Photo illustration: Fair Use vs Excerpt
Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes like commentary, criticism, or education, while an excerpt is a specific portion of content used to highlight key points. Discover detailed guidelines and examples to navigate Fair Use and excerpting on social media in this article.
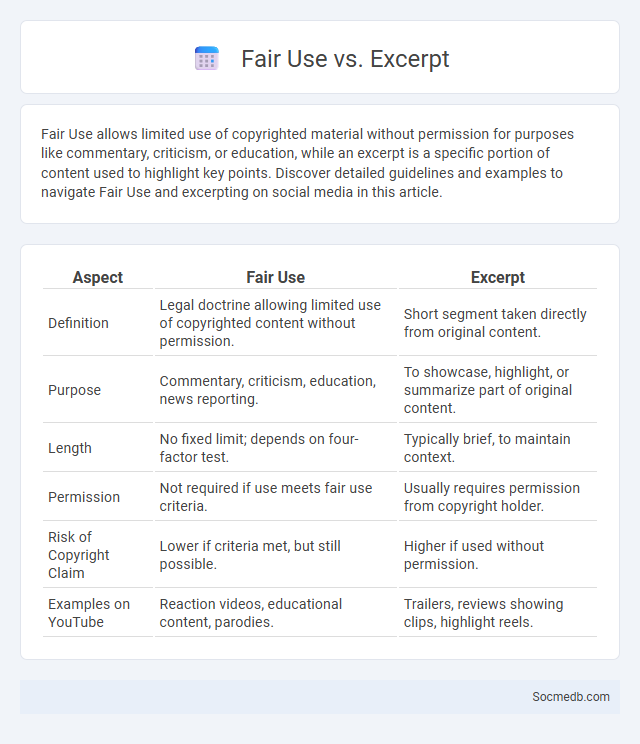
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Use | Excerpt |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal doctrine allowing limited use of copyrighted content without permission. | Short segment taken directly from original content. |
| Purpose | Commentary, criticism, education, news reporting. | To showcase, highlight, or summarize part of original content. |
| Length | No fixed limit; depends on four-factor test. | Typically brief, to maintain context. |
| Permission | Not required if use meets fair use criteria. | Usually requires permission from copyright holder. |
| Risk of Copyright Claim | Lower if criteria met, but still possible. | Higher if used without permission. |
| Examples on YouTube | Reaction videos, educational content, parodies. | Trailers, reviews showing clips, highlight reels. |
Understanding Fair Use: Definition and Principles
Fair use is a legal doctrine that permits limited use of copyrighted material without permission, essential for fostering creativity and free expression on social media platforms. Understanding its principles--purpose, nature, amount, and effect on market value--helps you navigate content sharing responsibly while respecting intellectual property rights. Mastering fair use empowers your social media strategy by balancing originality with compliance and avoiding copyright infringement.
What is an Excerpt? Legal Boundaries and Usage
An excerpt is a selected portion of a social media post, video, or article used to highlight key information while respecting copyright laws. Legal boundaries require fair use consideration, limiting excerpts to brief, transformative segments that do not diminish the original work's market value. Proper attribution is essential to avoid infringement claims and maintain ethical use on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Key Differences Between Fair Use and Excerpts
Fair use in social media allows limited use of copyrighted content without permission for purposes such as commentary, criticism, or parody, emphasizing factors like purpose, nature, amount used, and market impact. Excerpts involve selecting brief passages or segments from a work, often used to highlight or support your post but still require careful consideration of copyright restrictions. Understanding these distinctions helps you legally share content while respecting intellectual property rights and avoiding infringement.
Typical Scenarios Where Fair Use Applies
Typical scenarios where fair use applies in social media include commentary, criticism, and parody, allowing users to share and discuss content without infringement. Educational posts, news reporting, and transformative uses that add new meaning or message to the original material also fall under fair use protections. Understanding these contexts helps you navigate copyright issues while engaging creatively and legally on various platforms.
How Excerpts are Treated in Copyright Law
Excerpts from social media content are protected under copyright law as original works, meaning unauthorized use can constitute infringement. You must obtain permission or ensure your use meets fair use criteria, such as commentary, criticism, or education, to legally share or reproduce snippets from posts. Proper attribution and respecting platform-specific terms also play a crucial role in avoiding legal issues with social media excerpts.
Factors Determining Fair Use Eligibility
Fair use eligibility on social media platforms depends primarily on the purpose and character of the use, including whether it is for commercial or nonprofit educational purposes. The nature of the copyrighted work, the amount and substantiality of the portion used, and the effect of the use on the potential market for the original work are critical factors. Courts often consider how transformative the content is, such as adding new expression or meaning, which can weigh in favor of fair use status.
Excerpt Length: How Much is Too Much?
Excerpt length on social media should balance between capturing attention and maintaining reader interest, with studies suggesting optimal lengths of 40 to 80 words for maximum engagement. Excessively long excerpts can overwhelm users, leading to decreased interaction and higher bounce rates. Concise excerpts that highlight key points increase readability and encourage clicks, enhancing overall content performance on platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and Instagram.
Common Misconceptions: Fair Use vs Excerpt
Many users confuse fair use with simply excerpting content from social media posts without permission, but fair use is a legal doctrine that requires specific criteria such as purpose, nature, amount, and market effect to be met. Sharing brief excerpts alone does not guarantee protection under fair use and may still lead to copyright infringement claims. Understanding these nuances helps You respect content creators' rights and avoid legal risks on social media platforms.
Legal Risks of Misusing Fair Use or Excerpts
Misusing fair use or excerpts on social media can expose you to significant legal risks, including copyright infringement claims and costly lawsuits. Platforms may remove your content, suspend your accounts, or impose penalties if you fail to properly attribute or exceed permissible use boundaries. Understanding fair use doctrines and obtaining necessary permissions helps protect your rights and maintain compliance with intellectual property laws.
Best Practices for Content Creators: Staying Compliant
Content creators must adhere to platform-specific guidelines and legal regulations such as copyright laws and advertising disclosures to maintain compliance on social media. Regularly updating knowledge on data privacy policies and community standards ensures content remains within acceptable limits and avoids penalties. Utilizing tools for content scheduling, monitoring engagement metrics, and authenticating user-generated content helps sustain transparency and promote trustworthiness.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com