Photo illustration: Fair Use vs Public Domain
Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted material for purposes like criticism or education without permission, while Public Domain includes works no longer under copyright protection and freely available for use. Explore this article to understand key distinctions and legal implications of Fair Use versus Public Domain in social media content.
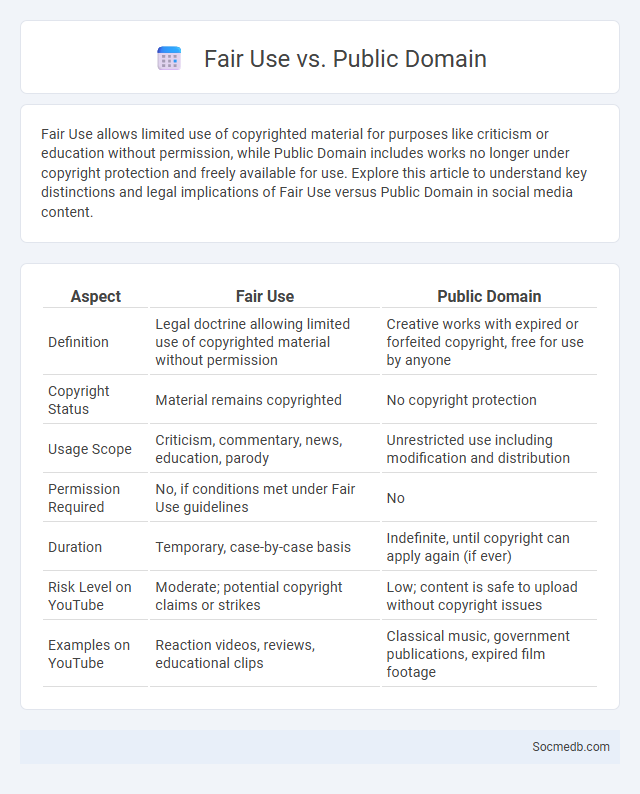
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Fair Use | Public Domain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Legal doctrine allowing limited use of copyrighted material without permission | Creative works with expired or forfeited copyright, free for use by anyone |
| Copyright Status | Material remains copyrighted | No copyright protection |
| Usage Scope | Criticism, commentary, news, education, parody | Unrestricted use including modification and distribution |
| Permission Required | No, if conditions met under Fair Use guidelines | No |
| Duration | Temporary, case-by-case basis | Indefinite, until copyright can apply again (if ever) |
| Risk Level on YouTube | Moderate; potential copyright claims or strikes | Low; content is safe to upload without copyright issues |
| Examples on YouTube | Reaction videos, reviews, educational clips | Classical music, government publications, expired film footage |
Understanding Fair Use: Key Concepts
Understanding Fair Use is crucial for navigating copyright issues on social media, as it allows limited use of copyrighted content without permission under specific conditions. Key concepts include the purpose of use, the nature of the copyrighted work, the amount used, and the effect on the market value. You should evaluate these factors carefully to ensure your content complies with fair use guidelines while engaging your audience effectively.
Defining the Public Domain
The public domain encompasses creative works and information not protected by intellectual property laws, making them freely accessible for use and distribution on social media platforms. Understanding the boundaries of public domain content on social media is essential for ensuring legal sharing, remixing, and repurposing of images, videos, and texts without infringement risks. Clear knowledge of public domain definitions facilitates user compliance and promotes open cultural exchange within social networking environments.
Fair Use vs Public Domain: Core Differences
Fair Use allows limited use of copyrighted content without permission for purposes like criticism, comment, news reporting, or education, while Public Domain refers to creative works free from copyright restrictions, available for unrestricted use. Social media users must navigate these distinctions to avoid infringement, as Fair Use is evaluated case-by-case based on factors like purpose and effect on market value, whereas Public Domain content can be freely shared and modified. Understanding these core differences helps content creators ensure legal and ethical sharing of multimedia on platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and TikTok.
Legal Foundations of Fair Use
The legal foundations of fair use in social media stem from Section 107 of the U.S. Copyright Act, which allows limited use of copyrighted material without permission for purposes such as commentary, criticism, news reporting, and educational use. Courts evaluate fair use based on four key factors: the purpose and character of the use, the nature of the copyrighted work, the amount used, and the effect on the market value of the original work. Social media platforms must navigate these principles carefully to avoid copyright infringement while promoting user-generated content and freedom of expression.
Criteria for Identifying Public Domain Works
Public domain works on social media are identified based on factors like expiration of copyright, release by the author, or absence of original authorship. You can use tools like Creative Commons licenses or government databases to verify these criteria. Ensuring the content meets public domain standards protects your usage rights and avoids infringement issues.
Common Myths About Fair Use
Common myths about fair use on social media often lead to misunderstandings about content sharing rights and copyright laws. Many believe that simply crediting the original creator or using content for non-commercial purposes automatically qualifies as fair use, which is not always true. You must evaluate factors such as purpose, nature, amount used, and market effect to determine if your content use is legally protected.
Benefits and Limitations of Public Domain
Public domain content on social media offers you a vast array of resources that can be freely used, shared, and adapted without copyright restrictions, enhancing creativity and collaboration. This accessibility promotes educational growth, unrestricted marketing opportunities, and cultural preservation across platforms. However, the limitations include potential misuse or misattribution, lack of quality control, and challenges in verifying authenticity, which can affect trustworthiness and legal security in content sharing.
Types of Works Protected by Fair Use
Fair use protects various types of works on social media, including user-generated content, commentary, and criticism that provide transformative value. Your posts or videos that add new expression or meaning to original works, such as memes or reaction videos, often qualify under fair use. Copyright laws safeguard creators' rights while allowing limited use for educational, commentary, or parody purposes without explicit permission.
How to Determine if a Work is in the Public Domain
Determining if a work is in the public domain involves checking the copyright expiration date, which varies depending on when and where the work was created, typically 70 years after the author's death in many countries. You can also verify the publication date and whether the copyright was renewed, especially for works published before 1978 in the United States. Your best approach includes consulting official databases like the U.S. Copyright Office or trusted public domain resources to ensure the work is free from copyright restrictions before sharing on social media.
Best Practices for Using Fair Use and Public Domain Content
To effectively leverage social media while respecting intellectual property, users should prioritize sourcing content from verified public domain repositories and apply fair use principles by using minimal, transformative portions of copyrighted works for commentary, critique, or educational purposes. Proper attribution and understanding platform-specific guidelines ensure compliance and minimize the risk of content removal or legal issues. Employing tools like rights clearance platforms and maintaining documentation of fair use rationale further strengthens responsible content sharing practices.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com