Photo illustration: Deepfake vs Synthetic Media
Deepfake technology uses AI to create hyper-realistic but manipulated videos or images, while synthetic media encompasses a broader range of AI-generated content including text, audio, and animations. Explore this article to understand the differences, risks, and future implications of deepfake and synthetic media on social platforms.
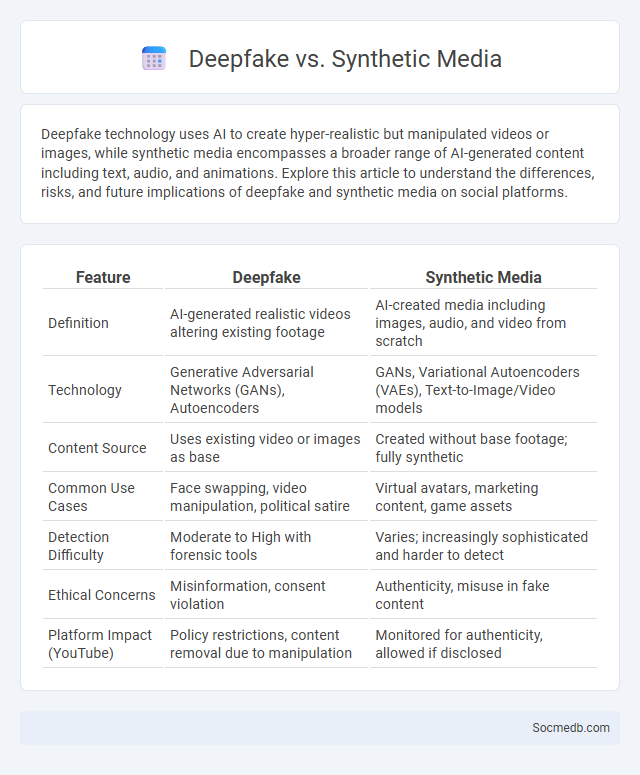
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Deepfake | Synthetic Media |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | AI-generated realistic videos altering existing footage | AI-created media including images, audio, and video from scratch |
| Technology | Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Autoencoders | GANs, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), Text-to-Image/Video models |
| Content Source | Uses existing video or images as base | Created without base footage; fully synthetic |
| Common Use Cases | Face swapping, video manipulation, political satire | Virtual avatars, marketing content, game assets |
| Detection Difficulty | Moderate to High with forensic tools | Varies; increasingly sophisticated and harder to detect |
| Ethical Concerns | Misinformation, consent violation | Authenticity, misuse in fake content |
| Platform Impact (YouTube) | Policy restrictions, content removal due to manipulation | Monitored for authenticity, allowed if disclosed |
Understanding Deepfake: Definition and Evolution
Deepfake technology involves using artificial intelligence to create highly realistic but fabricated videos or images, often depicting people saying or doing things they never did. Originating from advances in machine learning and neural networks, deepfakes have evolved from simple face-swapping apps to sophisticated tools capable of generating convincing synthetic media. The rise of deepfakes poses significant challenges for information authenticity, privacy, and security across social media platforms.
What is Synthetic Media? Key Concepts
Synthetic media refers to content generated or manipulated using artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies, including deepfake videos, AI-generated images, and text. Key concepts include GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), which create realistic but artificial media, and ethical concerns surrounding misinformation, authenticity, and digital trust. Your understanding of synthetic media is crucial for navigating social media platforms where this technology increasingly influences content creation and consumption.
Deepfake vs Synthetic Media: Core Differences
Deepfake technology utilizes AI-generated deep learning algorithms to manipulate existing videos or audio, creating hyper-realistic but altered representations of real people. Synthetic media, a broader category, includes AI-created content such as fully generated images, videos, text, or audio that do not rely on original source material but are generated from scratch. The primary distinction lies in deepfakes modifying real content to deceive, while synthetic media produces entirely new content, often employed for marketing, entertainment, or digital avatars.
Technology Behind Deepfakes
Deepfakes leverage advanced machine learning techniques, primarily Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), to create hyper-realistic, synthetic videos and images by analyzing vast datasets of facial expressions and movements. This technology uses powerful algorithms to manipulate visual and auditory content, making it increasingly challenging to distinguish real from fake on social media platforms. Understanding the technology behind deepfakes helps you recognize their potential impact on information authenticity and cybersecurity.
Applications of Synthetic Media in Various Industries
Synthetic media transformation in marketing leverages AI-generated visuals and personalized content to boost consumer engagement and brand loyalty. In entertainment, virtual influencers and deepfake technology enhance storytelling and create immersive experiences, revolutionizing content production. The social media industry harnesses synthetically generated avatars and audio to enable innovative user interactions and streamline content moderation.
Ethical Implications: Deepfake and Synthetic Media
Deepfake and synthetic media pose significant ethical challenges by enabling the creation of highly realistic yet fabricated content that can manipulate public opinion, deceive audiences, and distort reality. The proliferation of deepfake technology on social media platforms undermines trust in digital communications and raises concerns about misinformation, privacy violations, and malicious impersonation. Addressing these issues requires robust detection algorithms, transparent content labeling, and stringent regulatory frameworks to preserve authenticity and protect users from harm.
Detecting Deepfakes: Tools and Techniques
Detecting deepfakes on social media involves advanced tools like AI-based facial recognition and forensic analysis algorithms that identify inconsistencies in video frames and audio signals. Techniques such as blockchain verification, metadata analysis, and machine learning models analyze patterns that distinguish manipulated content from authentic media. Continuous improvements in neural network detection and real-time monitoring platforms enhance platforms' abilities to combat misinformation and maintain content integrity.
Legal Perspectives: Navigating Synthetic Content
Navigating synthetic content on social media requires understanding complex legal frameworks governing intellectual property, privacy rights, and misinformation. Your responsibility includes complying with regulations like the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) to avoid legal pitfalls. Courts increasingly address liability issues linked to AI-generated posts, making legal awareness crucial for creators and platforms alike.
The Future of Deepfake and Synthetic Media
The future of deepfake and synthetic media is rapidly transforming digital communication, enabling hyper-realistic content generation that challenges traditional notions of authenticity. Advances in AI-driven algorithms will empower creators to produce personalized and immersive experiences, while simultaneously raising critical issues around misinformation and digital trust. You must stay informed and adopt robust verification tools to navigate this evolving landscape securely.
Protecting Yourself From Manipulated Media
Protecting yourself from manipulated media on social media platforms involves verifying the authenticity of images, videos, and news through reputable fact-checking websites and reverse image searches. Awareness of common manipulation techniques such as deepfakes, photo editing, and misleading captions enhances critical consumption of content. Utilizing browser extensions and app features designed to flag altered media supports a safer online experience by reducing exposure to disinformation.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com