Photo illustration: Twitter Bot vs Web Scraper
Twitter bots automate posting and interactions on the platform, while web scrapers extract data from websites for analysis or reuse. Discover the key differences and best use cases of Twitter bots versus web scrapers in this article.
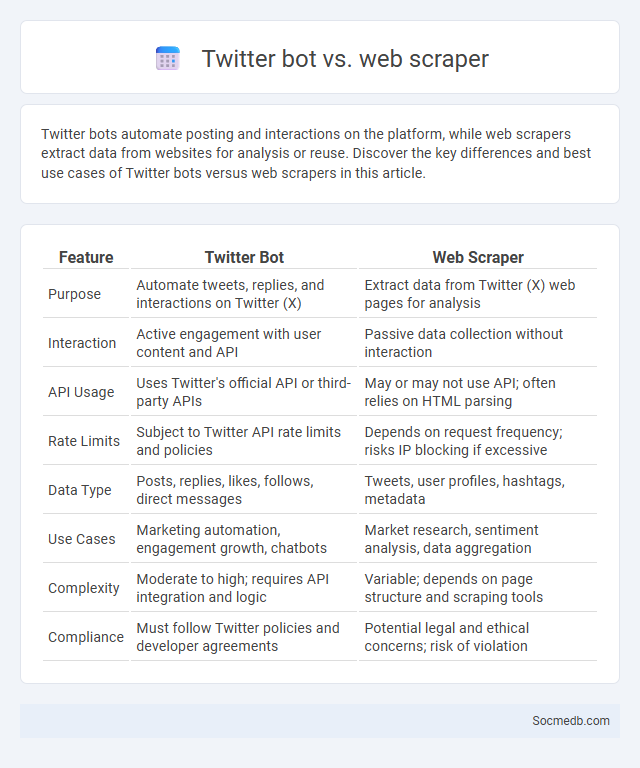
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Twitter Bot | Web Scraper |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Automate tweets, replies, and interactions on Twitter (X) | Extract data from Twitter (X) web pages for analysis |
| Interaction | Active engagement with user content and API | Passive data collection without interaction |
| API Usage | Uses Twitter's official API or third-party APIs | May or may not use API; often relies on HTML parsing |
| Rate Limits | Subject to Twitter API rate limits and policies | Depends on request frequency; risks IP blocking if excessive |
| Data Type | Posts, replies, likes, follows, direct messages | Tweets, user profiles, hashtags, metadata |
| Use Cases | Marketing automation, engagement growth, chatbots | Market research, sentiment analysis, data aggregation |
| Complexity | Moderate to high; requires API integration and logic | Variable; depends on page structure and scraping tools |
| Compliance | Must follow Twitter policies and developer agreements | Potential legal and ethical concerns; risk of violation |
Introduction to Automated Tools: Twitter Bots, Web Scrapers, and General Bots
Automated tools in social media, such as Twitter bots, web scrapers, and general bots, play a crucial role in managing and analyzing vast amounts of data. Twitter bots automate interactions like posting tweets, liking, and following to enhance engagement and marketing efforts. Web scrapers extract valuable information from social media platforms for insights, while general bots streamline repetitive tasks, improving efficiency in digital communication.
Defining Twitter Bots: Purpose and Functionality
Twitter bots are automated accounts designed to perform specific tasks such as posting tweets, liking content, or following users based on programmed algorithms. These bots can spread information rapidly, engage with trends, and amplify messages, impacting public opinion and marketing strategies. Understanding their purpose and functionality is essential for managing social media authenticity and detecting manipulation.
Understanding Web Scrapers: Key Features and Use Cases
Web scrapers are automated tools designed to extract data from websites, enabling efficient data collection and analysis. Key features include the ability to navigate web pages, parse HTML content, and gather structured information across various social media platforms. Use cases range from sentiment analysis and market research to competitive intelligence and trend monitoring, making web scrapers essential for businesses leveraging social media data.
What Are General Bots? Broad Capabilities and Types
General bots are automated software applications designed to perform a wide range of tasks on social media platforms, including content generation, user interaction, and data collection. Their broad capabilities encompass tasks such as posting updates, responding to comments, managing follower engagement, and analyzing trends through natural language processing and machine learning algorithms. Common types include chatbots for customer service, spam bots for promotional activities, and scraping bots that gather public data for analytics or marketing purposes.
Comparison of Core Technologies: Twitter Bots vs Web Scrapers vs Bots
Twitter bots utilize the Twitter API to automate interactions such as posting tweets, retweeting, and following users, leveraging real-time data access with rate limit constraints. Web scrapers extract structured information from public web pages by parsing HTML content without relying on APIs, often used for large-scale data harvesting across multiple platforms. General bots encompass various automation technologies, combining API integration, web scraping, and machine learning to perform complex tasks like sentiment analysis, content generation, and personalized user engagement on social media.
Common Use Cases: Practical Applications Across Platforms
Social media platforms serve diverse practical applications, including brand marketing, customer engagement, and community building across channels like Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn. Businesses leverage targeted advertising and influencer partnerships to increase reach and drive sales, while individuals use these platforms for networking, content sharing, and real-time communication. Social media analytics tools provide valuable insights into audience behavior and campaign performance, optimizing strategies for maximum impact.
Legal and Ethical Considerations: Compliance Risks and Best Practices
Social media platforms present significant compliance risks, including data privacy violations, intellectual property infringement, and misinformation dissemination, demanding strict adherence to regulatory frameworks like GDPR and COPPA. Organizations must implement robust content moderation policies, obtain explicit user consent for data collection, and ensure transparent communication to mitigate legal liabilities. Best practices include regular employee training on social media laws, continuous monitoring of platform activities, and establishing clear guidelines that balance freedom of expression with ethical accountability.
Performance and Scalability: Handling Data Collection at Scale
Social media platforms require robust performance and scalability to handle massive data collection at scale efficiently, processing millions of user interactions per second without lag or data loss. Advanced distributed systems and cloud-based infrastructures enable seamless scaling while maintaining real-time analytics and personalized user experiences. Ensuring Your system can dynamically adapt to traffic spikes and data volume growth is crucial for sustained engagement and operational excellence.
Security Implications: Protecting Data and Preventing Abuse
Social media platforms often collect vast amounts of personal data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks and data breaches. Your privacy is at risk if proper security measures such as strong passwords, two-factor authentication, and regular account monitoring are not implemented. Protecting your information safeguards against identity theft, cyberbullying, and unauthorized access, ensuring a safer online experience.
Choosing the Right Tool: Factors to Consider for Your Needs
Choosing the right social media tool involves evaluating factors such as platform compatibility, user engagement features, and analytics capabilities to align with your specific business goals. Consider audience demographics, content format support, and integration with existing marketing tools to ensure seamless workflow and maximize ROI. Prioritize tools offering robust security measures and scalability to adapt as your social media strategy evolves.
 socmedb.com
socmedb.com