Photo illustration: Fair Use vs Permission
Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted content on social media without permission for purposes like commentary, criticism, or education, while permission requires explicit consent from the rights holder for broader or commercial use. Discover how to navigate the complexities of Fair Use versus Permission effectively in this article.
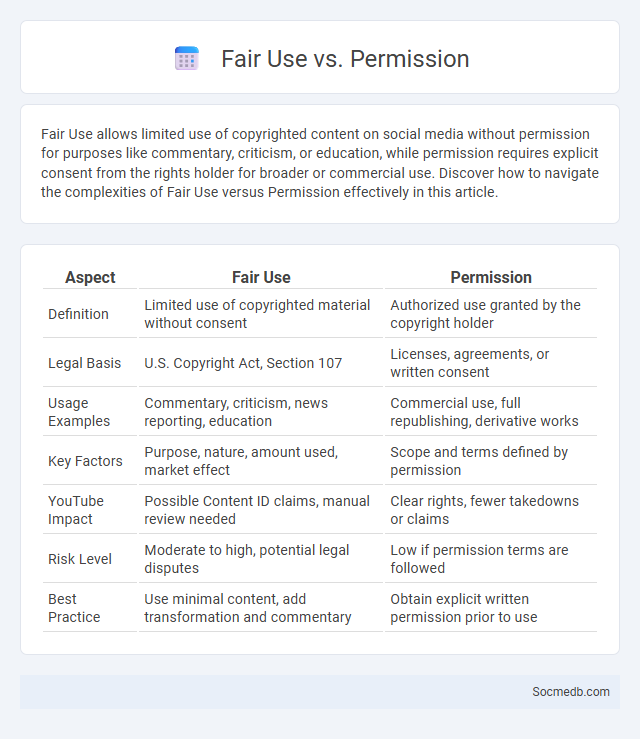
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Use | Permission |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Limited use of copyrighted material without consent | Authorized use granted by the copyright holder |
| Legal Basis | U.S. Copyright Act, Section 107 | Licenses, agreements, or written consent |
| Usage Examples | Commentary, criticism, news reporting, education | Commercial use, full republishing, derivative works |
| Key Factors | Purpose, nature, amount used, market effect | Scope and terms defined by permission |
| YouTube Impact | Possible Content ID claims, manual review needed | Clear rights, fewer takedowns or claims |
| Risk Level | Moderate to high, potential legal disputes | Low if permission terms are followed |
| Best Practice | Use minimal content, add transformation and commentary | Obtain explicit written permission prior to use |
Understanding Fair Use: Definition and Principles
Fair use allows limited use of copyrighted content without permission, primarily for purposes such as commentary, criticism, news reporting, education, and parody. Your content decisions should align with the four key principles: purpose and character of use, nature of the copyrighted work, amount used, and effect on the market value. Understanding these factors helps you navigate social media responsibly while protecting intellectual property rights.
What is Permission? Legal Requirements Explained
Permission in social media refers to obtaining explicit consent from users before collecting, using, or sharing their personal data, ensuring compliance with legal frameworks such as the GDPR and CCPA. Your social media strategy must incorporate clear consent mechanisms and transparent privacy policies to avoid legal penalties and build trust with your audience. Failure to secure proper permission can lead to data breaches, fines, and reputational damage under strict regulatory requirements.
Fair Use vs Permission: Key Differences
Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted content without permission for purposes like criticism, comment, or education, while Permission requires explicit consent from the content owner. Social media users must distinguish between transformative uses under Fair Use and uses needing license agreements to avoid infringement. Understanding these distinctions helps creators legally share content and maintain compliance with copyright laws.
The Four Factors of Fair Use
Social media content often falls under the Four Factors of Fair Use: purpose and character, nature of the copyrighted work, amount used, and effect on the market value. Transformative use, such as commentary or criticism, increases the likelihood of fair use protection on platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Twitter. Analyzing how much copyrighted content is used and its impact on the original creator's market is crucial for legal compliance in social media sharing.
When Do You Need Permission Instead of Relying on Fair Use?
Permission is required when using copyrighted content on social media that falls outside the scope of fair use, such as reproducing entire works, commercial use, or content not significantly transformed. Posting copyrighted images, videos, or music without proper authorization risks infringement claims and potential legal consequences. Fair use typically applies to limited, transformative uses like commentary, criticism, or educational purposes, but obtaining explicit permission is essential for broader or commercial applications.
Common Misconceptions About Fair Use
Common misconceptions about fair use on social media often include the belief that any content posted publicly is free to use or that credit alone grants permission for reuse. Fair use depends on factors like purpose, nature, amount used, and market effect, which means You cannot assume permission based solely on public availability. Understanding these nuances protects Your content rights and helps avoid potential copyright infringement issues.
Real-World Examples: Fair Use vs Permission
Fair use in social media allows creators to share copyrighted content like short video clips or images for commentary, criticism, or parody without explicit permission, exemplified by YouTubers reviewing movies or memes referencing popular TV shows. In contrast, obtaining permission is necessary for commercial use or when sharing substantial portions of content, as seen in brands licensing music tracks or influencers collaborating with photographers for original photos. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok enforce copyright policies balancing fair use protections with rights holders' demands, influencing content creators' strategies and legal compliance.
Risks of Misusing Fair Use or Skipping Permission
Misusing fair use or skipping permission on social media can lead to legal consequences such as copyright infringement claims and costly lawsuits. Unauthorized use of copyrighted content undermines creators' rights and damages brand reputation, resulting in account suspensions or content removal. Social media platforms employ automated detection systems that may flag or block content even if fair use is claimed, increasing risks for users who bypass proper permissions.
Best Practices for Content Creators
Content creators should prioritize authentic engagement by consistently delivering high-quality, relevant content tailored to their target audience's interests and platform algorithms. Utilizing data analytics tools helps optimize posting schedules and content formats, increasing visibility and interaction rates. Incorporating multimedia elements such as videos, infographics, and interactive stories enhances user experience and drives higher retention across major social media platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube.
Summary: Navigating Copyright with Fair Use and Permission
Navigating copyright on social media requires understanding fair use guidelines, which allow limited use of copyrighted material for commentary, criticism, or educational purposes. Securing permission from content creators ensures your posts avoid legal issues and respect intellectual property rights. Protecting your online presence means balancing creative expression with compliance to copyright laws.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com