these evolving threats and cautious sharing of biometric data on social networks.
Ethical Implications and Misinformation
Social media platforms often struggle with the ethical implications of spreading misinformation, which can distort public opinion and harm societal trust. Algorithms prioritize engagement, sometimes amplifying false or misleading content that affects your ability to discern accurate information. Promoting transparency, fact-checking, and digital literacy is essential to mitigate these risks and foster a responsible online environment.
Future Trends in Deepfake and Face Swap Technology
Deepfake and face swap technology are rapidly evolving, with future trends pointing toward enhanced realism driven by advancements in AI deep learning models and generative adversarial networks (GANs). Emerging tools will enable seamless and highly accurate manipulation of facial expressions, voice synthesis, and identity mimicry, posing significant challenges for authentication and privacy on social media platforms. Innovations in detection algorithms and blockchain-based verification systems are anticipated to combat misinformation and secure user-generated content against malicious deepfakes.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com