Photo illustration: Facebook Social Graph vs Social Graph
Facebook Social Graph maps detailed user connections and interactions within the Facebook platform, enabling personalized content and targeted advertising. Learn more about how Facebook Social Graph enhances online social networking in this article.
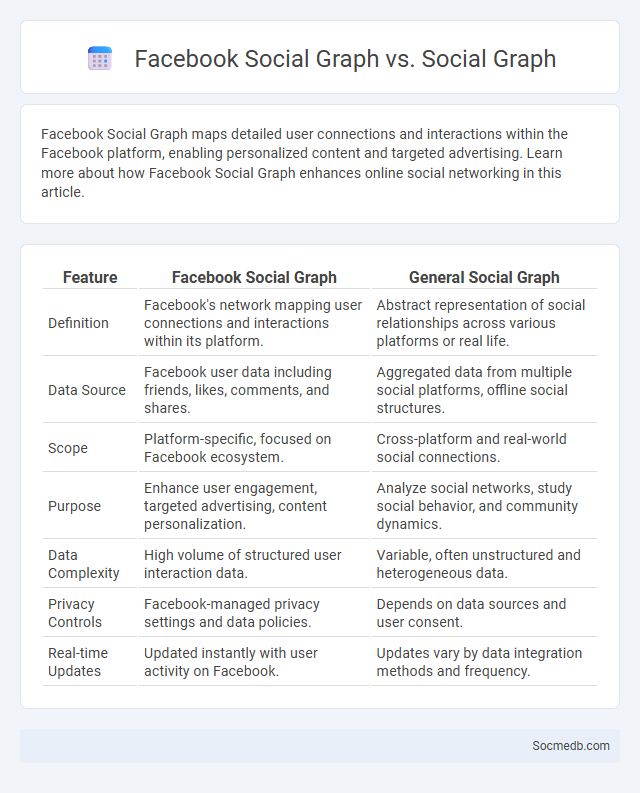
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Facebook Social Graph | General Social Graph |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Facebook's network mapping user connections and interactions within its platform. | Abstract representation of social relationships across various platforms or real life. |
| Data Source | Facebook user data including friends, likes, comments, and shares. | Aggregated data from multiple social platforms, offline social structures. |
| Scope | Platform-specific, focused on Facebook ecosystem. | Cross-platform and real-world social connections. |
| Purpose | Enhance user engagement, targeted advertising, content personalization. | Analyze social networks, study social behavior, and community dynamics. |
| Data Complexity | High volume of structured user interaction data. | Variable, often unstructured and heterogeneous data. |
| Privacy Controls | Facebook-managed privacy settings and data policies. | Depends on data sources and user consent. |
| Real-time Updates | Updated instantly with user activity on Facebook. | Updates vary by data integration methods and frequency. |
Introduction to Social Graphs
Social graphs represent the interconnected relationships between individuals on social media platforms, visualizing how users interact and share information. These graphs map connections such as friendships, follows, and group memberships, providing insights into community structures and influence patterns. Understanding social graphs enables businesses to optimize marketing strategies by targeting key nodes with high engagement potential.
Understanding the Facebook Social Graph
The Facebook Social Graph represents the interconnected network of users, their relationships, and shared content, enabling personalized experiences and targeted advertising. By analyzing data points such as friendships, likes, comments, and shared interests, algorithms can predict user behavior and deliver relevant content. Understanding this graph is essential for marketers aiming to optimize engagement and build community-driven campaigns on the platform.
Defining the Generic Social Graph
The generic social graph represents the network of social relationships and interactions among users on social media platforms, encompassing connections such as friendships, followers, and group memberships. It models the complex web of associations, mapping how individuals, brands, and content are interconnected through likes, shares, comments, and messaging. Understanding the generic social graph enables enhanced targeting, personalized recommendations, and improved community engagement in digital marketing strategies.
Key Components of a Social Graph
The key components of a social graph include nodes representing users or entities, and edges symbolizing the relationships or interactions between them. Attributes such as user profile data, types of connections (e.g., friends, followers), and interaction frequency contribute to the graph's depth and functionality. Social graphs enable platforms like Facebook and LinkedIn to map social networks, enhancing personalized content delivery and targeted advertising.
Facebook Social Graph vs Traditional Social Graph
Facebook Social Graph maps real-world relationships and interactions between users, pages, and content, enabling personalized user experiences and targeted advertising through data-rich connections. Traditional Social Graph models emphasize basic user-to-user relationships without integrating extensive behavioral or contextual data. The Facebook Social Graph's advanced integration of multimedia, likes, comments, and shared content surpasses traditional models by creating a dynamic and comprehensive network representation.
Data Privacy in Facebook vs Generic Social Graphs
Facebook's data privacy policies are scrutinized due to its vast collection of user information, enabling targeted advertising and personalized experiences but raising concerns over data sharing with third parties. Generic social graphs, representing relationships and interactions across various platforms, emphasize anonymized and aggregated data to protect individual privacy while analyzing social connections. Balancing data utility and privacy remains a critical challenge, with Facebook often facing criticism compared to the more privacy-conscious approach of generic social graph models.
Application Uses: Facebook Social Graph vs Others
Facebook Social Graph excels in mapping complex user relationships through interconnected nodes representing people, pages, and interactions, enabling precise content targeting and enhanced social discovery. Unlike platforms such as Twitter or Instagram, which emphasize real-time updates and visual content respectively, Facebook's graph structure supports sophisticated network analysis and personalized recommendations. Marketers leverage the Social Graph for dynamic audience segmentation, improved ad relevance, and deeper insights into user behavior across diverse social connections.
Visualization of Social Connections
Visualization of social connections on social media platforms reveals complex networks of interactions, friendships, and influences, enabling users and marketers to identify key influencers and community clusters with precision. Advanced graph theory algorithms and machine learning techniques enhance these visualizations by mapping relationships and interaction patterns in real-time. This data-driven insight supports targeted advertising strategies and strengthens user engagement through personalized content delivery.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Social Graph
Social media platforms leverage various social graphs, such as the friend graph, interest graph, and interaction graph, each offering unique benefits and challenges. The friend graph excels in building close-knit communities and trust but may limit diversity of content and perspectives. Interest graphs facilitate personalized content discovery and niche communities, yet they can lead to echo chambers and algorithmic bias, while interaction graphs promote dynamic engagement and real-time feedback but may prioritize popularity over meaningful connections.
Future Trends in Social Graph Technology
Future trends in social graph technology emphasize enhanced integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to create more personalized and predictive social experiences. Blockchain technology is expected to improve data security and user privacy within social networks, giving You greater control over your information. Advanced graph databases will drive real-time analytics and deeper insights into complex social connections, transforming how businesses and individuals interact online.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com